Skeleton Notes Religion
advertisement
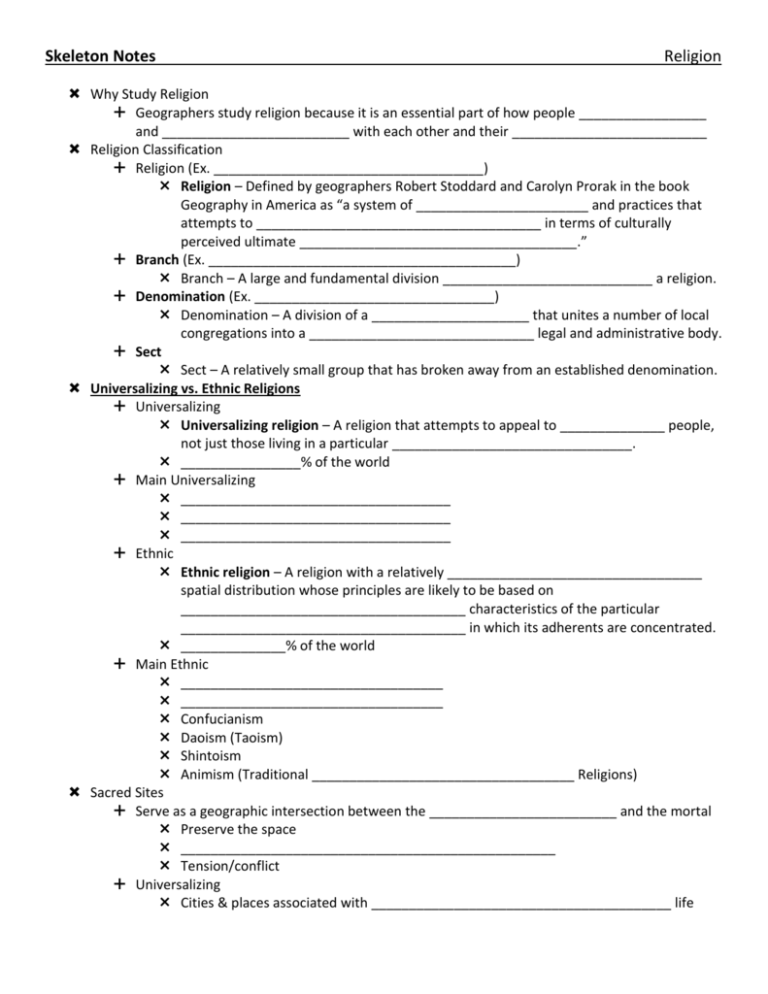
Skeleton Notes Religion Why Study Religion Geographers study religion because it is an essential part of how people _________________ and _________________________ with each other and their __________________________ Religion Classification Religion (Ex. ____________________________________) Religion – Defined by geographers Robert Stoddard and Carolyn Prorak in the book Geography in America as “a system of _______________________ and practices that attempts to ______________________________________ in terms of culturally perceived ultimate _____________________________________.” Branch (Ex. _________________________________________) Branch – A large and fundamental division ____________________________ a religion. Denomination (Ex. ________________________________) Denomination – A division of a _____________________ that unites a number of local congregations into a ______________________________ legal and administrative body. Sect Sect – A relatively small group that has broken away from an established denomination. Universalizing vs. Ethnic Religions Universalizing Universalizing religion – A religion that attempts to appeal to ______________ people, not just those living in a particular ________________________________. ________________% of the world Main Universalizing ____________________________________ ____________________________________ ____________________________________ Ethnic Ethnic religion – A religion with a relatively __________________________________ spatial distribution whose principles are likely to be based on ______________________________________ characteristics of the particular ______________________________________ in which its adherents are concentrated. ______________% of the world Main Ethnic ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Confucianism Daoism (Taoism) Shintoism Animism (Traditional ___________________________________ Religions) Sacred Sites Serve as a geographic intersection between the _________________________ and the mortal Preserve the space __________________________________________________ Tension/conflict Universalizing Cities & places associated with ________________________________________ life Ethnic Distinctive ________________________________ environment of its _______________ Sacred Sites Universalizing Buddhism __________________________ birthplace in S. ___________________________ _______________________________ other holy sites associated with important events in Buddha’s ________________________ Christianity ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Islam Muhammad’s birthplace (Makkah/___________________________) Tomb (Madinah/_____________________________________) Ethnic Hinduism ___________________________ River, Mt. Kailās, Benares in India Judaism ___________________________________________ ________________________________________ Wall Holy Days Universalizing Commemorate events in the __________________________________________ life Islam: Lunar calendar, _______________________ (holy month) varies, commemorates the Archangel Jibril (_______________________________) first visiting _________________________________________________ Christianity: Christmas: birth of __________________________________, Easter: ________________________________________________ of Jesus Buddhists: holy days on Buddha’s birth, ______________________________________________________ & death Ethnic Celebration of the ___________________________________________________ Judaism: ___________________________ Hashanah & Yom ____________________________ in autumn (___________________________________), ____________________________ (Pesach) in spring (____________________________________) Methods of Diffusion Universalizing Religions Relocation diffusion Christian ________________________________________________ Contagious Diffusion Muslims marrying non-___________________________________ Hierarchical Diffusion Emperor ______________________________________ converting to ________________________________________________ Ethnic Religions Most ________________________________________ diffusion _____________________________________________________ is an exception Burial Practices Religious ________________________________ promote the development of places or activities to _____________________ or _____________________________________ the dead Impose __________________________________________ on the landscape of a region Affect ___________________________________ use (land allocated to burial practices) Make the landscape _____________________________________________ compared to other ___________________________________________ areas Burial Practices Universalizing Buddhism _____________________________________ Christianity Park-like __________________________________________ _______________________________________________ Islam Park-like _______________________________________ Ethnic Hinduism _______________________________________ Judaism Park-like __________________________________________________ Animism ____________________________________________ _________________________________________ at sea Other practices Burial ________________________________________ Place Names Religious place names affect the ___________________________________________________ By promoting _________________________________________ distinctiveness Confirming the importance of religion in _______________________________________ Examples Use of __________________________________ names in French Canada (St. ___________________________________ river) U.S. Southwest (_________________________________ City, Los ________________________________) Medina (City of the ____________________________) or ________________________ Religion & the Environment ____________________________________________ influencing Religion Holy Places Especially in Ethnic religions ______________________________________________ Religions affecting the Environment __________________________________________ Function affects landscape Architecture Special buildings used for ________________________________/mediation/spiritual function Represents a ___________________________________________ history Christian churches: place to gather and worship, representation of ________________ Restricts/_________________________________________ the use of land 1. 2. 3. 4. Muslim mosques: place for the community to ___________________________________, worship = center of ____________________ Asian universalizing & ethnic more likely to house ________________________________________ to particular gods Attracts ___________________________________________ Hearths 3 Major Hearths Middle East Hearth ___________________________, Christianity, ____________________________ Northern India Hearth Hinduism, ___________________________________ East Asia Hearth _______________________________________, Taoism, Shintoism Major Universalizing Religions Buddhism Christianity Islam Buddhism Origins ____________________________________________________, 563 BCE, son of a __________ Age ____________, left his sheltered life & for _________ years meditated in a forest in India Emerged Buddha “____________________________________________ one” Spent _________ years preaching across India Buddhism Major Branches ____________________________ = “the way of the ______________________” Believe they are closer to Buddha’s __________________________________ ways Must renounce ___________________________________ & become a _____________ Cite Buddha’s wisdom & stress _______________________________________ Mahayana = “the bigger ________________” Less __________________________, all encompassing Can help more people Cite Buddha’s _________________________________ & stress ______________________ others Tantrayana Smallest branch Four Noble Truths The truth of ____________________________________ (Dukkha) 1. All living beings must endure suffering The truth of the origin of suffering (Sumudaya) 1. Three ________________________________ (origins of suffering): 1. Greed & _____________________________ 2. ______________________________ & delusion 3. ______________________________ & destructive urges The truth of the cessation of suffering (Nirodha) 1. Escape from suffering & reincarnation by achieving ___________________________________ (reaching _______________________________________) The truth of the path to the cessation of suffering (Magga) 1. Way to achieve Nirvana = ______________________________________ Path 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Right _________________________________________ Right Intention Right _________________________________________ Right _________________________________________ Right Livelihood Right Effort Right _________________________________________ Right Concentration Buddhism Current Distribution = _________________ million followers Mahayanist = _______% Theravadists = 38% Tantrayanists = 6% Locations M = __________________________, Japan & Korea Th = Cambodia, Laos, __________________________, Sri Lanka & Thailand Ta = _________________________ & Mongolia Christianity Origin Founded on teachings of _______________________________ Born in ____________________________________________________ between 8 & 4 BCE Died in ____________________________________________________ in 30 CE Christians believe the Jesus died for human __________________ and was __________________________________________ by God Christianity Major Branches Roman ____________________________________: teachings of Bible & Church Hierarchy (____________________) Seven _______________________________________________ Orthodoxy Split with Roman Catholicism beginning in the ______ c., finalized in ________________ Agree with RC on Sacraments, not on doctrines added after ___________ c. Protestantism _______________________________________ in 16th c. Martin _____________________________________ Personal salvation through ______________________________ rather than sacraments Seven Sacraments 1. ___________________________________ 2. Confirmation: confirm ___________________________ 3. _____________________________ (reconciliation): reconciling with ___________________ 4. Anointing the sick (___________________________________): recovery of health & spiritual strength 5. ____________________________________ 6. Holy Orders: lead others by bringing them _______________________________________________ 7. Eucharist: representative of ____________________________________________, becomes the body & blood of Jesus Christianity Current Distribution = __________ billion followers _________% R.C. 24% Protestant 11% ________________________ _________% other Christian churches Locations R.C.: S & W Europe, _________________________ America Protestant: ____________________ America, N. Europe, _____________________________ Orthodox: _________________________________________________________ Distribution South/Southeast _______________________________________ Midwest/Great Plains/Rust Belt/Corn Belt _______________________________________ Northern Border States _______________________________________ West (Utah, Idaho, Nevada) __________________________________________________________________________ Everywhere else _______________________________________ Factors for Baptist Distribution _____________________________________ religion Origins in __________________ towns & ___________________________ areas Based on ______________________________________________ brought from Europe Appealed to ____________________________________-Americans excluded by other protestant denominations Lack of in-migration ________________________________ region did not attract a lot of European migrants Factors for Lutheran Distribution Original migration from _____________ & _______________ Europe _________________________________________ & Scandinavians ___________________________________ migration as area began to thrive Lack of in-migration Lacked ___________________________ factor of __________________ cities Factors for LDS Distribution Original migration Began in ________________________________ U.S. & migrated to ________________ Later migrations Migrated to ________________________________ new areas of the West Lack of in-migration Lacked ___________________________ factor of __________________ cities Islam Origin Muhammad was born in 570 in ____________________________________ At 40, he received his first message from ________________________________ through the Archangel _________________________________________ _____________________________________________ is a record of God’s words as relayed to Muhammad from the angel Gabriel In 622, after much persecution Muhammad was commanded to move to _________________________________ (renamed Medina or “the City of the _____________________________”) Islam Major Branches ________________________________ (“People of the tradition of ______________________________________ and the consensus”) After Muhammad, came Abu ___________________________, Umar, Uthman & _____________________________ who were leaders or “____________________________” (successor of the ___________________________) Sunnis recognize all four as ___________________________________ religious leaders Shi’ites (_____________________) (“Followers of ____________________”) Shi’ites believe the only ___________________________ (who was Muhammad’s ______________________________-in-law) is the only legitimate caliph as he was Muhammad’s closest ________________________________________________ Five ________________________________________ of Islam 1. Shahadah 1. Profession of _______________________________, “There is no god worthy of worship except the one _______________________________, the source of all creation, and Muhammad is the ________________________________________ of God.” 2. Interpretations vary, “There is no God but _________________________________, and Muhammad is His messenger” 2. Salat 1. __________________________, 5 times daily, facing the city of __________________________ 3. Zakat 1. ___________________________________ to help the needy, act of purification & growth 4. Sawm 1. Fast during the month of _______________________________________, self-purification 5. __________________________ 1. Pilgrimage to _______________________________________ (if physically and financially able) Islam Current Distribution – _______________________ Billion people ________________________________ = 83% Shi’ites = ________________________% Locations Middle East North Africa to Central Asia Outside the Middle East = ______________________% of Muslims __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ “Muslim” ≠ “___________________________” Arab = _______________________________________________ Muslim = follower of ___________________________________________ _____________% of all Arabs are Muslims But ______________% of all Muslims are not Arabs Hinduism Origin 2500-1500 BCE, no single _______________________________________ Mingling of ___________________________ & _________________________________ beliefs ____________________________________________ – The blending of traits from two different cultures to form a new trait. Holy Sites ______________________________________ & Mt. Kailās (________________________) Practices Up to the individual to determine the best _____________________________ to God _________________________________________ Renunciation _________________________________________ Action Branches Vaishnavism (____________________________) = est. ____________________% Sivaism (______________________________) = ____________________% Autonomous religion Autonomous religion – A religion that does not have a ____________________________ authority but shares ideas and cooperates informally. Distribution _______________________% clustered in ________________________________________ Judaism Origin _____________________________________ moved to ________________________________ ________________________________________, differed from polytheistic groups surrounding Holy Sites Land in Eastern Mediterranean Canaan (__________________________________), ______________________________________ (Romans), _________________________ Distribution = _____________________________ million 1/3 in __________________________ 1/3 in __________________________ 1/3 elsewhere ____________________________________________________ Forced from Eastern Mediterranean by Romans during 70 CE ____________________________________________________ Set up the state of Israel Confucianism Origin (not exactly a religion, more an ____________________________________________ system) Confucius _____________________________________________ & teacher Stressed importance of ___________________ (correct behavior or propriety) Practices Orderly conduct Following ___________________________________________ Fulfilling obligations Treating others with _____________________________________________ Universe is made up of two forces: ____________________ & ________________________ Yin: _____________________, darkness, female, cold, depth, passivity & _______________________________ Yang: heaven, light, male, heat, height, activity, & ____________________________ Must be in ___________________________________________ Distribution __________________________________ Taoism (Daoism) Origin (also more of an ___________________________________ system) Lao-Zi (Lao Tse), contemporary of __________________________________________ Stressed mystical & magical aspects of life (as opposed to public service as Confucius stressed) Holy Sites Banned by the _______________________________________ in China in 1949 Practices Seek “____________________” (the way or _________________________________) “3 ______________________________________” Compassion, _______________________________________, Humility Branches Many different ______________________, practicing many different elements of magic Distribution Still practiced in _____________________________________ Legal & practiced in ___________________________________________ Shintoism Origin Forces of ____________________________________ = divine ____________________, Moon, rocks, ________________________, rivers Eventually deceased ___________________________________ & ancestors became deities Holy Sites ___________________________ shrines Community ________________________________________ places Practices Late 1800s Political change = _______________________________ religion All ____________________________________ people identified culturally as Shintoists Now: No longer __________________________________ religion, prayers praise ancestors Distribution _____________________________________ Animism Origin Difficult to trace due to lack of literary _______________________________________ ___________________________________________ Supreme God with “_________________________________” being animated objects Practices Passed down through ______________________________ tradition Distribution = ______________ million _____________% of Africa (________________% Christian & ________________% Muslim) Highest numbers in __________________________________, Cameroon, Togo, & Benin 1980 = ___________________ million Sikhism _________________________________________________ Religion Origin __________________________, lived in ___________________________________________ Combined elements of ________________________ & _________________________________ One Supreme Being (Creator) is perfect Practices Work toward continual _______________________________________ _____________________________ (Baptism) Men wear ______________________________________ & do not cut beards or hair Distribution = ____________________ million 20 million in ______________________________ region of _____________________________ Religious Conflicts Religion vs. _____________________________________________ Religion vs. _____________________________________________ Interfaith _________________________________________________ Religion vs. Politics __________________________________ “Religious Students” vs. Western Values Opposed leisure activities, instituted ______________________________________ policies (as they interpreted them) Religion vs. _______________________________________________ Communists removed religious institutions from government in _________________. Limited the role of _______________________________________ Christianity in Russia Following the collapse of the Soviet Union, there was a religious _________________________ Including Christianity in the _______________________________________ Europe & ________________________________________ in Central Asia Religion vs. Religion Interfaith Conflict Conflicts _________________________________ two religions Middle East Muslims, Jews & Christians battling for _________________ land in the Eastern Mediterranean _________________________________________: Christians vs. Muslims Palestine: Muslims vs. _____________________________ Religion vs. Religion Intrafaith Conflicts Conflicts _______________________________________ a religion Ireland Ireland = ___________________% Roman Catholic N. Ireland = Part of U.K. & 46% _____________________________________________ Discrimination against ________________________________________ in N. Ireland Irish __________________________________________ Army (IRA): goal of achieving Irish national _________________________________ by whatever means necessary Islam ________________________________ vs. Shia (____________________________) Non-Religious About ____________________ Billion people are considered “non-religious” __________________________________________________ Do not believe in any god(s) Agnostic God(s) may ________________________________, but it is uncertain ___________________________________________ “Not related to _____________________________________________;” belief system










