Biomes guided notes
advertisement
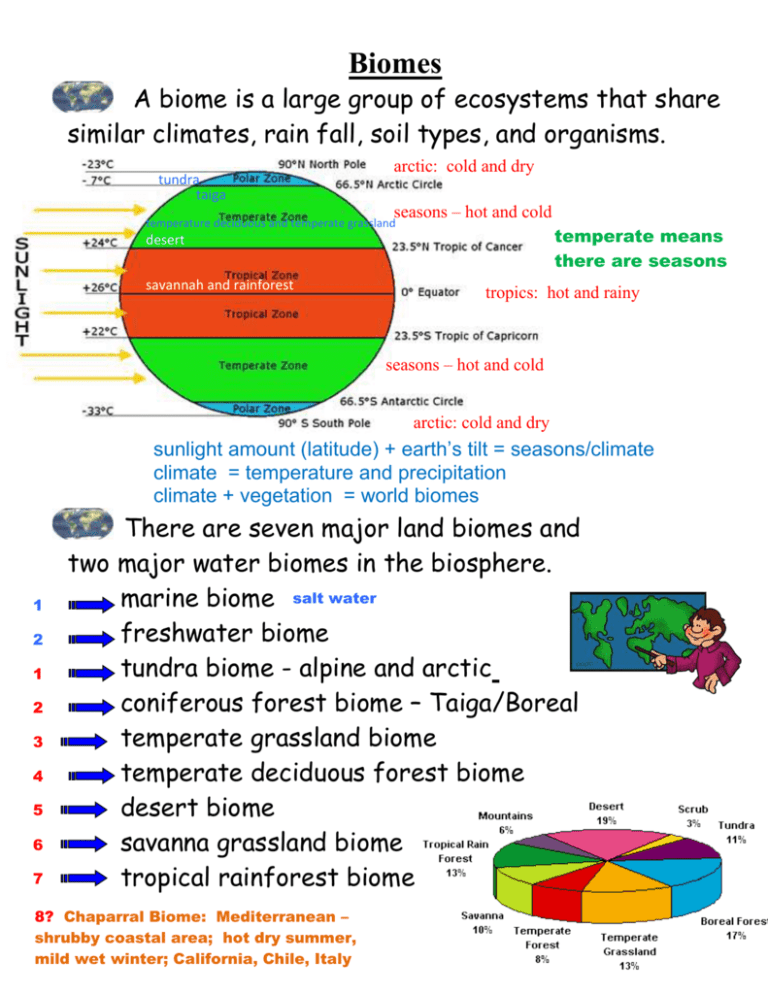
Biomes A biome is a large group of ecosystems that share similar climates, rain fall, soil types, and organisms. tundra taiga arctic: cold and dry seasons – hot and cold temperature deciduous and temperate grassland temperate means there are seasons desert savannah and rainforest tropics: hot and rainy seasons – hot and cold arctic: cold and dry sunlight amount (latitude) + earth’s tilt = seasons/climate climate = temperature and precipitation climate + vegetation = world biomes 1 2 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 There are seven major land biomes and two major water biomes in the biosphere. marine biome salt water freshwater biome tundra biome - alpine and arctic coniferous forest biome – Taiga/Boreal temperate grassland biome temperate deciduous forest biome desert biome savanna grassland biome tropical rainforest biome 8? Chaparral Biome: Mediterranean – shrubby coastal area; hot dry summer, mild wet winter; California, Chile, Italy Biomes - 2 http://www.blueplanetbiomes.org/world_biomes.htm Tundra Taiga Grasslands Deciduous Forest Chaparral Desert Desert-scrub Savanna Rainforest Alpine Biomes - 3 tundra biome: High latitudes – Siberia, Yukon Below 67° latitude; right below the arctic circle flat sloped land plateaus There are two types of tundra. Arctic tundra is near the poles. Glaciers - flat Alpine tundra is above the tree line of tall mountains. mountain – steep sloped 12-20 inches of rainfall each year. 54°F in the summer and - 14°F in the winter perpetually cold and windy. Biomes - 4 The tundra biome: soil is poor and allows only for shallow rooted plants to grow such as mosses, grasses, and small shrubs – no trees. Permafrost is the soil below the surface. It stays frozen year round. The ground is frozen 2-3 inches below the surface year round, so it cannot support deep rooted plants. Soggy/marshy – when it rains, there is nowhere for the water to go. Animals include polar bears, caribou, fox, owls. Biomes – 5 There are three types of forest biomes: evergreen trees – Coniferous – also called Taiga or Boreal higher latitudes that lose their leaves because of the Temperate deciduous trees seasons – middle latitudes Tropical rain tropical latitudes - hot and wet Taiga biome: just below the tundra 45° – 60° latitude mountains – northern temperate areas The coniferous forest biome: also called the Taiga or Boreal. 14-30 inches of rainfall each year. average temperatures are 57°F in the summer and 14°F in the winter; long cold winters and short growing season short cool summers Biomes – 6 The Taiga: areas consist mainly of thick forests of cone bearing evergreen trees. animals include squirrels, bears, wolves, mountain lions, and moose. temperate deciduous forest biome: middle latitudes 30° – 50° seasonal Angiosperms – flowers, fruits, leaves fall off each year - litter Biomes – 7 Temperate deciduous forest biome: 30-49 inches of rainfall each year. average temperatures are 83°F in the summer and 43°F in the winter. forests lose their leaves every Fall season which contributes to good soil. variety of animal life. Eastern Ohio thick soil for trees tropical rain forest biome: tropics: 0° – 25° latitude Biomes – 8 The tropical rain forest biome: contains more species than any other biome on the planet. up to 160 inches of rainfall each year. 4-5 times the rain amount in Ohio no seasons here. average temperatures are 93°F in the day and 68°F at night. top soil is very thin and poor for growing and farming because the rain washes the nutrients away – leaching; once trees are cut down, they do not grow back. most species live up in the tree tops or canopy Is the rainforest the lungs of the world? Oxygen? Plankton? 270 feet tall 130 feet tall 65 feet tall Biomes – 9 desert biome: subtropical high pressure - 30° Horse latitude 25° - 35° latitude all the world’s desert are found at this latitude The desert biome: less than 10 inches of rainfall each year. 100°F in the summer and 45°F in the night. cold at night nocturnal or diurnal soil is very poor. plants include cacti and wild-flowers. most animals are nocturnal and include snakes, lizards, small rodents, bats, and foxes. Biomes – 10 Grassland biomes: found between forests and deserts generally flat - plains two types - temperate and savannah temperate grassland biome: Bread basket of the world: The majority of the world’s food/grain is grown here! western Ohio – 38 inches of rain each year The temperate grassland biome: 20-35 inches of rainfall each year average. temperatures 86°F in the summer and middle latitudes – 30° to 50° 32°F in the winter. soil is rich and good for many plants animals include prairie dogs, mice, and large grazing animals such as bison. farmland - corn belt: North America has the best soil for growing crops in the world! Why? Climate and seasons – cycles of life and death that build the soil, plus lots of water and sunlight Biomes – 11 savanna grassland biome: tropics to subtropics 0° to 30° The savanna grassland biome: 60 inches of rainfall each year. average temperatures are 93°F in the summer and 61°F in the winter. no seasons tropical grassland with scattered clumps of small trees – shallow dirt trees. savannas of Africa are inhabited by some of the most diverse groups of large herbivores in the world such as zebras, giraffes, and elephants. Lots of rain (leaching/erosion) washes away the nutrients in the dirt and causes it to be bad for growing. Biomes – 12 The largest biome in the world is the marine biome. It based on salt water and contains all oceans and seas. Marine biomes can be divided into three zones depending on the biotic factors. top - surface planktic - floaters or drifters middle nektic - swimmers bottom benthic - bottom dwellers Water absorbs light, so sunlight can penetrate only about 200 m below the ocean’s surface. Because photosynthesis requires light, most marine producers are found near the surface. Phytoplankton are the base of the marine food web. They are one of the most important life forms on planet earth!!! Biomes – 13 Marine organisms that float or drift with the currents are called plankton. They are the most abundant form of life in the marine biome. Plankton range from microscopic algae to animals and organisms as large as jellyfish. Microscopic producers called phytoplankton produce the majority of oxygen in the atmosphere. Microscopic consumers are called zooplankton. Most zooplankton are immature or larval forms of much larger animals. Animals that actively swim, rather than drift with the currents are called nekton. Nekton include all swimming forms of fish, whales, and squid. All nektons are predators. Biomes – 14 Plants and animals living in or on the sea floor are called benthic. These include kelp (tall algae plants) crabs, snails, sea urchins, star fish, and flounders. Benthic organisms may either be: sessile - stationary their whole life like corals and clams epifauna - lives on the sediments at the bottom like crabs and corals suspension feeders food comes to it, eats food that falls to the bottom, often generates currents so the food moves to it Or motile - move around on the bottom like snails, worms, and crabs Or infauna - live in the sediments like clams and worms Or deposit feeders moves to decaying organic stuff on the bottom detritus feeders Biomes - 15 Marine biomes can be also be divided into various zones depending on the abiotic factors. manatees, seals, sea lions intertidal zone - where the ocean meets the land; may be above water part of the day when the tide is out; includes rocky shores, mud flats, and sandy beaches Brackish water – salt water mixing with fresh water 650 ft neritic - water gradually deeper up to 200 m deep on the continental shelf; lots of sunlight with diverse and colorful life barrier reefs pelagic zone – open water oceanic zone - past the continental shelf to the deep water of the open ocean; includes gyres and the Sargasso Sea middle of the ocean – no current, no life, like a desert benthic - sea floor; from the upper edge of the intertidal zone to the bottom of the deepest ocean waters bottom phototrophic zone – light, photosynthesis abyssal zone - dark Freshwater zones: (biotic and abiotic areas) Littoral Zone – shallow bank area Limnetic Zone – open water






