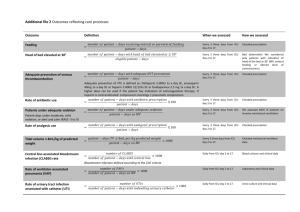
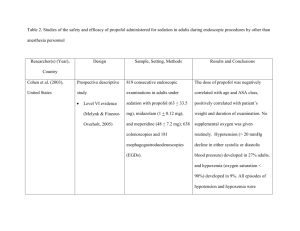
PRODEX-MIDEX
advertisement
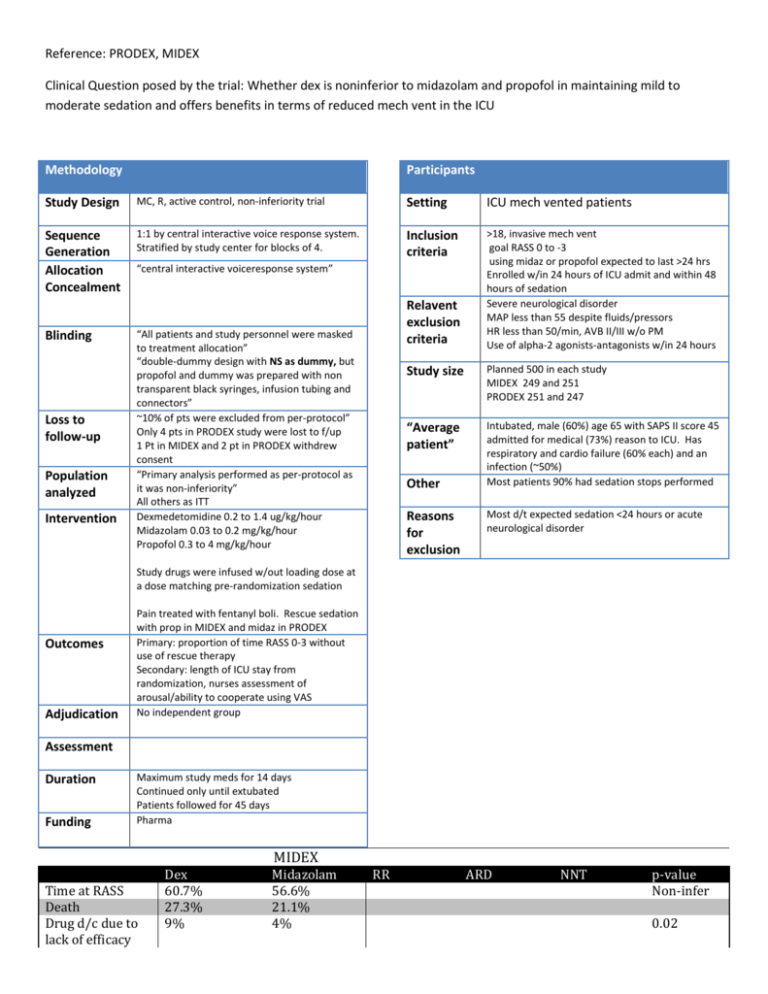
Reference: PRODEX, MIDEX Clinical Question posed by the trial: Whether dex is noninferior to midazolam and propofol in maintaining mild to moderate sedation and offers benefits in terms of reduced mech vent in the ICU Methodology Participants Study Design MC, R, active control, non-inferiority trial Setting ICU mech vented patients Sequence Generation Allocation Concealment 1:1 by central interactive voice response system. Stratified by study center for blocks of 4. Inclusion criteria >18, invasive mech vent goal RASS 0 to -3 using midaz or propofol expected to last >24 hrs Enrolled w/in 24 hours of ICU admit and within 48 hours of sedation Severe neurological disorder MAP less than 55 despite fluids/pressors HR less than 50/min, AVB II/III w/o PM Use of alpha-2 agonists-antagonists w/in 24 hours Blinding Loss to follow-up Population analyzed Intervention “central interactive voiceresponse system” Relavent exclusion criteria “All patients and study personnel were masked to treatment allocation” “double-dummy design with NS as dummy, but propofol and dummy was prepared with non transparent black syringes, infusion tubing and connectors” ~10% of pts were excluded from per-protocol” Only 4 pts in PRODEX study were lost to f/up 1 Pt in MIDEX and 2 pt in PRODEX withdrew consent “Primary analysis performed as per-protocol as it was non-inferiority” All others as ITT Dexmedetomidine 0.2 to 1.4 ug/kg/hour Midazolam 0.03 to 0.2 mg/kg/hour Propofol 0.3 to 4 mg/kg/hour Study size Planned 500 in each study MIDEX 249 and 251 PRODEX 251 and 247 “Average patient” Intubated, male (60%) age 65 with SAPS II score 45 admitted for medical (73%) reason to ICU. Has respiratory and cardio failure (60% each) and an infection (~50%) Most patients 90% had sedation stops performed Other Reasons for exclusion Most d/t expected sedation <24 hours or acute neurological disorder Study drugs were infused w/out loading dose at a dose matching pre-randomization sedation Outcomes Adjudication Pain treated with fentanyl boli. Rescue sedation with prop in MIDEX and midaz in PRODEX Primary: proportion of time RASS 0-3 without use of rescue therapy Secondary: length of ICU stay from randomization, nurses assessment of arousal/ability to cooperate using VAS No independent group Assessment Duration Funding Maximum study meds for 14 days Continued only until extubated Patients followed for 45 days Pharma MIDEX Time at RASS Death Drug d/c due to lack of efficacy Dex 60.7% 27.3% 9% Midazolam 56.6% 21.1% 4% RR ARD NNT p-value Non-infer 0.02 Mech Vent Hours ICU stay Hypotension Bradycardia Duration of drug use (median) 101 hrs 211 20.6% 14.2% 42 hours 147 hrs 243 11.6% 5.2% 43 hours 0.01 NSS 0.007 <0.001 0.15 PRODEX Time at RASS Death Drug d/c due to lack of efficacy Mech Vent Hours ICU stay Hypotension Duration of drug use (median) Critical Illness Polyneuropathy Dex 64.6% 17.1% 14% Propofol 64.7% 19.4% 5% RR ARD NNT p-value Non-infer 69 164 93 185 42 hours 47 hours 0.04 NSS NSS <0.001 2 11 0.02 <0.01 Nurses VAS assessments indicated that patients were more arousable, more cooperative and beter able to communicate their pain than patients receiving either midazolam or propofol Dex patients received less treatments for delirium Patients in the Dex group had more spontaneous breathing trials performed Major Limitations Methods: Did not confirm that blinding was maintained. They blinded propofol but would be easy to imagine this could be broken. No independent group adjudicated outcomes. Means that if blinding was broken the results would be more easily biased. Would have preferred primary outcome to be duration of ICU stay, mech vent or hospital stay rather than time in RASS target. In PRODEX, 36 patients in the dex group had treatment stopped for lack of efficacy (15 in 1st 24 hrs) and 29 for AE. It appears that these patients were still included in the per-protocol analysis but it is not clear how there data would have been included. NO standardized mechanical ventilation weaning protocol or criteria for extubation. Results Why did the patients in the PRODEX study require twice as much dex? (0.925 ug/kg/h vs 0.45 ug/kg/h) Included only health care workers assessment of sedation rather than patients. Generalizability Only applies to patients on continuous infusions of sedative medications which is somewhat rare now. Assessment Dexmedetomidine is similar in effectiveness to midazolam and propofol for maintaining target RASS in this group of study includable patients. Dex may reduce the duration of mech vent compared to midazolam and propofol (p=0.01 and 0.04 respectively), but had no significant difference in duration of ICU stay. Nurses assessments seemed to indicate that patients were better behaved and more interactive. No information on patients satisfaction with sedation. Higher rates of bradycardia and hypotension but less delirium. Conclusion Dex appears may reduce mechanical ventilation duration and delirium but does not reduce ICU stay. May be a useful sedative for some patients at high risk of delirium who will not be adversely affected by Dex side effects. Not sure that it would be easy to determine a priori in which patients the use of dex would be cost effective. Notes: o SAPS II http://www.sfar.org/scores2/saps2.html Patients in this study had a 35% predicted mortality