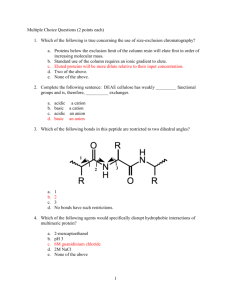
Which of the following is considered as a noncovalent bond
advertisement
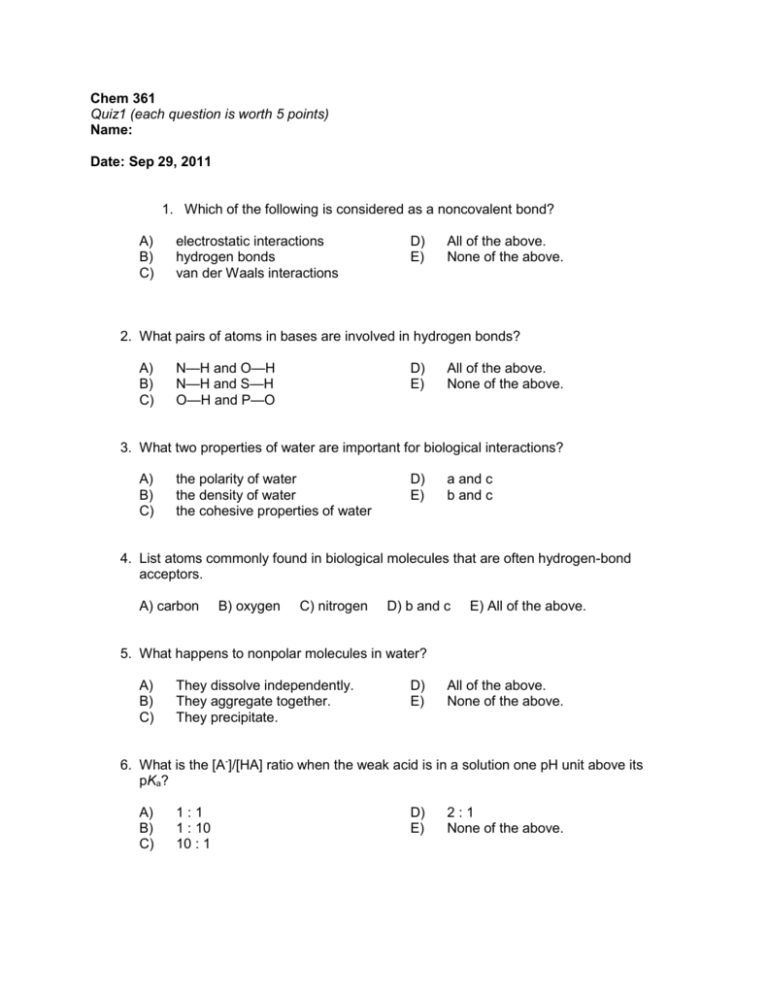
Chem 361 Quiz1 (each question is worth 5 points) Name: Date: Sep 29, 2011 1. Which of the following is considered as a noncovalent bond? A) B) C) electrostatic interactions hydrogen bonds van der Waals interactions D) E) All of the above. None of the above. 2. What pairs of atoms in bases are involved in hydrogen bonds? A) B) C) N—H and O—H N—H and S—H O—H and P—O D) E) All of the above. None of the above. 3. What two properties of water are important for biological interactions? A) B) C) the polarity of water the density of water the cohesive properties of water D) E) a and c b and c 4. List atoms commonly found in biological molecules that are often hydrogen-bond acceptors. A) carbon B) oxygen C) nitrogen D) b and c E) All of the above. 5. What happens to nonpolar molecules in water? A) B) C) They dissolve independently. They aggregate together. They precipitate. D) E) All of the above. None of the above. 6. What is the [A-]/[HA] ratio when the weak acid is in a solution one pH unit above its pKa? A) B) C) 1:1 1 : 10 10 : 1 D) E) 2:1 None of the above. 2 7. Stereochemistry can be easily depicted in a simple form using A) B) C) Ball-and-stick models. ribbon diagrams. Space-filling models. D) E) Fisher projections. None of the above. 8. Which of the following is the Henderson-Hasselbach equation? A) B) C) A- pH = pKa log HA A pH = pKa HA HA pH = pKa log - A D) A- pKa = pH log HA E) None of the above. D) E) None of the above. All of the above. 9. What determines a protein’s function? A) B) C) structure gene sequence N-terminal amino acids 10. Key properties of proteins include A) B) C) D) E) a wide range of functional groups. an ability to possess either rigid or flexible structures as dictated by functional requirements. the ability to interact with other proteins. a and b. All of the above. 3 11. At a pH of 1, what charged group(s) are present in glycine? A) -NH3+ B) -COO- C) -NH2+ D) a and b E) a, b, and c 12. Which amino acids contain reactive aliphatic hydroxyl groups? A) B) C) serine and methionine serine and threonine methionine and threonine D) E) cysteine and methionine cysteine and threonine 13. Name three amino acids that are positively charged at a neutral pH. A) B) C) lys, arg, and his his, arg, and cys cys, arg, and met D) E) lys, arg, and pro arg, glu, and his 14. In the following peptide, which amino acid is the N-terminus? Phe-Ala-Gly-Arg A) Ala B) Phe C) Phe and Arg D) Arg E) None of the above. 15. Which of the following affect the sedimentation of a particle? A) B) C) mass shape the density of the solution D) E) 16. Cyanogen bromide cleaves the peptide bond at A) B) C) D) E) the carboxyl side of Arg and Lys residues. the carboxyl side of Met residues. the amino terminus. None of the above. All of the above. All of the above. a and b 4 17. Trypsin cleaves the peptide bond at A) B) C) D) E) the carboxyl side of Arg and Lys residues. the carboxyl side of Met residues. the amino terminus. None of the above. All of the above. 18. Which of the following techniques can be used to determine the site of a disulfide bond? A) B) C) Edman degradation affinity chromatography diagonal electrophoresis Answer Key: 1. D 2. A 3. D 4. D 5. B 6. C 7. D 8. A 9. A 10. D 11. A 12. B 13. A 14. B 15. D 16. B 17. A 18. C D) E) MALDI-TOF SDS-PAGE