Warm-up: (10-5-15) *Ishmael Q`s in the hw tray! 1. List 2 economic
advertisement

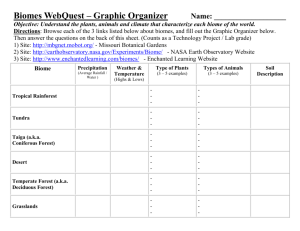
Warm-up: (10-5-15) *Ishmael Q’s in the hw tray! 1. List 2 economic consequences of an el nino year. 2. List 2 ways plants increase their genetic diversity. 3. Give 3 examples of microclimates. 4. The most important factor determining which biome is found in a particular area is _____. This is characterized by both _____ and _____. *Crossword answer for 7 down is “biopharming” 1. Fewer fish for S.America so less money and jobs, flooding damage 2. Mutations, pollination by wind or pollinator 3. Mountains, near bodies of water, cities, forests 4. Climate, temp, precipitation For Today’s lecture, each student will read a slide to the class. Chapter 7-2: Desert, Grasslands Mrs. Boyd Goals for today… Define biomes Identify the characteristics of desert and grassland biomes BIOMES: CLIMATE AND LIFE ON LAND Different climates lead to different communities of organisms, especially vegetation. Biomes – large land regions with similar: • Climate • Soil • Plants • animals Each biome contains many ecosystems whose communities have adapted to differences in climate, soil, and other environmental factors. BIOMES: CLIMATE AND LIFE ON LAND Biome type is determined mostly by precipitation but also temperature and soil type BIOMES: CLIMATE AND LIFE ON LAND Parallel changes in vegetation type: equator to the poles lowlands to mountaintops Place in the correct order from equator to north pole: Deciduous forest Coniferous forest Tropical forest Lichen and mosses DESERT BIOMES Deserts are areas where evaporation exceeds precipitation. Deserts have little precipitation and little vegetation. (annual precipitation- less than 10 inches or 25cm) Found in tropical, temperate and polar regions. Desert plants have adaptations that help them stay cool and get enough water. Plant adaptations: Why are deserts cold at night? How have deserts been misused by humans? GRASSLANDS Wet season, dry season. Wet season followed by drought Trees shed leaves, grass dries. Tundra Cold, treeless, biome with little precipitation. Across northern North America, Asia, and Europe. (ex. Alaska) Soil under the surface is frozen permanently: permafrost Trees do not grow in Tundra because: winters are too long roots can’t go very deep. Strong winds keep the ground frozen Cold temp. slow down the rate of decay. How does the slow decaying of organic material affect the soil? Summer is short. Only a few months. In summer, ice melts and ponds form for migrating ducks. Plants must grow and reproduce quickly. Ex. Grasses, mosses, lichen are dominant producers. What are the main producers of the tundra? Why is the tundra such a fragile biome that takes longer to recover if it is damaged? Check for Understanding: 1. Why are inland deserts cold at night? 2. How have deserts been misused? 3. Describe the producers of the tundra. 4. How can so many hoofed animals live in the savannas?