Unit 7 Units Perimeter Area and Volume
advertisement
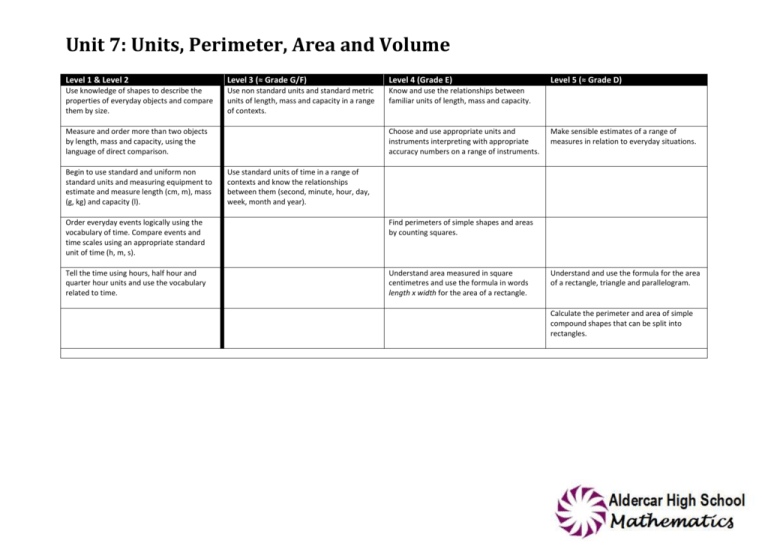
Unit 7: Units, Perimeter, Area and Volume Level 1 & Level 2 Level 3 (≈ Grade G/F) Level 4 (Grade E) Use knowledge of shapes to describe the properties of everyday objects and compare them by size. Use non standard units and standard metric units of length, mass and capacity in a range of contexts. Know and use the relationships between familiar units of length, mass and capacity. Measure and order more than two objects by length, mass and capacity, using the language of direct comparison. Begin to use standard and uniform non standard units and measuring equipment to estimate and measure length (cm, m), mass (g, kg) and capacity (l). Choose and use appropriate units and instruments interpreting with appropriate accuracy numbers on a range of instruments. Level 5 (≈ Grade D) Make sensible estimates of a range of measures in relation to everyday situations. Use standard units of time in a range of contexts and know the relationships between them (second, minute, hour, day, week, month and year). Order everyday events logically using the vocabulary of time. Compare events and time scales using an appropriate standard unit of time (h, m, s). Find perimeters of simple shapes and areas by counting squares. Tell the time using hours, half hour and quarter hour units and use the vocabulary related to time. Understand area measured in square centimetres and use the formula in words length x width for the area of a rectangle. Understand and use the formula for the area of a rectangle, triangle and parallelogram. Calculate the perimeter and area of simple compound shapes that can be split into rectangles. Unit 7: Units, Perimeter, Area and Volume Level 5 (≈ Grade D) Level 6 (≈ Grade C) Use and interpret scales and make simple scale drawings. Make sensible estimates of a range of measures in relation to everyday situations. Level 7 (≈ Grade B) Use and interpret scales and maps. Construct scale drawings to solve problems. Level 8 and E.P. (≈ Grade A/A*) Appreciate the imprecision of measurement and recognise that a measurement given to the nearest whole number may be inaccurate by up to one half in either direction. Understand and use compound measures such as speed and density. Understand and use the formula for the area of a rectangle, triangle and parallelogram. Deduce and use the formulae for the area of triangles, parallelograms and trapeziums. Calculate the perimeter and area of simple compound shapes that can be split into rectangles. Calculate the area of compound shapes that can be split into rectangles, triangles, parallelograms and trapeziums. Understand and use appropriate formulae for finding circumferences and areas of circles and shapes made from circles. Calculate surface areas of cuboids. Deduce and use appropriate formulae for finding volumes of cuboids. Calculate the surface area of cylinders. Calculate lengths, areas and volumes in plane shapes and right prisms. Calculate volumes of cones, cylinders and spheres. Distinguish between formulae for perimeter, area and volume by considering dimensions.