Atomic Radius Graphing Activity

Name Date Period
Introduction to Periodic Trends
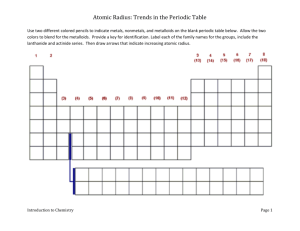
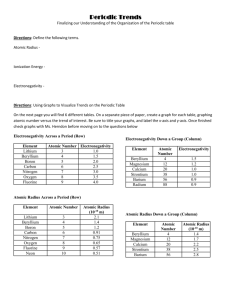
Objective: You will investigate the group and period trend for atomic radius or the size of the atom.
Background Information: Atomic radius is a measure of an element’s size. To determine the atomic radius, it is generally considered to be the distance between the nucleus and the boundary of the surrounding electron cloud.
Pre-Lab Questions
1.
What is a group or family on the periodic table?
2.
What is a periodic on the periodic table?
Procedure
1.
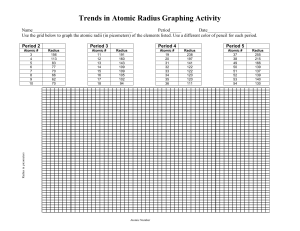
Generate a graph of atomic radius versus atomic number for the first eighteen elements using the data below.
Be sure to label your axes and give your graph an appropriate title.
Graph
Element
Name hydrogen helium lithium beryllium boron carbon nitrogen oxygen fluorine
Atomic
Number
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Atomic Radius
(in pm)
37
32
152
111
88
77
70
66
64
Element
Name neon sodium magnesium aluminum silicon
phosphorus sulfur chlorine argon
Atomic
Number
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
Atomic Radius
(in pm)
70
186
160
143
117
110
104
99
94
______________________
200
180
160
140
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
0 5 10 15
____________________________________
20
Analysis
1.
Highlight the elements of the third period in pink or yellow. What happens to the atomic radius or the size of the atoms as you move across the period from left to right? Explain why in one complete sentence.
2.
Circle the first two elements in the alkaline earth metal family in blue or green. What happens to the atomic radius or the size of the atoms as you move down the group? Explain why in one complete sentence.
3.
Using the information above, predict which element would be larger: Ca or K? Justify your answer.
4.
Using the information above, predict which element would be larger: Na or K? Justify your answer.