ANSWER KEY A C C B B B C D C A B D B A D C C C B A A A C B D
advertisement

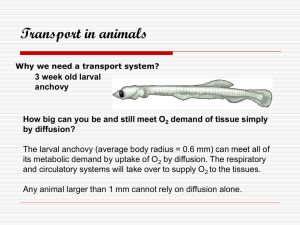
ANSWER KEY 1. A 2. C 3. C 4. B 5. B 6. B 7. C 8. D 9. C 10. A 11. B 12. D 13. B 14. A 15. D 16. C 17. C 18. C 19. B 20. A 21. A 22. A 23. C 24. B 25. D 26. A 27. C 28. D 29. C 30. B 31. D 32. C 33. C 34. A 35. C 36. B 37. C 38. C 39. B 40. C 41. D 42. C 43. SAnode, right atrium b) The AV node stimulates the Purkinje fibres; This causes the ventricles to contract. 44. A 45. C 46. B 47. B 48. A 49. D 50. Artery: is thick-walled with elastic tissue to be able to withstand the forces of blood pressure. Semi-lunar valve: has cusps (flaps) which open in one direction only in order to prevent back flow. Capillary: is thin-walled in order to facilitate the exchange of materials 51. Oxygen-oxyhemaglobin; hydrogen ions - reduced haemoglobin; carbon dioxide- carbaminohemoglobin 52. Artery b) • maintains blood pressure • carries blood away from the heart • carries nutrients and oxygen to the tissues • controls amount of blood going to various parts of the body 53. U,Z,W,X b) Name: oval opening Function: Allows blood to move from the right to the left atrium, bypassing the pulmonary circuit. Name: arterial duct Function: Allows blood to move from the pulmonary artery and the aorta, bypassing the pulmonary circuit. Name: umbilical arteries Function: Take blood containing wastes to the placenta. Name: umbilical vein Function: Brings nutrient-rich blood from the placenta. Name: venous duct Function: Allows blood to flow from the umbilical vein to the inferior vena cava. Name: umbilical cord Function: Carries O2 / nutrients from the placenta; carries wastes to the placenta. 54. a) White blood cells produce antibodies that inactivate the antigen.• White blood cells phagocytize the antigen. b) • Heart rate increases resulting in higher blood pressure.• Arterioles constrict resulting in higher blood pressure. c) Heart rate increases to raise blood pressure d) Platelets release a clotting protein to help seal the wound. 55. - The pulmonary vein returns blood from the lungs to the heart and therefore contains a higher concentration of oxygen and a lower concentration of carbon dioxide. The pulmonary artery carries blood, which has returned from the systemic circulation, from the heart to the lungs, and therefore contains a higher concentration of carbon dioxide and a lower concentration of oxygen. - The blood in the posterior vena cava has picked up carbon dioxide and dropped off oxygen at the tissues.The blood in the aorta has picked up oxygen and dropped off carbon dioxide at the lungs. 56. X: • The right ventricle has blood with a higher concentration of carbon dioxide (carbaminohemoglobin, bicarbonate ions, reduced hemoglobin) and a lower concentration of oxygen. (1 mark) Y:• The left ventricle has blood with a lower concentration of carbon dioxide (carbaminohemoglobin, bicarbonate ions, reduced hemoglobin) and a higher concentration of oxygen. (1 mark) b) • The left ventricle is thicker-walled and more muscular (1 mark) to contract and send blood with increased pressure throughout the body because the blood has a greater distance to cover than blood leaving the right ventricle (1 mark). 57. X: jugular vein; • to carry blood from the head to the anterior (superior) vena cava Y: inferior vena cava; • to carry blood from the legs and lower body to the heart b) i) • It is between the right and left atria; to allow blood to bypass the lungs ii) Blood low in oxygen from the right side of the heart would mix with oxygenated blood from the left side of the heart. 58. • The lymphatic capillaries pick up excess tissue fluid and return it to the blood system. • The lymph nodes purify the lymph of any infectious organisms or debris through the action of white blood cells. • The lymph capillaries (lacteals) absorb fats in the intestinal villi and transport them to the blood stream. • The lymphocytes produce antibodies. • The spleen purifies the blood. • Red bone marrow produces red and white blood cells. • Produces histamine as part of the inflammatory reaction. • Spleen acts as a blood reservoir. • Fights infection. 59. SA node: in upper wall of RA. Function: Sends nerve impulses to the AV node; acts as a pacemaker; causes both atria to contract; initiates the heartbeat Purkinje fibres: throughout muscle tissue surrounding both ventricles; Function: deliver impulse from AV node to walls of ventricles; causes ventricles to contract 60. a) • to act as a buffer • to carry oxygen / form oxyhemoglobin • to carry hydrogen ions / form reduced hemoglobin • to carry carbon dioxide / form carbaminohemoglobin • to increase the pH of the blood by picking up hydrogen ions b) • The pulmonary artery will have more reduced hemoglobin than the pulmonary vein. / The pulmonary vein will have less reduced hemoglobin than the pulmonary artery. • The pulmonary artery will have more carbaminohemoglobin than the pulmonary vein. / The pulmonary vein will have less carbaminohemoglobin than the pulmonary artery. • The pulmonary vein will have more oxyhemoglobin and the pulmonary artery will have less oxyhemoglobin. 61. a)RBC:• Carry oxygen. • Act as a buffer. • Carry hydrogen ions. • Carry carbon dioxide. WBC: • Fight infections. • Produce antibodies. • Phagocytize. PLATELETS: • Initiate blood clotting. • Form a temporary clot. b) Red blood cells are produced in the bone marrow