SR Chromatography Lab
advertisement

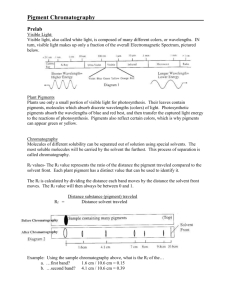
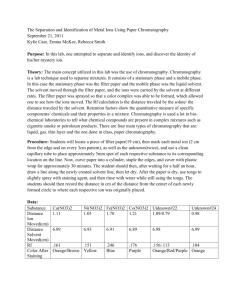
Name _________________________________ Date ___________ Period ________ Chromatography Lab How do plants obtain energy for photosynthesis? In this lab you will explore just what is inside of the leaves of a plant that captures light. Background Information: Paper chromatography is a technique used to separate colored chemicals. The colors in your pens and markers are a mixture of different colors. In paper chromatography substances are distributed between a stationary phase and a mobile phase. The stationary phase is usually a paper strip. The mobile phase is a liquid solvent (water or rubbing alcohol) that travels up the stationary phase, carrying the samples with it. Components of the sample will separate according to how strongly they absorb on the stationary phase versus how easily they dissolve in the mobile phase. Different types of molecules are moved different distances by solvents. Generally due to the ease with which each particular molecule is dissolved in and can remain dissolved the longest are moved farthest by the moving solvent, while those less soluble are left behind. This causes the components of the mixture to separate, making a chromatogram. This technique is used to analyze dye composition of fibers in forensics, detection of pesticides or insecticides in foods, determinations of pigments that a plant contains, and identifying compounds present in a given substance. Materials Chromatography paper Pencil Spinach leaf Coin Ruler Coffee Stirrer Stapler Graduated cylinder Solvent Directions Check off the procedure as you finish each step. 1. Make a pencil line 1cm from one end of chromatography paper (this will be the bottom of the paper). 2. Place a piece of spinach over the pencil line and use the edge of the coin to rub across the leaf along the drawn line so that it is covered with plant material. It is important that the strip contain a single, narrow, horizontal green line. 3. Staple the top of the chromatography paper to a stirrer (paper strips will be pre-cut). 4. Stand the strip of chromatography paper in the empty graduated cylinder with the coffee stirrer at the top. The bottom of the paper will hang very close to the bottom of the tube. 5. Remove the chromatography paper from the graduated cylinder. Name _________________________________ Date ___________ Period ________ 6. Carefully pour solvent into the tube until there is about 1cm. 7. Place the chromatography strip in the tube so that the bottom of the strip is in the solvent yet the solvent level is below the pencil line. 8. Allow the solvent to move up the chromatography strip. As the solvent moves up the strip, it will carry the pigments in the sample at different rates. (approx 30 minutes) 9. While waiting, read Color Article and complete Paint the Picture. 10. When the solvent gets close to the top of the strip, remove the strip from the solvent. Let the strip dry. Observe different colored bands. 11. Record observations below. Photo credit: http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/labbench/lab4/design1.html Analysis Questions 1. Leaves have color because of the pigments that they contain. What is a pigment? 2. Using evidence from your lab, how many different pigments are contained in spinach? 3. In what cell organelle is the green pigment, chlorophyll found? 4. What wavelength(s) of light does this pigment reflect? What wavelength(s) does this pigment absorb? Name _________________________________ Date ___________ Period ________ 5. What is the benefit of having several pigments within the leaves of a plant? 6. What is the source of energy for photosynthesis? How do plants obtain energy for use in photosynthesis? 7. When building your hydroponics system, would it be beneficial to your basil to use a green light? Why or why not?