15. Unit CW 2
advertisement

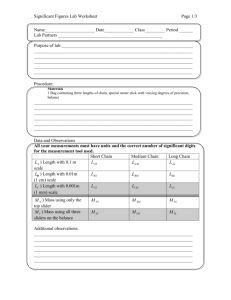
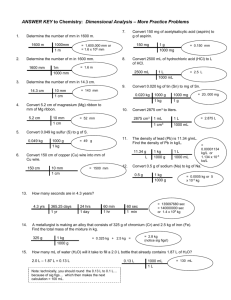
Unit Conversion CW 2 1 Students are asked to determine the density of an object. Use the data table to answer the questions below: Actual Values Group 1 Group 2 Group 3 Mass (g) 12.34 14.56 14.44 14.21 Volume (mL) 7.33 7.21 7.35 7.48 Density (g/cc) a. Determine the density of the object and the resulting density of each group. b. What can you say about the accuracy and precision of the groups’ measurements? (List for mass, volume) 2 Calculate the volume of an object with a density of 3.48 g/cc with a mass of 47.33 g. 3 Determine the mass of lead, r = 11.342 g/cc, with a volume of 125.2 mL. 4 Put each set of measurements below into order, (smallest to largest): a. 1.44 x 106 nm 4.89 x 104 mm 8.39 x 102 cm b. 0.0095 kg 7.45 g 5.2 x 106 m g c. 8.37 cL 3.7 x 103 kL 5.280 x 106 nL 5 Round the following numbers to 3 sig figs: a. 1.49703 b. 33,490 c. 6.310 x 1013 6 Determine the density of an object with the following properties: 38.4 cc and 45.21 g 7 Calculate the volume of copper, r = 8.96 g/cm3, with a mass of 1.273 kg. 8 Solve the following with the appropriate number of sig figs: a. (3.21 x 1013) (4.002 x 107) b. (4.00 x 105) / (2.0 x 10-4) c. 123.4 + 7.399 – 0.0346 9 What is the mass of 3.488 m L of mercury, r = 13.534 g/cm3. 10 What is wrong with each of the following: a. 45.330 x 104 has 4 significant figures b. If m = 12.45 g and V = 9.40 cc then r = 1.324 Unit Conversion CW 2 Ans 11 Students are asked to determine the density of an object. Use the data table to answer the questions below: Mass (g) Volume (mL) Density (g/cc) Actual Values 12.34 7.33 1.68 Group 1 14.56 7.21 2.02 Group 2 14.44 7.35 1.96 Group 3 14.21 7.48 1.90 a. Determine the density of the object and the resulting density of each group. (in table) b. What can you say about the accuracy and precision of the groups’ measurements? (List for mass, volume) Mass: High precision, low accuracy Volume: high accuracy and precision 12 Calculate the volume of an object with a density of 3.48 g/cc with a mass of 47.33 g. m 47.33 (cross multiply to get) r = 3.48 = V V 3.48V = 47.33 (divide both sides by 3.48 ) V = 13.6 mL 13 Determine the mass of lead, r = 11.342 g/cc, with a volume of 125.2 mL. m (multiply both sides by 125.2) m = 1.420 x 103 g 11.342 = 125.2 14 Put each set of measurements below into order, (smallest to largest): a. 1.44 x 106 nm 4.89 x 104 mm 8.39 x 102 cm -3 1 1.44 x 10 m 4.89 x 10 m 8.39 x 100 cm Smallest Largest Middle 15 b. 0.0095 kg L 7.45 g M c. 8.37 cL M 3.7 x 103 kL L Round the following numbers to 3 sig figs: a. 1.49703 1.50 b. 33,490 33,500 c. 6.310 x 1013 6.31 x 1013 5.2 x 106 m g S 5.280 x 106 nL S 16 Determine the density of an object with the following properties: 38.4 cc and 45.21 g r = 45.21 / 38.4 r = 1.18 cc 17 Calculate the volume of copper, r = 8.96 g/cm3, with a mass of 1.273 kg. 1g Mass must be in g 1.273 kg = 1,273 g 1x10 -3 kg 1, 273g 8.96 = 8.96 V = 1,273 V = 142 mL V 18 Solve the following with the appropriate number of sig figs: a. (3.21 x 1013) (4.002 x 107) 1.28 x 1021 b. (4.00 x 105) / (2.0 x 10-4) 2.00 x 109 c. 123.4 + 7.399 – 0.0346 130.8 19 20 What is the mass of 3.488 m L of mercury, r = 13.534 g/cm3. Convert 3.488 m L 3.488 x 10-3 mL m 13.534 = (cross multiply first) m = 0.04721 g 3.488 ´10 -3 What is wrong with each of the following: a. 45.330 x 104 has 4 significant figures 1st Decimal in wrong place 4.5330 x 105 nd 2 the number has 5 sig figs (trailing w/ decimal) b. If m = 12.45 g and V = 9.40 cc then r = 1.324 1st Units on r 1.324 g/mL 2nd, answer should have 3 sig figs 1.32 g/mL