WordPress About CEFR
advertisement

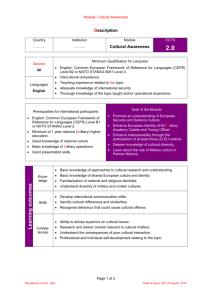
About CEFR Introduction What are CEFR's main goals? What are the CEFR's central components or 'building blocks'? a. Can-do statements b. Language activities c. Communicative competences How are all these connected? 4 CEFR Domains Introduction From Chile to China, EFL teachers and students are now working with the CEFR – Common European Framework of Reference (Council of Europe, 2000) for teaching and learning foreign languages. The CEFR descriptors for teaching EFL were developed by internationally recognized researchers who worked together with leading EFL experts, such as University of Cambridge and British Council. This comprehensive framework describes typical language learners’ ability in terms of speaking, reading, listening, writing and interacting with others at six proficiency bands or levels: CEFR Level Israeli Equivalent A1 Beginners Trom Besisi A2 Elementary Besisi B1 Intermediate Mitkadmim Aleph B2 Upper Intermediate Mitkadmim Bet C1 Advanced ???????? C2 Mastery ????????? What are CEFR's main goals? Communicative effectiveness - to enable language learners to communicate more effectively. - to create a plurilingual society in which language is used for better communication and collaboration between speakers of different language backgrounds (Council of Europe, 2002). This emphasis on communicative effectiveness drives the types of activities, strategies and competences which teachers and students choose to focus on. 'Common language' for describing objectives, methods and assessment - to provide a 'common language' for describing objectives, methods and assessment which applies to all languages in Europe. - to facilitate comparison of language learners' levels. - to facilitate co-operation among educational institutions in different countries. What are the CEFR's central components or 'building blocks'? a. Can-do Statements b. Language Activities c. Communicative Competences a. Can-do Statements A set of core "can-do" statements describe language activities and communicative competences that learners can typically do at 6 CEFR levels: CEFR Level Israeli Equivalent A1 Beginners Trom Besisi A2 Elementary Besisi B1 Intermediate Mitkadmim Aleph B2 Upper Intermediate Mitkadmim Bet C1 Advanced ???????? C2 Mastery ????????? b. Language activities CEFR defines language activities as what a learner is “able to do with a language” (CEFR p. 43). 6 types of language activities include: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Reception / written - reading comprehension Reception / spoken - listening comprehension – TV, TED talks, lectures. Production / written - reports, essays, creative writing Production / spoken – prepared presentations Interaction / written – at least 2 people participate in a written exchange - emails, electronic forums 6. Interaction / spoken – everyday conversations, class discussions, videoconference calls. c. Communicative competences - sets of knowledge, aptitudes, skills and attitudes. All 3 competences contribute in different ways to the learners' ability to communicate. 3 key sets of communicative competences include: i. ii. iii. Linguistic competence Socio-linguistic competence Pragmatic competence i. Linguistic competence Linguistic competence comprises the knowledge and skills related to dimensions of language as a system: lexis – range and quality of lexical knowledge, how this knowledge is stored in routine expressions. phonology syntax and grammar ii. Sociolinguistic competence This refers to sociocultural conditions of language use - knowledge and skills in using language in a social context. These include sensitivity to norms and customs that affect communication – social norms that affect rules of address, greetings, politeness etc. iii. Pragmatic competence Pragmatic competence involves the functional uses of linguistic resources (scenarios or predetermined scripts of interactional exchanges), mastery of cohesiveness, coherence and discourse. How are all these connected? Relationship between language activities and communicative competences: 'Practice makes Perfect' According to the CEFR, the relationship between language activities and communicative competences is cyclic: Learners use a range of “toolboxes” or communicative competences to carry out the above six types of language activities. Performing these 6 types of activities then strengthens the key competences. From: CEFR: Activities, Competences, Levels by Hodel, (2007). 4 CEFR Domains Language activities are contextualized within 4 domains: Domain What does this cover? Educational Learning/training contexts (usually related to an institution) where the aim is to acquire specific knowledge or skills. Occupational Everything related to a person's occupation and workplace. Public Everything connected to ordinary social interaction (business, administration, public services, cultural and leisure activities, the media etc.) Personal Complements public domain - family relations and individual social practices.