Motivation & Emotion
advertisement
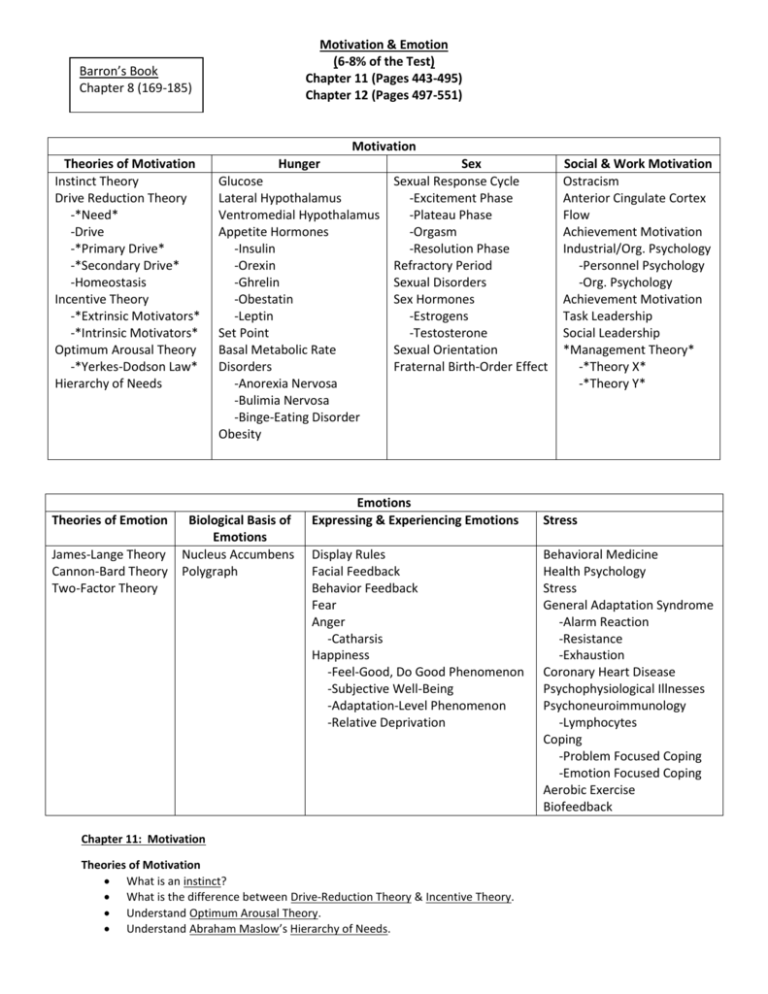
Motivation & Emotion (6-8% of the Test) Chapter 11 (Pages 443-495) Chapter 12 (Pages 497-551) Barron’s Book Chapter 8 (169-185) Motivation Theories of Motivation Instinct Theory Drive Reduction Theory -*Need* -Drive -*Primary Drive* -*Secondary Drive* -Homeostasis Incentive Theory -*Extrinsic Motivators* -*Intrinsic Motivators* Optimum Arousal Theory -*Yerkes-Dodson Law* Hierarchy of Needs Theories of Emotion James-Lange Theory Cannon-Bard Theory Two-Factor Theory Hunger Glucose Lateral Hypothalamus Ventromedial Hypothalamus Appetite Hormones -Insulin -Orexin -Ghrelin -Obestatin -Leptin Set Point Basal Metabolic Rate Disorders -Anorexia Nervosa -Bulimia Nervosa -Binge-Eating Disorder Obesity Biological Basis of Emotions Nucleus Accumbens Polygraph Sex Sexual Response Cycle -Excitement Phase -Plateau Phase -Orgasm -Resolution Phase Refractory Period Sexual Disorders Sex Hormones -Estrogens -Testosterone Sexual Orientation Fraternal Birth-Order Effect Emotions Expressing & Experiencing Emotions Display Rules Facial Feedback Behavior Feedback Fear Anger -Catharsis Happiness -Feel-Good, Do Good Phenomenon -Subjective Well-Being -Adaptation-Level Phenomenon -Relative Deprivation Chapter 11: Motivation Theories of Motivation What is an instinct? What is the difference between Drive-Reduction Theory & Incentive Theory. Understand Optimum Arousal Theory. Understand Abraham Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs. Social & Work Motivation Ostracism Anterior Cingulate Cortex Flow Achievement Motivation Industrial/Org. Psychology -Personnel Psychology -Org. Psychology Achievement Motivation Task Leadership Social Leadership *Management Theory* -*Theory X* -*Theory Y* Stress Behavioral Medicine Health Psychology Stress General Adaptation Syndrome -Alarm Reaction -Resistance -Exhaustion Coronary Heart Disease Psychophysiological Illnesses Psychoneuroimmunology -Lymphocytes Coping -Problem Focused Coping -Emotion Focused Coping Aerobic Exercise Biofeedback Hunger Understand the roles played by the Lateral Hypothalamus & the Ventromedial Hypothalamus. Know the function of hormones related to appetite (Insulin, Orexin, Ghrelin, Obestatin, Leptin). Understand the arguments for & against Set Point Theory. How do cultural influences (i.e. Social Facilitation & Unit Bias) affect eating? Understand the different Eating Disorders & their causes. What Biological Factors, Psychological Factors, & social-cultural factors influence eating. Understand the causes of Obesity & its various personal & social risks. Sexual Motivation Be able to explain the stages of the Sexual Response Cycle. How is sexual motivation influenced by hormones (i.e Estrogens & Testosterone)? What internal stimuli & external stimuli influence sexual motivation? Be able to explain what factors (Especially biological ones) influence Sexual Orientation. Social & Work Motivation For what reasons might humans feel a desire to “belong?” What is the difference between Personnel Psychology & Organizational Psychology? What factors can negatively influence interviews & performance evaluations? What is the difference between Task Leadership & Social Leadership? Chapter 12: Emotion Theories of Emotion Match William James, Carl Lange, Water Cannon, Philip Bard, & Stanley Schachter to their theory. Be able to explain each of the 3 theories of emotion & how they differ from each other. Embodied Emotions Be able to explain how the Autonomic Nervous System controls emotional arousal. What are the similarities and differences in how the human body expresses different emotions? How do our thoughts (Cognitions) & feelings (emotions) affect each other? Expressing Emotions Does ones’ gender affect their ability to detect nonverbal expressions? If so, how? Understand Paul Ekman’s research into the effect of culture on nonverbal expressions. Do our facial expressions have an effect on our feelings? Experiencing Emotions Understand Carol Izzard’s discovery. What are the environmental causes & biological causes of fear? What role does the Amygdala play in fear? What are the negative consequences of Anger? Does “venting” work? What are the positive consequences of Happiness? How is the long-term effect of positive or negative life-events on our happiness? What effect does wealth have on happiness? Have a general idea of what factors are & are not related to happiness (Table 12.1). Stress Explain how the Fight-or-Flight response works. What effects do the hormones Cortisol & Oxytocin have on stress response? Be able to explain Hans Selye’s General Adaptation Syndrome & it’s 3 phases. What are the negative consequences of stress on the heart? Understand the difference between Type A & Type B Personalities & their relation to stress. What effect does stress have on the immune system, and our ability to resist AIDS & Cancer. Managing Stress Understand what can be done to reduce ones’ level of stress Understand how Biofeedback works.