Name ______________________________ Period ___
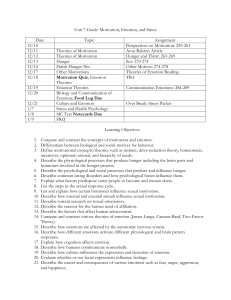
Unit # 4 -- MOTIVATION, EMOTION and STRESS
Motivation is….
An instinct is…
Do humans seem to be motivated by instincts?
Explain the drive-reduction theory.
o How does homeostasis relate to this theory?
o Give an example of the homeostasis process at work in your body.
o What are incentives and how do they influence our behavior?
Explain the “optimum arousal” theory.
Describe Abraham Maslow’s hierarchy of needs- draw the diagram and explain it.
Physiology of Hunger
How do glucose levels affect hunger?
Explain the hypothalamus’s role in hunger, including the 2 parts of the hypothalamus.
RG 4E
pg. 327-348
Part:
Part:
Role in hunger:
Role in hunger:
Explain the concept of a set point.
How does one’s basal metabolic rate influence set point and hunger?
Does a “set point” really exist? Explain.
Psychology of Hunger
Are our taste preferences due to biology or culture? Explain.
Anorexia Nervosa is….
Bulimia Nervosa is…
Discuss the differences in the families of anorexics and bulimics.
What causes eating disorders?
Discuss the research concerning women’s body image/body shapes.
Sexual Motivation
Briefly describe/explain Kinsey’s research.
Explain the 4 stages of the sexual response cycle.
●
●
●
●
RG 4Fpg. 348-362
How do hormones affect sexual behavior?
How are the motives of hunger and sex different? Alike?
What is sexual orientation?
What causes one’s sexual orientation (summarize)?
The brain –
Genetics –
Prenatal hormones –
The controversy…
The Need to Belong
● Aiding survival – How has our need to belong helped us survive?
● Wanting to belong – How important are relationships?
● Acting for acceptance – Describe how our behaviors indicate our “need to belong.”
● Maintaining relationships – What happens when relationships break down? How does this impact
our overall well-being?
● Ostracism – What is it? How do we respond, physically and psychologically to it?
● Health – How is health impacted by the relationships we have?
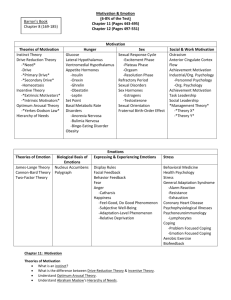
Introduction to Emotion
RG 4G pg. 366-384
Emotions are…
Explain each of the following theories of emotion:
● James-Lange Theory
● Cannon-Bard Theory
● Schachter-Singer Two-factor Theory
Describe what physically happens to your body when you are experiencing emotional arousal.
Explain the relationship between performance and arousal.--> IMPORTANT
How does brain activity differ when people experience negative vs. positive emotions?
Explain Zajonc’s beliefs cognition and emotion.
Give an example of evidence that supports this view.
What did Lazarus say about emotion and cognition?
Expressing Emotion
How do we communicate nonverbally?
How do women and men differ in expressing emotion?
How do real and fake emotional expressions differ?
How good are we at detecting the difference? Explain.
Explain Ekman’s research on our accuracy in detecting emotions.
How does computer-based communication impact emotion and meaning?
Do facial expressions have different meanings in different cultures?
What did Darwin say concerning this similarity in facial expressions?
Do cultures similarly express emotion? Explain?
What did Darwin say concerning the “expression of emotion”?
Does more recent studies/evidence support or reject this “facial/behavioral feedback” theory?
Explain.
Experienced Emotions
List the 10 basic emotions identified by Carroll Izard.
What purpose does fear have in our lives?
How do we learn to fear?
RG 4H pg. 384-406
What brain structure is involved in fear? How so?
Describe phobias and how they differ from an average fear.
How angry are we?
Explain the catharsis hypothesis.
Does “blowing off steam” really help? Explain.
List the two suggestions offered by experts for handling anger.
Explain the feel-good, do-good phenomenon.
What is subjective well-being?
How does wealth seemingly influence happiness?
Adaptation-Level phenomenon vs. relative deprivation
List the six factors that have been shown to be positively correlated with feelings of happiness.
List five factors that are evidently unrelated to happiness
Stress is…
Explain Selye’s phases of the general adaptation syndrome (GAS).
○ 1 – alarm reaction
○ 2 – resistance
○ 3 -- exhaustion
What has other research shown in relation to experiencing prolonged stress.
Explain how each of the following events can be stressors…
● Catastrophes
● Significant life changes
● Daily hassles (including burnout)
To what extent does stress contribute to heart disease?
Discuss Type A vs. Type B “personalities”
How does negative emotions/pessimism impact ones physical as well as sense of wellness?
Explain psychophysiological illnesses.
How does stress impact our immune systems?
Give one example from the text of this…