Atomic Theory, Periodic Table, Solubility Review
advertisement

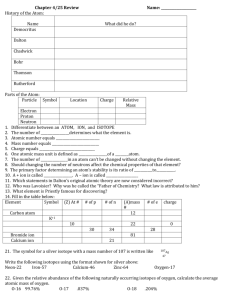
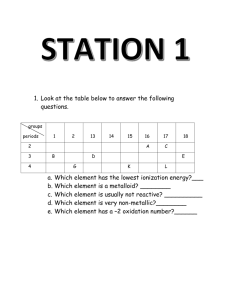
Chemistry 11 Unit 1: Safety, Atomic Theory & Matter Review 1. What is WHMIS? 2. What is a MSDS? Give three pieces of information that could be found on an MSDS. 3. State what each of the following contributed to the knowledge of the atom: a) John Dalton b) JJ Thompson c) Ernest Rutherford d) Neils Bohr 4. Complete the following table (the first one is done for you): Isotope symbol Atomic # Mass # protons neutrons electrons charge chlorine – 37 atom 37 17 Cl 17 37 17 20 17 0 silicon-28 atom 0 nitrogen-14 ion 39 aluminum-27 ion 10 27 3+ 13 Al 16 33 oxygen-18 atom 28 8 18 2O 8 0 9 0 18 oxygen-16 ion 10 26 Feb 2012 1- 41 18 56 24 2+ Chemistry 11 5. Determine the atomic mass of the following elements: Isotope Boron-10 Boron-11 Abundance in nature (%) 19.6 80.4 Relative mass of atom (based on 12C) 10.0129 11.0093 Carbon-12 Carbon-13 98.89 1.11 12.0000 13.0034 Oxygen-16 Oxygen-17 Oxygen-18 99.76 0.04 0.20 15.9949 16.9991 17.9992 Calculation Atomic Mass 6. Distinguish between the terms atomic mass and mass number. 7. Explain how the isotopes carbon-12 and carbon-13 are similar and how they are different, based on atomic structure. 8. Indicate how many electrons are in each energy level (Bohr Diagrams) for each of the following atoms or ions: Ca N3- Ca2+ Ne 9. Using the Electron Energy Chart, determine the electron configuration (spdf) for the following atoms. a) S b) Rb c) Ne d) Br 10. Periodic Table Trends a) Which diagram represents: Ionization Energy and Atomic Radius (An arrow shows direction of increase) ________________ Feb 2012 _______________ Chemistry 11 b) Explain why the atomic radius trend is seen above. Explain the differences we see as we go along the period and down a group. c) Using the Diagram below, indicate with arrow heads the direction of the trend described: Electronegativity Increases Electronegativity Increases d) What is the relationship between an atom’s Electronegativity (EN) and their Ionization Energy (IE)? 11. Identify important properties for each of the following families: Alkali Metals: a) ___________________ b) ______________________ c) __________________ Alkaline Earth Metals: a) __________________ b) __________________ c) ________________ Halogens: a) ___________________ b) __________________ c) _____________________ 12. What type of bond would you expect from the following (ionic or covalent): a) H and O ___________ d) Ca and Br ____________ b) K and I ___________ e) N and F _____________ c) Ni and Cl __________ f) I and I ____________ 13. Distinguish between the terms solvent and solute: 14. Classify each of the following as either: heterogenous mixture, solution, element, compound, molecule, or ion. NaCl _________ Feb 2012 Na ________ N2 _________ concrete Mg+2 sea water _________ __________ _________ Chemistry 11 15. Draw a Lewis structure (electron dot diagram) for each of the following: a) NF3 b) NH4+ c) NO3- d) CO2 e) N2 f) PO43- g) CO32- h) SCN- i) C2O42- (the shape is shown below) O O C O 16. a) Give an example of a chemical and a physical property. b) What is a chemical change? What is a physical change? 17. Give an example of a qualitative and a quantitative observation. Feb 2012 C O