station 1
advertisement
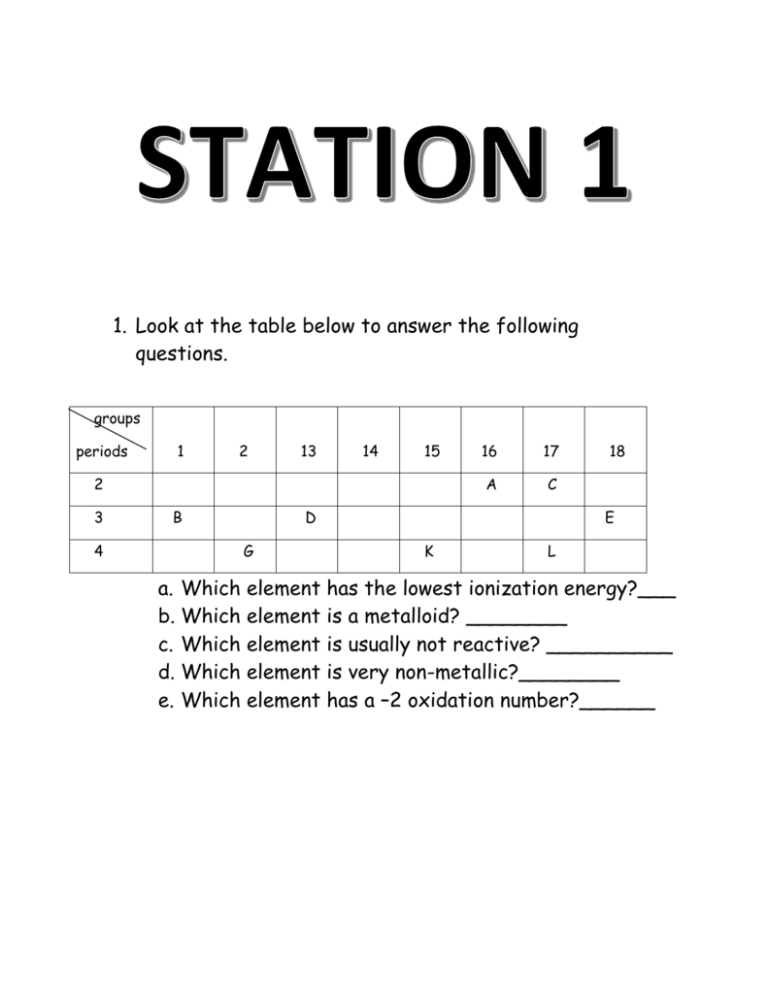
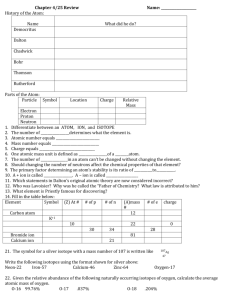
1. Look at the table below to answer the following questions. groups periods 1 2 13 14 15 2 3 4 B 16 17 A C D G 18 E K L a. Which element has the lowest ionization energy?___ b. Which element is a metalloid? ________ c. Which element is usually not reactive? __________ d. Which element is very non-metallic?________ e. Which element has a –2 oxidation number?______ Complete the following: a. Name of element that is in the same group as Beryllium and period as Bromine b. Halogen that is a non-metal and is a solid at room temperature. c. Element that is a metalloid in period 3 d. What group would X be in the following compound MgX? e. What group would X be in XCl3? f. What group would X be in X3P2? Use the following elements to answer the questions: Beryllium and Oxygen a. Draw the Bohr diagram for each element below. b. Going across the period what are you adding to each element? c. What stays the same across the period? d. What is the radius for each element? e. Explain in terms of structure what happens to the radius going across the period. Use the following elements to answer the questions below: Sodium and Cesium a. Draw the Bohr diagram for each element below. b. Going top to bottom in a group what are you adding to each element? c. What stays the same in a group? d. What is the radius for each element? e. Explain in terms of structure what happens to the radius in a group as the atomic number increases. Consider lithium, a. Is it a metal or a nonmetal? b. What type of ion (positive or negative) does your element form? c. Why does it form the ion? d. List 4 other characteristics about metals. e. Draw the Bohr diagram for your element as an atom and then an ion. f. In terms of atomic structure compare the atomic radius of your atom and ion. Consider sulfur, a. Is it a metal or a nonmetal? b. What type of ion (positive or negative) does your element form? c. Why does it form the ion? d. List 4 other characteristics about non-metals. e. Draw the Bohr diagram for your element as an atom and then an ion. f. In terms of atomic structure compare the atomic radius of your atom and ion. Consider copper, a. What group is this element found in? b. What is special about this metal? c. What type of metal is it? d. What are the oxidation states of your metal?