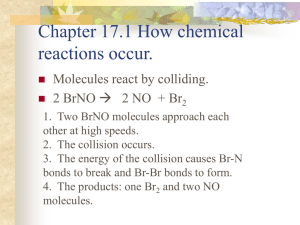
ozone dioxide
advertisement
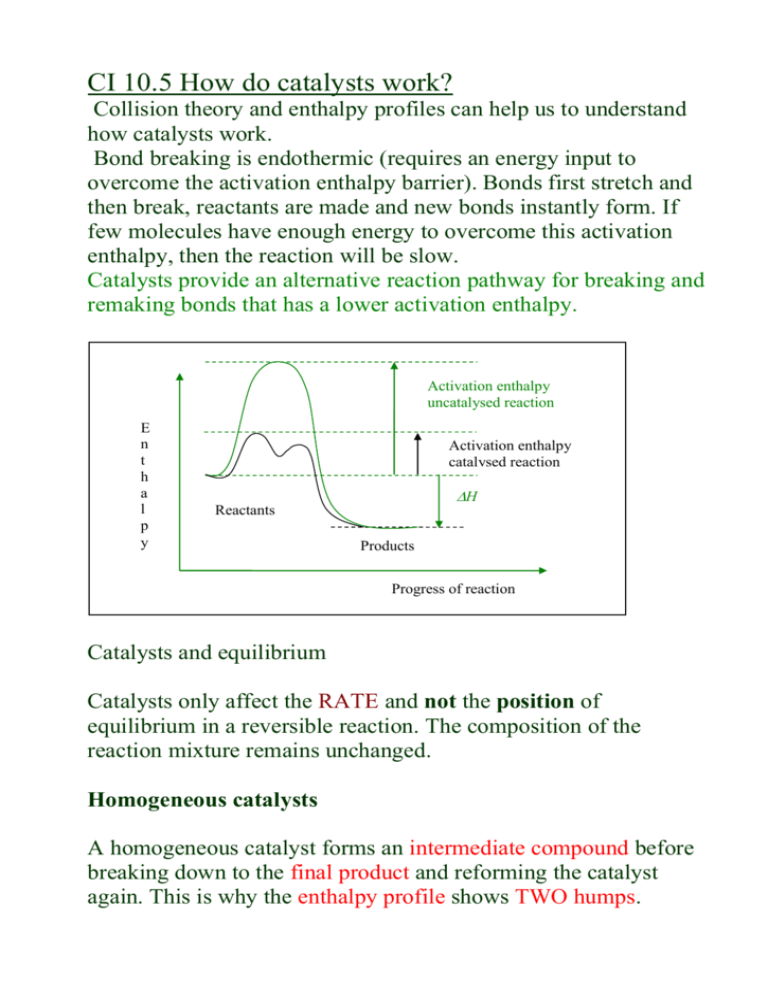
CI 10.5 How do catalysts work? Collision theory and enthalpy profiles can help us to understand how catalysts work. Bond breaking is endothermic (requires an energy input to overcome the activation enthalpy barrier). Bonds first stretch and then break, reactants are made and new bonds instantly form. If few molecules have enough energy to overcome this activation enthalpy, then the reaction will be slow. Catalysts provide an alternative reaction pathway for breaking and remaking bonds that has a lower activation enthalpy. Activation enthalpy uncatalysed reaction E n t h a l p y Activation enthalpy catalysed reaction H Reactants Products Progress of reaction Catalysts and equilibrium Catalysts only affect the RATE and not the position of equilibrium in a reversible reaction. The composition of the reaction mixture remains unchanged. Homogeneous catalysts A homogeneous catalyst forms an intermediate compound before breaking down to the final product and reforming the catalyst again. This is why the enthalpy profile shows TWO humps. Enthalpy Intermediate compound Final product H Reactants Products Progress of reaction CFCs act as homogeneous catalysts in the stratosphere, breaking down ozone. Cl atoms catalyse the reaction, forming the intermediate ClO: Cl + O3 O2 + ClO intermediate ClO + O Cl + O2 O3 + O O2 + O2 overall change A single Cl atom can catalyse the reaction of many ozone molecules through a catalytic cycle. Industry uses mostly heterogeneous catalysts. However homogeneous catalysts can be more specific and controllable. Eg. Methanol Rhodium (aq) ethanoic acid Conversion is 99% with soluble rhodium compounds. Do problems for 10.5 p.243 questions 1 and 2. SL: Other ways ozone is removed Radicals such as hydroxyl and nitrogen monoxide can destroy ozone, as well as chlorine and bromine. In general: X + O3 XO + O2 XO + O X + O2 Overall reaction: O + O3 O2 + O 2 Hydroxyl radicals (HO) form in the stratosphere when water molecules react with oxygen. The reaction with ozone is: HO + O3 HO2 + O2 HO2 + O HO + O2 The reformed HO radicals can react with more ozone, in a catalytic cycle. Nitrogen monoxide (NO) forms nitrogen dioxide and dioxygen when it reacts with ozone. NO and NO2 are relatively stable radicals which can be collected in ordinary ways. do assignment 8, p.71 a) Write an equation to show the formation of HO radicals from O atoms and water. H2O(g) + O(g) HO + HO b) Write equations to show how nitrogen monoxide can destroy ozone in a catalytic cycle. NO + O3 NO2 + O2 NO2 + O NO + O2 SL A4: The CFC story In the early 1970s there was concern about jet aircraft releasing NO in their exhausts. Levels were not significant at the time. In 1974 CFCs became a concern… read about it p.71-74 and do assignments 9 and 10.