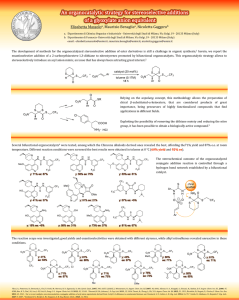
Diapositive 1 - Groupe Charette
advertisement
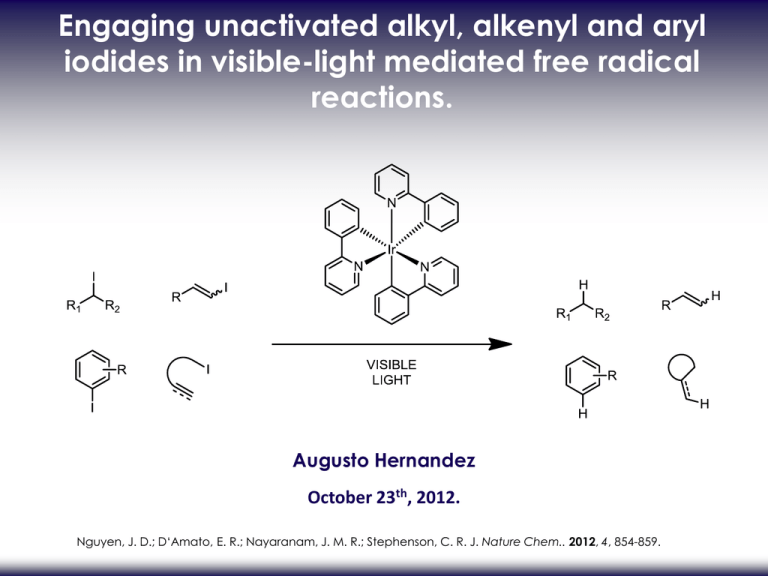
Engaging unactivated alkyl, alkenyl and aryl iodides in visible-light mediated free radical reactions. Augusto Hernandez October 23th, 2012. Nguyen, J. D.; D‘Amato, E. R.; Nayaranam, J. M. R.; Stephenson, C. R. J. Nature Chem.. 2012, 4, 854-859. RADICAL REDUCTION DEHALOGENATION. Alkyl, alkenyl and aryl iodides conventional reduction methods1: 1- Metal-halogen exchange 2-Hydride source •Not functional group tolerant •Undesired side reactions possible 3-Radical reductive dehalogenation •Common system: •Organotin (nBu3SnH with AIBN) •Samarium(II) iodide •Trialkylborane (Et3B and air) Use in the total synthesis of (±)-hirsutene2: (1)Alonso, F., Beletskaya, I. P.; Yus, M. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 4009–4091. (2) Curran, D. P. & Rakiewicz, D. M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1985, 107, 1448–1449. RADICAL REDUCTION DEHALOGENATION. Radical reductive dehalogenation •Common system: •Organotin (nBu3SnH with AIBN) •Samarium(II) iodide •Trialkylborane (Et3B and air) Advantages: •Most used method • Mild conditions (pH neutral) •Short reaction time •High product yield Disadvantages: toxic3 unstable to air4 pyrophoric5 (3) Neumann, W. P. Synthesis 1987, 665–683. (4) Krief, A.; Laval, A-M. Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 745–777. (5) Medeiros, M. R., Schacherer, L. N., Spiegel, D. A. & Wood, J. L. Org. Lett. 2007, 9, 4427–4429. NEW SYSTEMS. •Ground-state neutral electron donors (tetraazaalkene)6,7: Aryl and alkyl iodides: • Cobalt-catalyzed Heck-type cyclization8: Alkyl and stannyl-cobaloxime catalyst: Alkyl iodides only Yield: 70-90% (6) Murphy, J. A., Khan, T. A., Zhou, S. Z., Thomson, D. W.; Mahesh, M. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 1356–1360. (7) Murphy, J. A. et al. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 3673–3676. (8) Weiss, M. E., Kreis, L. M., Lauber, A.; Carreira E. M. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 11125–11128. GOAL. Develop a new mild and efficient radical reductive deiodination protocol •Broad functional group tolerance •Easy-to-handle catalyst •Inexpensive and readily available hydrogen atom donor Metal-based photocatalyst (Ru or Ir) : Generates radical intermediates from activated carbon-halogen bond Bromomalonates9 Electron-deficient benzyl bromides12 Polyhalomethanes10,11 -halo carbonyl13 Glycosyl bromides14 (9) Nguyen, J. D., Tucker, J. W., Konieczynska, M. D.; Stephenson, C. R. J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 4160–4163. (10) agib, D. A., Scott, M. E.; MacMillan, D. W. C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 10875–10877. (11) Dai, C., Narayanam, J. M. R.; Stephenson, C. R. J. Nature Chem. 2011, 3, 140–145. (12) Shih, H. W., Vander Wal, M. N., Grange, R. L.; MacMillan, D. W. C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 132, 13600–13603. (13) Tucker, J. W.; Stephenson, C. R. J. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 5468–5471. (14) Andrews, R. S., Becker, J. J.; Gagné, M. R. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 9, 7274–7276. PREVIOUS WORK. •Tin-free alternative using of [Ru(II)(bpy)3]Cl2 photocatalyst: Use of iPr2NEt with HCOOH or Hantzsch ester15 •Tin-free radical cyclization reactions using of [Ru(II)(bpy)3]Cl2 photocatalyst16 Use of Et3N (15) Narayanam, J. M. R., Tucker, J. W.; Stephenson, C. R. J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 8756–8757. (16) Tucker, J. W., Nguyen, J. D., Narayanam, J. M. R., Krabbe, S. W.; Stephenson, C. R. J. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 4985–4987. PHOTOCATALYST TUNING. •Reduction of unactivated carbon-iodide bonds is difficult due to high reduction potential •Photocatalyst tuning to stronger reduction potential: change of ligand (bipyridyl to phenylpyridyl) OPTIMIZATION. •Best reductant: tributylamine •Acetonotrile gives better conversion •Argon sparging increase conversion than freeze-pump-thaw degassing SCOPE - REDUCTION OF ALKYL IODIDES AND ARYL IODIDES. •Excellent functional group tolerance. •Bu3N and HCO2H give acceptable reaction times (52h vs 24h). •Aryl bromide and chloride are not reduced. •Bu3N and HCO2H are not suitable for alkyl iodide (low yields). SCOPE - REDUCTION OF ALKENYL IODIDES. •Increase of Bu3N and HCO2H to achieve acceptable reaction times. •Procedure is effective for intramolecular cyclization1 •No substitution or elimination product observed •Scope of products -tetrahydrofuran -indoline -indole -dihydrobenzofuran -carbocycle GRAM SCALE REACTION / FLOW REACTION. Gram scale reaction •7,5 times more substrate •20 times less photocatalyst Flow reaction Increase of conversion rate Flow reaction: 0,900 mol/h Batch reaction: 0,020 mol/h (17) Tucker, J. W., Zhang, Y., Jamison, T. F.; Stephenson, C. R. J. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 4144–4147. MECHANISM. Radical based mechanism •Visible light and photocatalyst necessary •HCO2H/trialkylamine or Hantzsch ester/trialkylamine are electron donor/hydrogen atom donor Acetonitrile is not an hydrogen atom donor •Photocatalyst acts only as an initiator •No catalyst turnover without electron donor •Propagation chains are short-lived 0% deuterium incorporation MECHANISM. •Reductive cleavage gives Ir(ppy)3+ and carbon radical •Hydrogen abstraction from Bu3N, Hantzsch ester or formic acid •Bu3N is oxidize to regenerate Ir(ppy) (17) Tucker, J. W., Zhang, Y., Jamison, T. F.; Stephenson, C. R. J. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 4144–4147. CONCLUSION. Visible light photoredox-mediated reductive deiodination protocol •Can undergo intramolecular cyclization •Mild conditions •Low catalyst loading with high yields •Electron and hydrogen donors are inexpensive and readily available •High functional group tolerance •Easy to scale-up •Short reaction time with flow reaction