File
advertisement

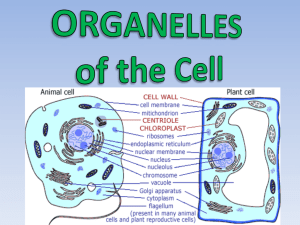
THE CELL AND ITS ORGANELLES SCIENTISTS OF CELLS Hooke viewed cork; coined the term “cells” van Leeuwenhoek first to view cells under the microscope Schleiden plants made of cells Schwann animals made of cells Virchow new cells only come from division of other cells ALL THESE SCIENTISTS LED TO THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE CELL THEORY! CELL THEORY All living things are composed of cells Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things New cells are produced from existing cells CELL CATEGORIES Prokaryotes no membrane bound organelles genetic material not in the nucleus Cell membrane Small Eukaryotes (YOU!) Have organelles Genetic material contained in nucleus Cell membrane Large CATEGORIES OF CELLS Bacteria Prokaryotes animal cells plant cells Eukaryotes CELLS AND THE WORK OF LIFE gas exchange: O2 in vs. CO2 out take in & digest food make energy ATP build molecules proteins, carbs, fats, nucleic acids remove wastes control internal conditions respond to external environment What are they responding to? build more cells growth, repair, reproduction & development CELL ORGANELLES Carry out specialized functions within the cell Lots of different ones found in eukaryotic cells Cytoplasm is a thick, liquid residing between the cell membrane holding all living material inside the cell doesn't contain the nucleus. CYTOSKELETON Acts as skeleton and muscle Provides shape and structure Helps the cell with movement Microtubules Microfilaments CELL WALL Found in plant and bacterial cells Rigid, protective and supportive barrier Located outside of the cell membrane Porous Made from fibers of carbs and proteins Plant Cell Walls are made from Cellulose Plasmodesmata: holes or channels in the cell wall that allow for transport/communication 1ST MAJOR FUNCTION: CELLS NEED TO MAKE ENERGY! To fuel daily life & growth, the cell must… take in food & digest it take in oxygen (O2) make ATP (energy) remove waste Organelles that do this work… cell membrane vacuoles lysosomes mitochondria CELL MEMBRANE Boundary of the cell Made of a phospholipid bilayer CELL MEMBRANE (CTD.) phosphate “head” Function separates cell from outside environment controls what enters or leaves cell recognizes signals from other cells O2, CO2, food, H2O, nutrients, waste allows communication between cells Structure Double layer of fat Protein molecules (50%) phospholipid bilayer Receptor proteins Structural proteins Protein channels carb chains ID cards lipid “tail” LYSOSOMES Garbage disposal of the cell THEY GET RID OF THE CELL JUNK Contain digestive enzymes that break down wastes and food Food needs to be broken down into useable forms Breakdown organelles that aren’t functioning properly VACUOLES Large central vacuole usually in plant cells Many smaller vacuoles in animal cells Storage container for water, food, enzymes, wastes, pigments, etc. FOOD & WATER STORAGE plant cells food vacuole animal cells central vacuole contractile vacuole MITOCHONDRIA Nickname: “Powerhouse of the cell” Function: Convert chemical energy stored in food into compounds that are usable by the cell Cellular respiration occurs here Bound by a double membrane Has its own DNA, ribosomes, and can make its own protein! MITOCHONDRIA ARE IN BOTH CELLS!! animal cells plant cells mitochondria CHLOROPLAST Found only in plant cells Contains the green pigment chlorophyll Site of food (glucose) production Bound by a double membrane SECOND IMPORTANT FUNCTION CELLS NEED TO MAKE PROTEINS! Making proteins to run daily life & growth, the cell must… read genes (DNA) build proteins structural proteins (muscle fibers, hair, skin, claws) enzymes (speed up chemical reactions) signals (hormones) & receptors organelles that do this work nucleus ribosomes endoplasmic reticulum (ER) Golgi apparatus NUCLEUS Function: Control center of the cell Contains DNA Contains instructions for making protein Surrounded by a double membrane Usually only one per cell RIBOSOME Small particles of RNA and protein Function: Site of protein synthesis Found attached to rough ER or floating free in cytoplasm Produced in a part of the nucleus called the nucleolus ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM Nickname: “ER” Connected to nuclear membrane “Highway of the cell” Rough ER: studded with ribosomes; it makes proteins Smooth ER: no ribosomes; functions in detoxification; it makes lipids! GOLGI APPARATUS Function: Stores, modifies and packages proteins Nickname: Post office of the cell Molecules transported to and from the Golgi by means of vesicles THIRD IMPORTANT JOB! CELLS NEED TO MAKE MORE CELLS! To replace, repair & grow, the cell must… copy their DNA make extra organelles divide the new DNA & new organelles between 2 new “daughter” cells Organelles that do this work Nucleus Microtubules Centrioles MICROTUBULES Made up of proteins known as tubulins Important in cell division mitotic spindle separates chromosomes CENTRIOLE Help coordinate cell division Found only in animal cells One pair in each cell Made of microtubules