cell
advertisement
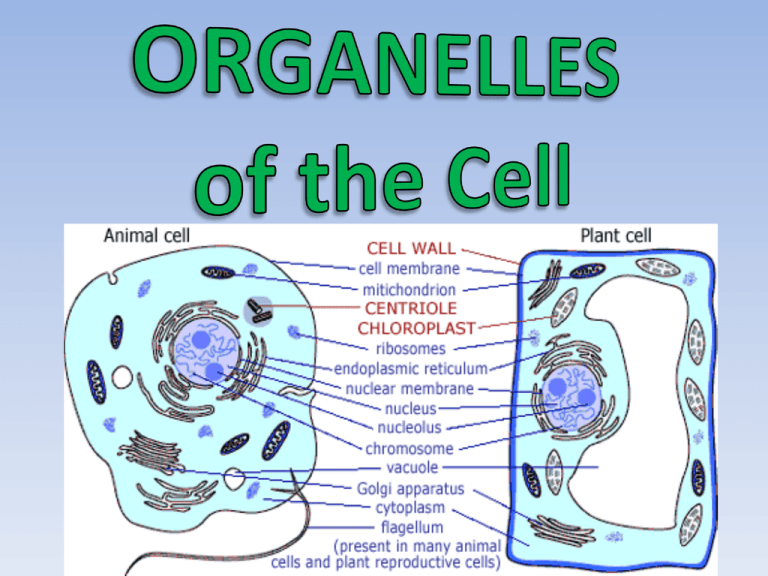
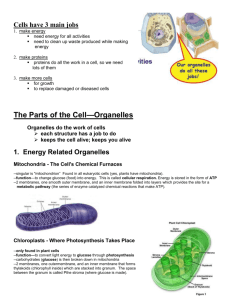
• Appearance: Large Oval • Location: varies • Function: Control center for all cell functions • Appearance: Clear fluid • Location: Inside the cell membrane • Function: Suspends organelles; site of chemical reactions • Appearance: Round structure inside the nucleus • Location: Inside the nucleus • Function: • Site of RNA synthesis • Produces ribosomes • Appearance: surrounds cell • Location: –Plant: inside the cell wall –Animal: outer layer »Semipermeable »Composed of lipids & proteins • Function: Controls materials in and out of the cell • Appearance: mesh of hollow sheets with ribosomes attached • Location: Connected to the nucleus and plasma membrane • Function: • Rough: acts like a conveyer belt and transports proteins Rough ER • Appearance: mesh of hollow sheets • Location: Connected to the nucleus and plasma membrane • Function: • Smooth: produces lipids • Appearance: Small, dense granules • Location: Free in the cytoplasm; attached to the ER -proteins made are used by the cell or moved out and used by other cells • Function: Synthesize proteins • Appearance: Flattened sacs • Location: Near the ER • Function: Temporary storage, packaging and secretion of proteins and fats – Produces lysosomes • Appearance: usually bean shaped with folded membranes (greater surface area-hence more energy) • Location: Many mitochondria in a cell! • Function: Powerhouse of the cell (energy production ATP) • Appearance: Cavities filled with fluid • Location: • Plant: usually 1 large water-filled vacuole (maintains structure) • Animal: many tiny vacuoles • Function: Storage of water, starch, fats, etc • Two types: –Contractile vacuole: removes water and wastes –Food vacuole: breaks down food • Appearance: Egg shaped-membrane bound structure • Produced by the Golgi Bodies • Location: ONLY found in animal cells • Function: Contain digestive enzymes that break down molecules • Aid in the digestion of nutrients • Break down destructive cells (bacteria) • Appearance: Network of thin, fibrous proteins (microtubules & microfilaments) • Location: Entire cell • Function: Acts as sort of a scaffold to provide support for organelles – Helps maintain cell shape • Appearance: Long, threadlike proteins • Location: A part of cytoskeleton • Function: Associated with muscle contractions in large organisms – Associated with cell movement • Appearance: Thin, hollow cylinders of proteins • Location: A part of cytoskeleton • Function: Provide shape and rigidity to the cell • Assist organelles to move from place to place within the cell • Appearance: thin hair-like projections • Location: Formed from specialized microtubules • Attached to outside of cell • Function: Aid in movement and locomotion (intestinal cells) • Appearance: Whiplike tails • Location: Formed from specialized microtubules • Attached to outside of cell • Function: Aid in movement and locomotion (sperm) • Appearance: Strings of “spaghetti” • Location: inside nucleus • Function: Uncoiled DNA; involved in duplicating the cells – Coils into chromosomes during cell division • Appearance: Coiled chromatin • Location: inside nucleus • Function: Contains genetic information (DNA) • Appearance: Two small structures • Location: Found inside the centrosome (only in animal cells) • Function: Moves chromosomes during cell division • Appearance: varies • Have own DNA • Location: ONLY in plants • Function: based on type: Leucoplast (store starch), chromoplast (store pigments), chloroplast • Appearance: Small, circular, green (contains chlorophyllgreen pigment • Location: ONLY in plants • Function: Site of photosynthesis • Appearance: • Made of cellulose • Rigid, strong, stiff structure • Location: Surrounds cell membrane (only in plants) • Function: Support & protection • Allows H2O, O2, CO2 to pass into and out of cell • All the organelles work together! –For example, after some proteins are made by the ribosomes, the rough ER transports these proteins to the golgi apparatus, then the golgi makes vesicles that can fuse with the cell’s plasma membrane to release proteins to the environments outside the cellor used within the cell.. Microfilaments Golgi Body Ribosomes Nucleolus Mitochondria Chromatin Microtubule Rough ER Smooth ER Nucleus Plasma Membrane Ribosomes Microtubule Microfilaments Nucleolus Mitochondria Plasma Membrane Golgi Body Chromatin Smooth ER Nucleus Rough ER