File
advertisement

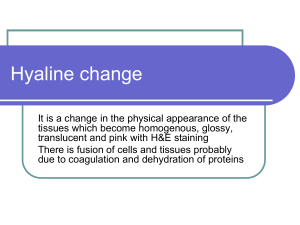
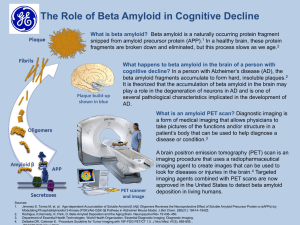
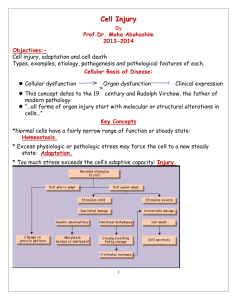
Amyloidosis Dr. Amitabha Basu What is amyloid (amylin : starch-like)? ► Def : Homogeneous, Pink, extra cellular , pathologic material. Nature of Amyloid A. Physical Nature : non branching protein fibrils 7.5 -10 nm in diameter. Beta pleated sheet. B. Chemical nature : 95% Protein Fibril Beta-Pleated Sheet Chemical nature ► Amyloid = 95% Protein Fibril + 5% Glycoprotein P component - pentagonal molecule ► Many different chemical types of amyloid ► Common types Amyloid associate ( AA) Amyloid light chain (AL) Pathogenesis ► Precursor of AA = SAA ( Serum Amyloid Associate protein from liver): chronic inflammation. ► Precursor of AL = Immunoglobulin from plasma cells = ? Multiple Myeloma . Amyloidosis ► Def : Disease characterized by deposition of amyloid in the tissue. Classifications of Amyloidosis A. Systemic amyloidosis 1. Primary amyloidosis 2. Secondary amyloidosis B. Localized amyloidosis 1. Senile cerebral 2. Senile cardiac 3. Type 2 diabetes. Primary systemic amyloidosis Disease name Multiple Myeloma Type of Precursor amyloid in the tissue AL Ig lambda (or kappa chains) Secondary systemic amyloidosis Disease name Type of amyloid in the tissue Chronic inflammatory disease. AA Hemodialysis associate amyloidosis in chronic renal failure. A-beta 2 micro globulin. (Aβ2- micro globulin) Rheumatoid arthritis AA Localized amyloidosis : mainly due to aging Disease name Type of amyloid in the tissue Senile cerebral Amyloid beta amyloidosis: protein Alzheimer's (Aß) disease Type 2 diabetes Islet amyloid polypeptide ( AIAPP) in islet of Langerhans Disease and amyloid Multiple Myeloma ( Primary) AL Rheumatoid arthritis/ TB AA ( secondary, reactive) Senile systemic amyloidosis, TTR familial polyneuropathies Acute Familial Mediterranean Fever Hemodialysis associated AA Alzheimer's disease Amyloid beta Medullary CA thyroid calcitonin Aβ2 micro globulin Special stain and amyloid ► Lugals iodine: Used only on gross specimen ► PAS: Stain P component ( in Biopsy specimen) ► Congored : Most important (in Biopsy specimen) Special stain and amyloid ► Lugals heart. iodine : Brown in gross specimen of Special stain and amyloid Congo red ( normal light) Congo red ( polarized light) Brick red Apple green birefringence Morphology ► Gross of any organ with amyloidosis : Waxy in nature. Amyloidosis of kidney ; amyloid deposit in the mesengeum of the glomerular tuft Amyloid in heart : name the stain and viewing light Clinical manifestation Kidney Nephrotic syndrome, protenuria, renal failure Tongue , GIT Macroglossia, malabsorpton Heart Cardiomegaly, heart failure Bone marrow Fracture/ Multiple involvement in myeloma Multiple Myeloma. Laboratory findings 1. Biopsy from gingiva and rectum and special stain. 2. Diagnosis of Multiple Myeloma associated amyloid (AL). 1. Presence of M-band in electrophoresis. 2. Bens-Jones protein in the urine. 3. Increased light chain and monoclonal Ig. Presence of M-band in electrophoresis Disease and Amyloid ► Primary amyloidosis: AL, ► Secondary amyloidosis : AA, ► Hereditary (familial) amyloidosis: ATTR Disease and amyloid Multiple Myeloma ( Primary) AL Rheumatoid arthritis/ TB AA ( secondary, reactive) Senile systemic amyloidosis, TTR familial polyneuropathies Acute Familial Mediterranean Fever Hemodialysis associated AA Alzheimer's disease Amyloid beta Medullary CA thyroid calcitonin Aβ2 micro globulin Thank you