Radiometric dating - PowerPoint
advertisement

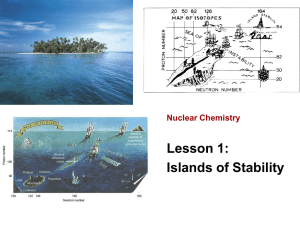
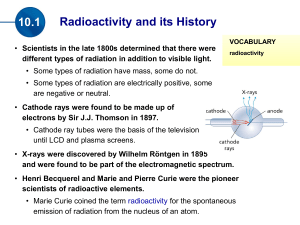
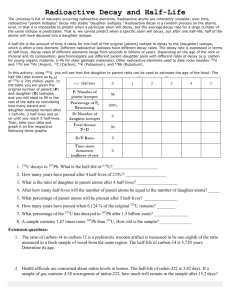
Absolute Dating by the Use of Radioactive Isotopes What is Absolute Dating? Age of fossil or rock is given in years instead of relative terms like before and after, early and late. Does not mean it isn’t without error Radiometric dating is the most common type of absolute dating. Atoms and Isotopes: Let’s review the basics Chemical symbol for element Mass # (protons + neutrons) A Z X The number of protons in an atom determines which element it is. If you change the # of protons, the element changes & the mass changes. If you change the # of neutrons, the element stays the same, but the mass changes ISOTOPES - atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons Atomic # (protons) http://www.saskschools.ca/curr_content/c hem30/images/e_deuterium.jpg Why Are Some Isotopes Radioactive? Isotopes that have the right amount of neutrons are called stable. They always stay the same. Some isotopes have a few too many neutrons or not enough - This makes them unstable and radioactive. The nuclei of these radioactive atoms change or decay by giving off radiation in the form of particles or electromagnetic waves until the atom reaches a stable state. Radioactive Decay During radioactive decay, the number of protons in the atom changes, and one element transforms into another. Parent isotopes decay into daughter isotopes. Radioactive Decay is like popping popcorn. Each radioactive parent always decays to a specific daughter. There is no way to predict which atoms will decay first. Radioactive atoms decay at a specific rate. Once they decay, they can not change back. How Long Does Radioactive Decay Take? Half-Life - the time it takes for half of the radioactive or parent isotopes in a sample to decay to daughter isotopes. Each parent has a 50% chance of decaying during 1 half-life. Measured in seconds, minutes, years, etc. Each isotope has its own unique half-life. From thousandths of a second to billions of years Starting the Stopwatch If you measure the ratio of parent to daughter isotopes, you can determine how many half-lives have passed. Find the half-life of the parent isotope # of half-lives length of half-life = age of sample Example: 3 half-lives; 1 half-life = 200 years Atoms Don’t Age the Way We Do 1 2 3 4 Start with 16 baby aliens Have 70 year half-lives 4 half-lives = 280 years Each atom has a 50% chance of decaying during a half-life. http://www.colorado.edu/physics/2000/isotopes/ima ges/age280_baby.jpg How to Choose Which Isotope to Use K-40: feldspar & mica Uranium: zircon Estimate the age of your sample and choose an isotope with an appropriate range. First find out what minerals are in your sample. The minerals in your rock need to have the element you want to use for dating. Carbon-14 can only be used to date samples that were once living (organic) Ex: Wood, bone, cloth, paper Let’s Practice Absolute Dating