problem set
advertisement
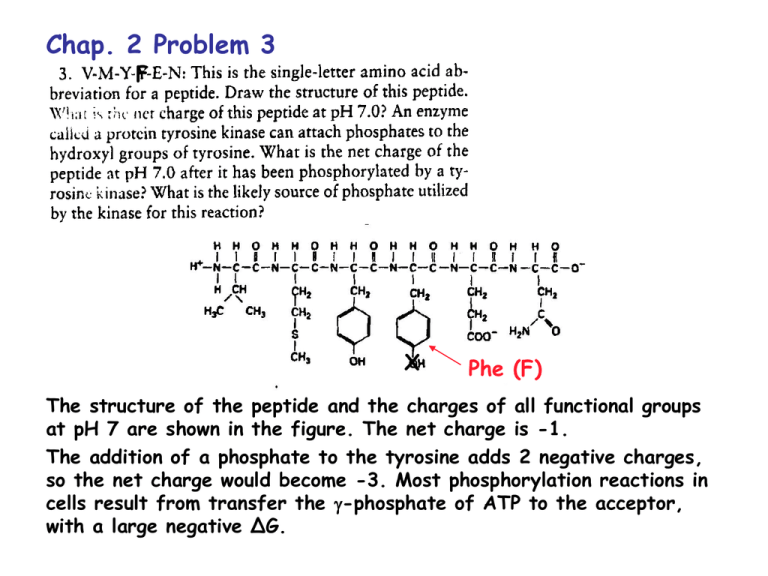
Chap. 2 Problem 3 F X Phe (F) The structure of the peptide and the charges of all functional groups at pH 7 are shown in the figure. The net charge is -1. The addition of a phosphate to the tyrosine adds 2 negative charges, so the net charge would become -3. Most phosphorylation reactions in cells result from transfer the -phosphate of ATP to the acceptor, with a large negative ∆G. Chap. 2 Problem 9 Ammonia is a weak base that can pick up protons at acidic pH. Thus ammonia is protonated inside lysosomes forming ammonium ion. The [H+] of the lysosome compartment decreases, and thus the pH of the lysosome increases. Chap. 2 Meaning of the Kd Example: Protein (P) binding to DNA (D) P + D P.D Kd = [P][D]/[P.D] What is the ratio of [D]/[P.D] for different values of [P]? [P] = 0.1 x Kd [P] = Kd [P] = 10 x Kd [D]/[P.D] = 10/1 [D]/[P.D] = 1/1 [D]/[P.D] = 1/10 This shows that the DNA binding site is about 10% occupied when the concentration of [P] is 10-fold lower than the Kd, 50% occupied when [P] is the same as the Kd, and 90% occupied when [P] is 10-fold greater than the Kd. Chap. 2 Derivation of the HH Equation HA H+ + AKa = [H+][A-]/[HA] Take the log of both sides of the equation. log Ka = log [H+][A-]/[HA] Rearrange log Ka = log [H+] + log [A-]/[HA] Rearrange again log [H+] = log Ka - log [A-]/[HA] Multiply both sides by -1 -log [H+] = -log Ka + log [A-]/[HA] Substitute pH and pKa pH = pKa + log [A-]/[HA] Chap. 2 Problem 11 What is the ionization state of phosphoric acid in the cytoplasm & why is phosphoric acid a physiologically important compound? The pH of the cytosol is 7.2. This happens to be equivalent to pKa2 of phosphoric acid. (Refer to Fig. 2.28, next slide) The relevant equilibrium reaction therefore is H2PO4- H+ + HPO42The Henderson Hasselbach Eq is pH = pKa + log [HPO42-]/[H2PO4-] Since pH = pKa2 = 7.2, the HH Eq becomes 100 = [HPO42-]/[H2PO4-] And 1/1 = [HPO42-]/[H2PO4-] Thus, these 2 compounds are present at a 50/50 ratio in solution. Phosphoric acid is physiologically important because it serves as the buffering agent in the cytosol. Fig. 2.28 pKa2