Why are some elements more stable than others?
advertisement

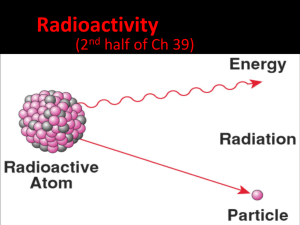
Why are some elements (isotopes) more stable than others? The Nucleus The Electric Force Protons hate Protons Strong Force Facts • Neutrons act like cement • Strong Force is very strong over a small distance (about the distance of two protons) • Small elements, 1 proton to 1 neutron will do Large Elements http://www.ptable.com/ Beta Particle Thorium Protactinium (Th) (Pa) Alpha Particle Protactinium Actinium (Ac)(Pa) Beta Gamma & Alpha Radiation Radiation Quick Quiz • What is the difference between the electric force and the strong force? • What are the three types of radiation that are present in radioactive decay? Example Uranium 238 How can radioactive decay be useful? Dating • The time it takes for half of the original quantity to decay • The half-life of an element is constant, and not affected by external conditions Iodine-131 decays to Xenon-131 32 40 Day: 116 824 Half-life: 8 days Number of 02 8 Iodine: 4116 16 12 814 0 Xenon: 15 Radiometric Dating (isotopic dating) Organic: • Radiocarbon dating • Range: 50,000 years • Carbon in atmosphere not constant Inorganic: • Uranium to Lead dating • Range: 7 million to 4.5 billion years Quick Quiz 2 • What is half-life? • Is radiocarbon dating extremely accurate, why or why not? Radiation is dangerous! How do they measure radiation! Rad • a unit of absorbed radiation dose • 1 rad = 10 mj Rem • amount of biological damage due to radiation dose • 1000 rem or higher will be fatal Geiger counter Table of rad vs rem Radiaton rad rem Gamma 1 1 X-Ray 1 1 Beta particle 1 1 Alpha particle 1 20