C Program Workshop
advertisement

THE C PROGRAM
WORKSHOP
Workshop Features
Bins for parts and supplies
Door for expected
results to go out
A
B
C
D
Door for unexpected
results to go out
WORKSHOP
Door for requests
to go in
Communication
with other shops
X
Y
Z
Various tools
Instructions and
operating procedures
A computer program written in C
is like a workshop
Current Data
(Information)
main
Transformed Data
(Information)
It brings data into the program from the outside world,
performs some processing with it, makes some changes to it,
and then returns it to the outside world in a different form
C Program Entrances and Exits
Constants and variables
STANDARD
OUT (stdout)
A
B
C
D
STANDARD
ERROR (stderr)
main
STANDARD
IN (stdin)
File and Device
Input/Output
X
Y
Z
Operations and
functions
Instructions and
operating procedures
Data Types
•
•
•
•
•
•
Integers (int)
Numbers with decimal points (float)
Characters (char)
Words and Phrases (ex. char phrase[10])
Tables (ex. int values[10], float matrix[20][30])
Records (ex. struct myRecordType)
Data Storage Locations
int aNumber;
float aValue;
char aSymbol;
char phrase[LENGTH];
int values[15];
Simple Operations
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Storage (=)
Addition (+)
Subtraction (-)
Multiplication (*)
Division (/)
Modulo (%)
Comparison (==, !=, <, <=, >, >=)
Instructions and Decisions
• variableLocation = expression
– Ex. count = 17 * MAX_LOOPS;
• if (Boolean condition) statement else statement
– Ex. if (numberIsValid)
count++;
else
count--;
• while (Boolean condition) statement
– Ex. while (count > MAX_LOOPS)
count = count – 5;
• for (statement; condition; statement) statement
– Ex. for (i = 0; i < size; i++)
printf(“%d\n”, table[i]);
Technical Vocabulary:
C Keywords
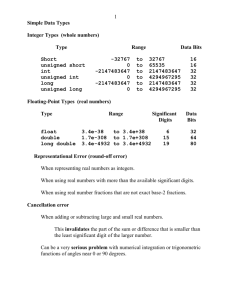
auto
break
case
char
const
continue
default
do
double
else
enum
extern
float
for
goto
if
int
long
register
return
short
signed
sizeof
static
struct
switch
typedef
union
unsigned
void
volatile
while
(Note: Keywords in bold-face font are used with data types)
Standard C Library Functions
• Standard Input and Output:
– printf, scanf, getchar, gets
• Conversion of Data:
– isalpha, isdigit, tolower, toupper
• Math:
– sin, cos, tan, sqrt, log, exp
• Working with Files:
– fopen, fclose, fscanf, fprintf, fgets
Example Program - C Source Code
int main(void)
{
int theCheckNbr;
char theAccount;
char theTaxCode;
float theAmount;
float theBalance;
theBalance = 2391.52;
printf("Ck Nbr
printf("------
Acct
----
Tax
---
Amount
------
Balance\n");
-------\n");
theCheckNbr = 234;
theAccount = ‘B';
theTaxCode = ‘Z';
theAmount = 34.56;
theBalance = theBalance - theAmount;
printf("%6d
%2c
%2c
%6.2f
%7.2f\n", theCheckNbr,
theAccount, theTaxCode, theAmount, theBalance);
return 0;
} // End main
Example Program Output
Ck Nbr
-----234
Acct
---A
Tax
--Z
Amount
-----34.56
Balance
------2356.96
Example Program Exercise
• Using the current pattern of statements in the program,
add the source code to display the last two lines of the
report shown below
• Also, change the order of the report columns
Ck Nbr
-----234
235
236
Amount
-----34.56
192.73
75.00
Acct
---B
T
G
Balance
------2356.96
2164.23
2089.23
Tax
--Z
W
X