kotler05exs
advertisement

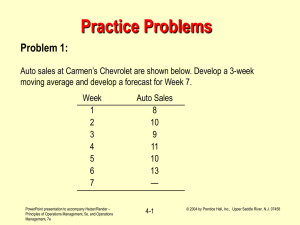
Chapter 5 Understanding Markets, Market Demand, and the Marketing Environment PowerPoint by Karen E. James Louisiana State University - Shreveport ©2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2nd Edition Slide 0 in Chapter 5 Objectives Identify the major components of a marketing system. Understand how marketers can improve marketing decisions through intelligence systems, marketing research, and marketing decision support systems. ©2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2nd Edition Slide 1 in Chapter 5 Objectives Learn how demand can be more accurately measured and forecasted. Understand key demographic, economic, natural, technological, political-legal, and socio-cultural developments. ©2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2nd Edition Slide 2 in Chapter 5 Supporting Marketing Decisions A Marketing Information System is defined as . . . “people, equipment, and procedures that gather, sort, analyze, evaluate, and distribute needed, timely, and accurate information to marketing decision makers.” ©2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2nd Edition Slide 3 in Chapter 5 Supporting Marketing Decisions Marketing Information Systems compile information from: – Internal records systems – Marketing intelligence systems – Marketing research – Marketing decision support analysis ©2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2nd Edition Slide 4 in Chapter 5 Supporting Marketing Decisions Internal Records Systems – Order-to-payment cycle is key – Timely sales reports help to better manage inventory – Customer, product, salesperson and other databases can be mined for fresh insights ©2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2nd Edition Slide 5 in Chapter 5 Supporting Marketing Decisions Improving the Quality of Marketing Intelligence System Data Requires: – Training and motivating sales force to report developments – Motivating channel members to share important intelligence – Collecting competitive intelligence ©2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2nd Edition Slide 6 in Chapter 5 Supporting Marketing Decisions Improving the Quality of Marketing Intelligence System Data Requires: – Developing a customer advisory panel – Purchasing information from commercial data sources – Establishing a marketing information center within the company ©2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2nd Edition Slide 7 in Chapter 5 Supporting Marketing Decisions The Marketing Research Process: – Defining the problem and research objectives – Developing the research plan – Collecting the information – Analyzing the information – Presenting the findings – Making the decision ©2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2nd Edition Slide 8 in Chapter 5 Supporting Marketing Decisions Developing the Research Plan Involves: – Gathering secondary and primary data – Selecting one or more research approaches for primary data collection – Using the appropriate research instrument – Developing a sampling plan – Determining subject contact methods ©2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2nd Edition Slide 9 in Chapter 5 Supporting Marketing Decisions Approaches for primary data collection include: – Observational research – Focus-group research – Survey research – Behavioral data – Experimental research ©2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2nd Edition Slide 10 in Chapter 5 Supporting Marketing Decisions A Marketing Decision Support System is defined as a . . . “coordinated collection of data, systems, tools, and techniques with supporting software and hardware by which an organization gathers and interprets information from business and the environment and turns it into a basis for marketing action.” ©2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2nd Edition Slide 11 in Chapter 5 Forecasting and Demand Measurement Essential Aspects Market Potential market The market Available market Market demand Target market (served market) Company demand and sales forecasts Current demand Qualified available market Future demand Penetrated market ©2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2nd Edition Slide 12 in Chapter 5 Forecasting and Demand Measurement Essential Aspects The market Measuring demand Company demand and sales forecasts Current demand Future demand ©2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. Market demand – – – – Market minimum Market forecast Market potential Nonexpansible vs. expansible markets – Primary vs. secondary demand Market forecast Market potential To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2nd Edition Slide 13 in Chapter 5 Forecasting and Demand Measurement Essential Aspects Company demand The market Company sales forecast Measuring demand Sales quota Company demand and sales forecasts Sales budget Current demand Future demand ©2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. Company sales potential To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2nd Edition Slide 14 in Chapter 5 Forecasting and Demand Measurement Essential Aspects The market Measuring demand Company demand and sales forecasts Current demand Total market potential Area market potential – Market-buildup method Future demand ©2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2nd Edition Slide 15 in Chapter 5 Forecasting and Demand Measurement Essential Aspects The market Measuring demand Company demand and sales forecasts Current demand Future demand ©2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. Many Forecasting Methods: – Buyer intentions survey – Composite of sales force opinions – Expert opinion – Past-sales analysis – Market-test method To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2nd Edition Slide 16 in Chapter 5 Macroenvironmental Trends and Forces Demographic Environment – Worldwide population growth – Population age mix – Ethnic markets – Educational groups – Household patterns – Geographic population shifts – Rise of micromarkets ©2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2nd Edition Slide 17 in Chapter 5 Macroenvironmental Trends and Forces Economic Environment – Income distribution – Savings, debt, and credit availability ©2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2nd Edition Slide 18 in Chapter 5 Macroenvironmental Trends and Forces Natural Environment – Shortage of raw materials – Increased energy costs – Anti-pollution pressures – Changing role of governments ©2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2nd Edition Slide 19 in Chapter 5 Macroenvironmental Trends and Forces Technological Environment – Accelerating pace of technological change – Unlimited opportunities for innovation – Varying R&D budgets – Increased regulation of technological change ©2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2nd Edition Slide 20 in Chapter 5 Macroenvironmental Trends and Forces Political-Legal Environment – Legislation regulating business – Growth of special interest groups ©2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2nd Edition Slide 21 in Chapter 5 Macroenvironmental Trends and Forces Socio-Cultural Environment – World views that consumers hold of themselves, others, society, organizations, nature, and the universe – High persistence of core values – Existence of subcultures ©2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2nd Edition Slide 22 in Chapter 5