File - Ms. Nay`s Biology Class Website

Materials: worksheet
**Turn in McMush lab to front tray
Catalyst: Identify all examples of macromolecules in the passage below. Write down the example and what type of macromolecule it is.
A Big Butt Is A Healthy Butt: Women With Big Butts Are Smarter And
Healthier
Scientists from the University of Oxford have discovered that women with larger than average butts are not only increasingly intelligent but also very resistant to chronic illnesses.
According to ABC News, the results found that women with bigger backsides tend to have lower levels of cholesterol and are more likely to produce hormones to metabolize sugar. Therefore, women with big butts are less likely to have diabetes or heart problems.
And having a big butt requires an excess of Omega 3 fats, which have been proven to catalyze brain development. The researchers also found that the children born to women with wider hips are intellectually superior to the children of slimmer, less curvy mothers.
Elite Eight Trait Check-Up
1. Respect the Threshold
1. Everyone on time?
2. Silent for First Five?
2. Be Prepared (2 min)
1. Seated
2. Have materials
3. Working on catalyst
Class Motto
If there is a problem,
We look for a solution.
If there is a better way,
We find it.
If we need help,
We ask.
If a teammate needs help,
We give.
Announcements
• Quick tutorial today 3:15-3:45
• Cram Jam this Saturday 9-noon. EC will be given.
Standard
• SB1b. Explain how enzymes function as catalysts.
Objectives
• I can describe how molecules interact in a chemical reaction.
• I can describe how a catalyst interacts with reactants in a chemical reaction.
• I can use controlled experiments to measure the effect of four variables on a chemical reaction: temperature, concentration, surface area, and catalysts.
• I can explain why increasing temperature, reactant concentrations, surface area, and the numbers of catalyst molecules raise the rates of chemical reactions.
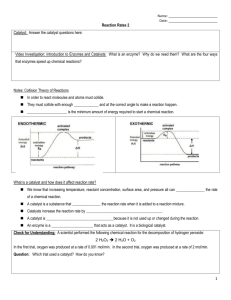
Notes 2.3: Enzymes and Catalysts
Chemical Reactions
• Change one substance to another by breaking and forming bonds
2H + O ➝ H
2
O
Reactants = Substrates: come BEFORE the arrow
Products: come
AFTER the arrow
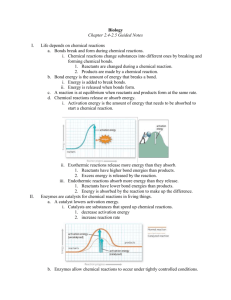
Catalysts
• Catalysts speed up reactions by lowering the activation energy
• Basically they make it easier to get to the intermediate, so the reaction happens faster
• Biological catalysts are called enzymes
E
A
= Activation Energy= Energy to get to the intermediate
Determines the speed of the reaction
E
A
is lowered by the enzyme
Analogy (Notes)
• Which would you prefer? Bigger or shorter hill?
Hill Height=
Activation Energy
Required
A= Reactants
B= Products
Enzymes (Think & Share)
Which type of organic molecule are enzymes considered?
What do enzymes do?
Enzyme Factors (Notes)
Enzymes are affected by…
1) Temperature
2) pH
3) Concentration
4) Surface area
HIGH Temperature and
LOW pH (ACIDS)
DENATURE enzymes
Factors which affect the speed of a reaction
• Surface area – the measure of the amount of exposed area an object has
• Concentration – a measure of how much of a given substance is mixed with another substance
• Half life - the time required for one half of the reactant molecules to react.
Materials: worksheet
Catalyst: answer these 2 questions on your gizmo worksheet
**Turn in McMush Lab
• Suppose you added a spoonful of sugar to hot water and another to ice-cold water. Which type of water will cause the sugar to dissolve more quickly? ___________________
• Suppose you held a lighted match to a solid hunk of wood and another match to a pile of wood shavings. Which form of wood will catch fire more easily? ______________________
Materials: none
• Get out Gizmo Worksheet
• Find a partner at your table
• Log on to Explorelearning.com
Panther Pass
Guided Practice
• A chemical reaction causes the chemical compositions of substances to change.
Reactants are substances that enter into a reaction, and products are substances produced by the reaction. The Collision Theory
Gizmo™ allows you to experiment with several factors that affect the rate at which reactants are transformed into products in a chemical reaction.
Guided Practice
•
• You will need blue, green, and orange markers or colored pencils for the first part of this activity.
• Look at the key at the bottom of the SIMULATION pane. In the space below, draw the two reactants and two products of this chemical reaction.
Reactants: Products:
Guided Practice
• Click Play ( ). What do you see? __________
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
Independent Practice
Activity A
• Reset the Gizmo, then complete Activity A.
• Write your responses on the Student Exploration
Sheet.
Activity C
• Reset the Gizmo, then complete Activity C.
• Write your responses on the Student Exploration
Sheet.
Panther Pass
1. What is the role of a catalyst?
2. What organic molecule is an enzyme made of?
3. Why does increasing temperature cause the reaction to proceed more quickly?
4. What are 2 ways that enzymes are denatured?