PDSA and Continuous Improvement Planning
advertisement
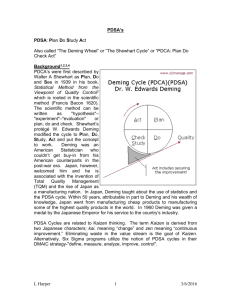
PDSA and Continuous Improvement Planning Sunset Ridge 2010-2011 Vision to Action T.E.A.M. School “Together Everyone Achieves More” You will learn the 8 Step PDSA Process You will practice creating a PDSA using the 8 Step PDSA Process Objectives for the presentation We are not experts, we are just excited about using a streamlined process for working with data to improve student achievement! Disclaimer Priority Area: Organizational Effectiveness and Efficiency Goal 4 – Implement a systems approach for continuous improvement at classroom, school, department and district level. Strategic Plan 2010-2013 Describe your current knowledge level of PDSA’s 1. Thumb Down – What is a PDSA? 2. Thumb Sideways – Heard about it and know the why, what and how. 3. Thumb Up – I am ready to try it! Pre-Test Fad Diet “An Event” Has short term loss based on “quick” fix Everyone is doing it! Little effort for quick results No change to lifestyle Healthy Lifestyle Change Slower weight loss but more permanent Eating habits change Has multiple layers like diet, exercise, new eating habits DDD vs. PDSA Knowing what my students need to know and be able to do. Determining the critical learning requirements: ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Unpacking the standards Manage the standards Link assessment to the standards Plan for aligned instruction A Systems Approach to Learning Our job as teachers is to create the kind of learning system in which all of our students learn and demonstrate proficiency in all content and program areas – not just those tested annually by the state. You can get the required results with a regular and frequent improvement process of planning, doing, studying and acting DDD vs. PDSA Data Driven Decision Making Collect Data – AIMS, DIBELS, Check Point Charlie Analyze the Data Create ILP’s Anything Else?? PDSA Plan for frequent cycles of learning by setting short term learning targets Doing by teachers and students to ensure that everyone meets the goal Study the results if the strategies used in the learning cycle Action plan and make adjustments for the next cycle of learning A Practical Way of Getting Better Results Step Step Step Step Step Step Step Step 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 – Learning Requirements – Class Learning Goal – Class Learning Results – Class, Course or Program Mission - Plan – Do – Study - Act Eight Steps to Action Plan Step Step Step Step 1 2 3 4 – – – – Learning Requirements Class Learning Goal Class Learning Results Class, Course or Program Mission Do steps 1-4 at the beginning of the class, semester, or program by subject area, department, or grade level. Step Step Step Step 5 6 7 8 - Plan – Do – Study - Act Used for PDSA Cycles Step 1 - Learning Requirements Students can tell you what they will be able to do as a result of being in this class. What do they need to know to be proficient on the skills in the Math Assessment? Step 2 – Class Learning Goal Example - By the end of the year, 100% of the students will score 80% or better on the Check Point Charley Assessment. Getting Started Step 3 – Chart and Analyze class learning results Create a bar graph for charting learning results showing where the class is starting compared to where if needs to be. Establishing a Baseline Step 4 – Class, Course or Program Mission Statement Ask students this: Why are we here? What do have to do well together? How will we make this happen? Example “The mission of the members of Room 442 is to work together to become proficient in all the 4th grade math standards so that we will be prepared for the future.” Write this with input form the kids! Step 5 Plan – Short Term Learning Goals Example - This week we will make sure all sentences we write begin with a capital letter and end with a period. Communicate the learning expectation at the start of each learning PDSA cycle Step 6 Do – Determine what the students and teacher need to do to ensure that everyone learns the target; what high-yield strategies will be used. When the goals are learner centered, schools are for “learning” not for “teaching” Teacher will do: 1. Model using scientific notation 2. Give us several examples 3. Let us work on teams 1. 2. Student will do: Sort/classify numbers in scientific notation with those in standard notation Work as a team to create a Frayer Model for scientific notation. Step 6 -What will we do to learn? Step 7 – Study Study the results of the of the strategies used for the learning; what helped us learn and what changes should we consider in the next cycle. Step 8 – Act Make adjustments for the next cycle of learning Continuous Improvement…there is no finish line! Plus What helped us learn? Delta What should we change to improve our learning processes? Step 8 Act - To-Do’s for Next Week Use the 8 Step Method to Create a Healthy Lifestyle Diet Change “Program” 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Diet Requirement – I can… Diet Goal – What is your weight goal? Baseline - Starting Weight Mission for Your Diet – Why, What and How? Plan – What will you do this week? Do – What are you going to do? Study - Results of one week of dieting Act – What will you do next week to stay on the diet? Try It! Describe your current knowledge level of PDSA’s 1. Thumb Down – What is a PDSA? 2. Thumb Sideways – Heard about it and know the why, what and how. 3. Thumb Up – I am ready to try it! Post Test