Introduction to Visual Art
advertisement

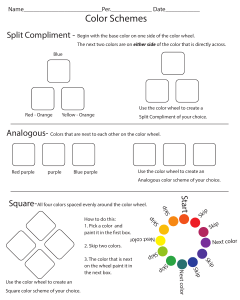
Before you sit down… Get your binder Also get red, blue, yellow, green, purple, and orange crayons or coloring pencils (you may need to share) ELEMENTS OF ART Line An element of art that is the path of a moving point through space. Van Gogh – Thatched Cottage in Cordeville What types of lines do you see? What do the lines do? Piet Mondrian – Kompositsioon A Describe the lines in this work. How are they different from the lines Van Gogh used? Shape A defined two dimensional area. Has height and width. May be geometric or free form. Ellsworth Kelly – White Black Shape is used in this work to make a striking statement. How do you think people reacted to this sort of art when it was new? Georgia O’Keefe Describe how shape is used in the work of art. Form An object with three dimensions. Has height, width, and depth. May be geometric or free form. Richard Sweeney – Paper Sculpture What kind of form would you describe this as? Geometrical or free form? Richard Deacon – Between Fiction and Fact This sculpture uses a mixture of both Geometrical and Free Forms. Why do you think the artist gave it this title? Texture The element of art that refers to how things feel, or look as if they might feel if touched. Objects can have rough or smooth textures and matte or shiny surfaces. Rough Smooth Matte Shiny Anselm Kiefer – The Unknown Painter What do you think this painting would look like in person? Space The elements of arts that refers to the emptiness or area between, around, above, below, or within objects. Shapes and forms are defined by space around and within them. Value The element of art that describes the darkness or lightness of an object. Francisco de Goya – Saturn Devouring his Son What do you notice about the value of the light in this painting? Does it help set the mood or the work? Color An element of art that is derived from reflected light. The sensation of color is aroused in the brain by response of the eyes to different wavelengths of light. Color Terms Primary – Red, Yellow, Blue Secondary – Orange, Green, Purple (Violet) Intermediate (Tertiary) – Mixed colors of Primary and Secondary Intensity – Hue is full intensity Hue – Pure color Shade – Pure + Black - Duller Tint – Pure + White - Brighter Primary Secondary Tertiary/Intermediate Color Harmony Use of Analogous or complementary colors Analogous – Next to each other on the wheel Complementary /Contrasting– Across the wheel Analogous Colors next to each other on the wheel Complementary Across the color wheel Triadic Triadic colors are high-energy colors that are found by choosing three colors that are separated by 120 degrees on the color wheel. The primary (red, blue, and yellow) and secondary (purple, orange, green) colors are examples of triadic colors Andy Warhol – Shot Orange Marilyn How would you describe the color in this print? Art Criticism Look at the painting to the right (The Old Guitarist by Pablo Picasso). Think about what you see and make some notes about subject/object, use of color, the mood/meaning, and your judgment of the work. As a class we’ll discuss it using the steps of art criticism.