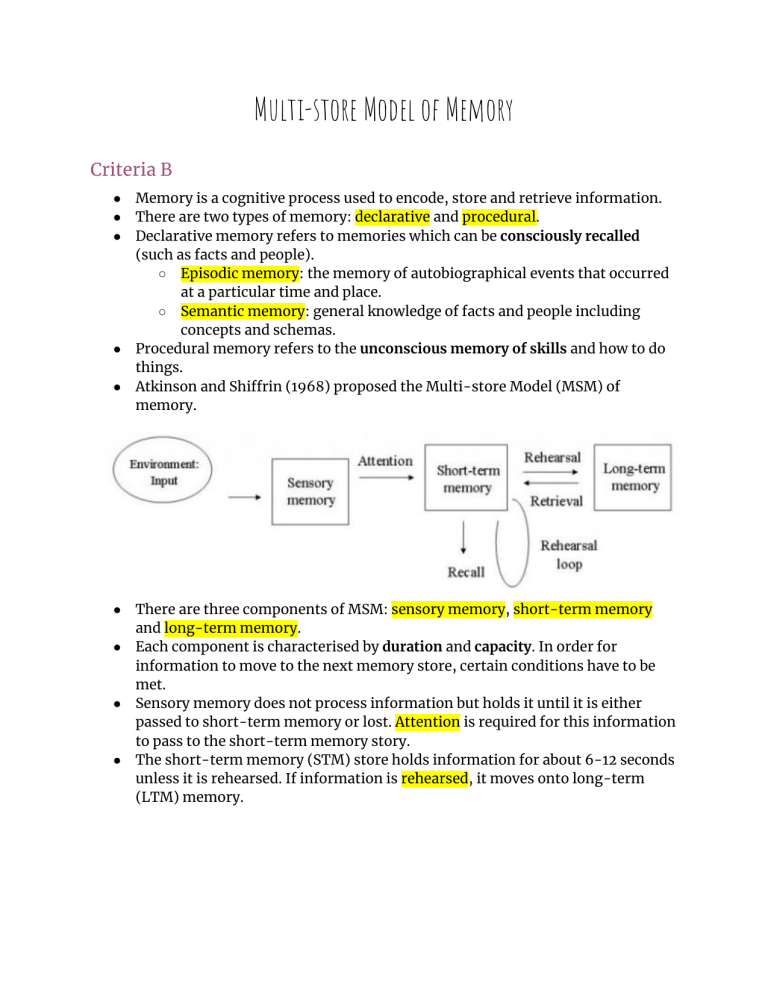
Multi-store Model of Memory Criteria B ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● Memory is a cognitive process used to encode, store and retrieve information. There are two types of memory: declarative and p rocedural. Declarative memory refers to memories which can be consciously recalled (such as facts and people). ○ Episodic memory: the memory of autobiographical events that occurred at a particular time and place. ○ Semantic memory: general knowledge of facts and people including concepts and schemas. Procedural memory refers to the u nconscious memory of skills and how to do things. Atkinson and Shiffrin (1968) proposed the Multi-store Model (MSM) of memory. There are three components of MSM: s ensory memory, s hort-term memory and long-term memory. Each component is characterised by duration and c apacity. In order for information to move to the next memory store, certain conditions have to be met. Sensory memory does not process information but holds it until it is either passed to short-term memory or lost. Attention is required for this information to pass to the short-term memory story. The short-term memory (STM) store holds information for about 6-12 seconds unless it is rehearsed. If information is rehearsed, it moves onto long-term (LTM) memory. Criteria C Study #1: Miller’s Magic Number 7 (1956) Aim To investigate the capacity and duration of STM. Procedure 1. Participants had to memorise a string of numbers, increasing each time by one digit. 2. The participants had to recall the numbers. Findings/Results The basic finding was that participants could recall between 5 to 9 items. Conclusion ● ● Miller concluded that the STM was limited in both capacity and duration which was why only those number of items were recalled. Miller also concluded that chunking helped people to better recall information. Criteria D Evaluation of study Low ecological validity ● The experiment was conducted in an artificial environment causing the participants to show demand characteristics or not act the way they would in a real situation. Cowan (2010) study ● In Cowan’s study, participants were given a running span of numbers and didn’t know how long the list was. ● He found that participants recalled 3-5 digits. ● Cowan’s findings are supported by biological research. Brain activity increases in the parietal cortex until four digits. Then activity levels out. Criteria C Study #2: G lanzer and Cunitz (1966) Aim To investigate serial position effect to show there are two process involved in retrieving information. Procedure 1. US Army-enlisted males were the participants. They had to memorise 15 items and then do a free-recall task. 2. There were two conditions for the recall. One condition had to recall immediately after seeing the list. The second had a timed delay. Findings/Results ● ● From the first condition, participants were better at remembering items at the start of the list (primacy effect) and the end of the list (recency effect). In the second condition, participants were able to remember items at the start of the list (primacy effect) but not the end. Conclusion ● ● ● The researchers concluded that the first items on the list tend to get rehearsed more, moving to LTM which is unaffected by delay. The last words on the list aren’t rehearsed as much which is why they disappeared from the STM in the second condition. This shows that STM and LTM have separate mechanisms behind them. Criteria D Evaluation of study Low ecological validity & demand characteristics ● The experiment was done in a lab which is an artificial environment. This may have caused the participants to show demand characteristics Sample bias ● Only males were used for the experiment. The results may not be the same for females. ● Furthermore, the sample consisted of men from the army. Their career may have affected their ability to memorise. Criteria D Evaluation of theory Strengths ● There is empirical support for separate memory stores from cognitive research and biological case studies (patients with brain damage). ● The model helped psychologists understand memory and build off of this model. Limitations ● The theory is reductionist. It focuses on the structure of the model rather than the process. The problem with this is it doesn’t explain how information flows, only that there are different stores which work independently. ● The model doesn’t explain memory distortion. ● It doesn’t explain how we are sometimes able to remember something without rehearsal. ● There are times when we rehearse the information countless times but it is not transferred to LTM.