Lesson 1 PowerPoint
advertisement

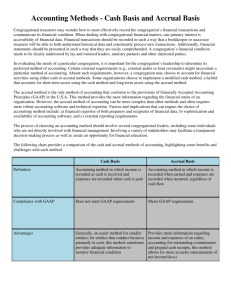
Theoretical Structure of Financial Accounting I N T ERMEDIATE ACCOU N T I NG I CHA PT ER 1 Financial Accounting Environment The primary focus of financial accounting is on the information needs of investors and creditors. Financial statements convey financial information to external users. Financial Statements The primary means of conveying financial information to investors, creditors, and other external users is through financial statements and related notes. The financial statements most frequently provided are: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Balance sheet or statement of financial position Income statement or statement of operations Statement of cash flows Statement of shareholders' equity Either a) a statement of other comprehensive income immediately following the income statement, or b) a statement of comprehensive income (including information on the income statement as well as on the statement of other comprehensive income). Cash vs Accrual Basis of Accounting Two primary methods of measuring income exist Cash basis – income is only recognized when received in cash Accrual basis – income is recognized when earned regardless of whether or not cash has been received Measuring the same activities by the accrual accounting model provides a more accurate prediction of future operating cash flows. Cash vs Accrual Basis of Accounting Two primary methods of measuring income exist Cash basis – income is only recognized when received in cash Accrual basis – income is recognized when earned regardless of whether or not cash has been received Measuring the same activities by the accrual accounting model provides a more accurate prediction of future operating cash flows. Exercise 1-1, page 38 (adjusted) Listed below are several transactions that took place during the first two years of operations for the law firm of Pete, Pete, and Roy. In addition, you learn that the company incurred utility costs of $35,000 in year 1, that there were no liabilities at the end of year 2, no anticipated bad debts on receivables, and the insurance policy covers a three-year period. Determine the amount of net income to be recognized each year using accrual basis accounting. Exercise 1-1, page 38 (adjusted) Solution Pete, Pete, and Roy Income Statements Revenues Expenses: Salaries Utilities Insurance Net Income Year 1 $170,000 Year 2 $220,000 (90,000) (35,000) (20,000) $ 25,000 (100,000) (35,000) (20,000) $ 65,000 Explanation of Utilities Expense: $35,000 of utilities were incurred in Year 1 and should therefore be recognized in Year 1. Since only $30,000 of the $35,000 of utilities were paid in Year 1, $5,000 of utilities payable were carried into Year 2. Therefore, $5,000 of the $40,000 paid in Year 2 was actually incurred in Year 1 leaving $35,000 of utilities actually incurred, and therefore recognized, in Year 2. The Conceptual Framework A coherent system of interrelated objectives and fundamentals that is intended to lead to consistent standards and that prescribes the nature, function, and limits of financial accounting and reporting. Underlying foundation for accounting standards Underlying concepts of accounting that guide the selection of events to be accounted for, the measurement of those events, and the means of summarizing and communicating them to interested parties Provides structure and direction to financial accounting and reporting Does not set GAAP See Conceptual Framework, Intermediate Accounting text, page 20 Financial Accounting and Reporting Standards Generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) are a set of guidelines companies follow in measuring and reporting financial information. The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has the authority to set accounting standards for companies, but always has delegated the task to the accounting profession. The Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) currently sets accounting standards. Qualitative Characteristics of Accounting Information To be useful for decision making, accounting information should possess the primary characteristics of relevance and faithful representation. PRIMARY QUALITATIVE CHARACTERISTICS Relevance Predictive value – helps to predict a future condition Confirmatory value – assists users in validating or changing a prior assessment of a company’s condition Materiality (enhancing aspect) – has an effect on decisions Faithful representation Completeness – All information that is necessary for faithful representation. Neutrality – Accounting standards should be set with overall societal goals and specific objectives in mind, and should try not to favor particular groups or companies. Free from error Financial Accounting and Reporting Standards ENHANCING QUALITATIVE CHARACTERISTICS Comparability - Ability to help users see similarities and differences among events and conditions (also includes consistency). Verifiability - Consensus among different measurers. Timeliness - Available to users before a decision is made. Understandability - Users must understand the information. Financial Accounting and Reporting Standards CONSTRAINT Cost Effectiveness – The benefits received should exceed the cost to generate the benefits Underlying Assumptions Economic Entity Assumption All economic events can be identified with a particular economic entity. Going Concern Assumption In the absence of information to the contrary, it is anticipated that a business entity will continue to operate indefinitely. Periodicity Assumption The life of a company can be divided into artificial time periods to provide timely information to external users. Monetary Unit Assumption Financial statement elements should be measured in terms of the United States dollar. Recognition, Measurement and Disclosure Concepts It is important to accurately determine when the financial elements should be recorded and how they should be measured and disclosed. General Recognition Criteria An item should be recognized in the basic financial statements when it meets the following criteria: Definition — the item meets the definition of an element of financial statements. Measurability — the item has a relevant attribute measurable with sufficient reliability. Relevance — the information about it is capable of making a difference in user decisions. Reliability — the information is representationally faithful, verifiable, and neutral. Revenue Recognition: Realization and Matching Principles Realization Principle Revenue should be recognized only after the earnings process is virtually complete and there is reasonable certainty of collecting the asset. Revenue should be recognized in the period it is earned, not necessarily in the period in which cash is received. Matching Principle Expenses are recognized in the same period as the related revenues. T1-14 MEASUREMENT Measurement — Associating numerical amounts to the elements. GAAP uses a “mixed attribute” model including Historical Cost – measurement is based on the amount given or received in the exchange transaction Net Realizable Value – measurement is based on the amount of cash into which the asset or liability could be converted in the ordinary course of business Current Cost – measurement is based on the current replacement cost Present Value of Future Cash Flows – measurement is based on future cash flows discounted for the time value of money Fair Value – measurement is based on the price that would be received to sell assets or transfer liabilities in an orderly market transaction Theoretical Structure of Financial Accounting I N T ERMEDIATE ACCOU N T I NG I – CHA PT ER 1 E N D OF P R ESENTATION