What is an IT Failure?
advertisement
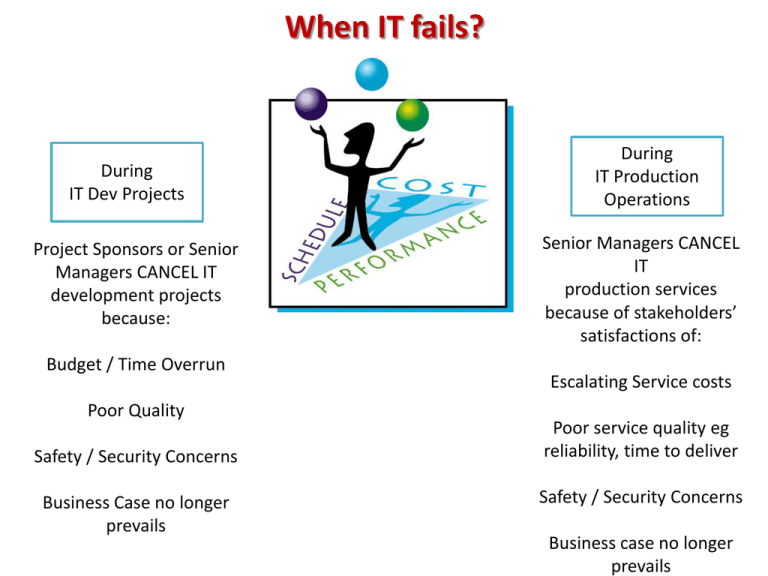
When IT fails? During IT Dev Projects Project Sponsors or Senior Managers CANCEL IT development projects because: Budget / Time Overrun Poor Quality Safety / Security Concerns Business Case no longer prevails During IT Production Operations Senior Managers CANCEL IT production services because of stakeholders’ satisfactions of: Escalating Service costs Poor service quality eg reliability, time to deliver Safety / Security Concerns Business case no longer prevails Key Causes of IT Project failures 1. Lack of Strategic Alignment between Business & IT (CORRESPONDENCE FAILURE) No or weak upfront business case with no clear program logic and related KPI measures justifying the project Business case may exist but business conditions have changed, invalidating business case while project is underway 2. Project scope creep (PROCESS FAILURE) – development scope of requirements increased beyond what was originally planned requiring more $, resources & time blowing out planned budget, resource availability and deadlines 3. Poor communications among stakeholders (INTERACTION FAILURE) what is planned does not deliver what is expected due to misinterpretations and/or no communications Why Projects fail ** https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4a4ZxOAQifE 3 Models for Identifying IT Failures Factor Based Models Identifying a checklist of conditions that cause IT project & production failures Stakeholder Analysis Models Identifying power brokers that cause IT project & production failures These condition based or risk factors can be classified by: Power plays between stakeholders can, especially during decision making, can also result in IT cancellations • Cultural, managerial & technical categories (Feghali & Zbib, 2007) • Leadership, communications, skills and resources, budget and project management categories (Oz & Sosik, 2000) • Project management, top management, technology, organisational, complexity size and process categories (Al-Ahmad, 2009) • etc 3D Sphere Models Identifying organisational drivers that cause IT project & production failures Dimensional modelling of organisational Risk factors that can contribute to IT failures – classified by • 4 Managerial Risk Factors • 7 Cultural Risk Factor • 18 Technical Risk factors IT Failures – Risk Management Practice Models Risks – Causes of IT Failures Issues – Problems when risks eventuate IT Project or Production Cancellation = Failure Literature Comparison of Software Project Risks Schmidt, Lyytinen, Keil & Cule OZ & Sosik Fairley & Whillshire Lack of top management commitment to project Poorly communicated goals/deliverables Excessive schedule pressure Failure to gain user commitment Lack of Corporate Leadership Changing Needs Lack of User involvement Poor project management Lack of documented & maintained project plan Lack of required knowledge/skills Budget & schedule deviations Excessive & secondary innovations Lack of frozen requirements Requirement / scope creep Changing scope/objectives Lack of scientific methods Introduction of new technology Ignoring the Obvious Failure to manage user expectations Unethical behaviours Insufficient / inappropriate staffing Conflict between user departments (Tesch, Kloppenborg & Frolick, 2007) Top 10 Risks in IT System Replacement Projects Risk Mitigation Tips Ineffective user involvement Involve users in project planning, change mgt & training; foster frequent communications; choose small team of decision makers who knows the users well; have clear roles, responsibilities & expectations Ineffective executive support Clearly define the sponsor role at the beginning of the project; decision making rules Scope Creep Evaluate and redefine RFP requirements to eliminate ambiguous, incorrect, inconsistent, and/or unverifiable language; don’t get blog down into deep technical details Schedule flaws Use agile iterative methods and factor 20% contingency Staff Turnover Establish process standards; rotate duties, embrace communications and team work Unrealistic Expectations Promote a culture that embraces continuous improvement and evolution. Don’t oversell your capabilities. Ineffective project management Get experienced people Specification breakdown “Reduce complexity by focusing on outcomes. Avoid over-specification and the lure of being ‘perfect’. Provide mechanisms for continuous improvement and evolution.” Technology and Uncertainty Reduce concurrent project streams; defer integration of peripheral systems eg KM; focus on delivery required outcomes not bells and whistles Excessive Direction (micro management) Develop trust within team to delegate work and share decision making; use KPI measures as work appraisal measures. (Komperud, 2012) Organising Risks via PMBOK – Process Groups Project Initiation Planning Project Planning Execution Controlling Closing Factored Risks Mgt in these Areas Project Integration Mgt Project Scope Mgt Project Time Mgt Project Cost mgt Project Quality Mgt Project HR Mgt Project Comms Mgt Project Procurement Mgt Project Risks Mgt Covers other Risks (details see http://www.softexpert.com/regulation-pmbok.php) NOW we are into Collaborative Projects Across Multiple Sites Project risks and issues are high Project Management is Complex • • • • Requires : Common project language across sites Shareable project information across sites Coordinated workflow management across sites More complex project risks management new international external risks – political, economic, social, technology and environmental differences cross cultural communication and management factors Communication Strategies in Collaborative projects (2.26m) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=f60dheI4ARg Case study – application of stakeholder analysis Evaluation their Coalition Identify stakeholders What do they want in the IT projects? Map out interests