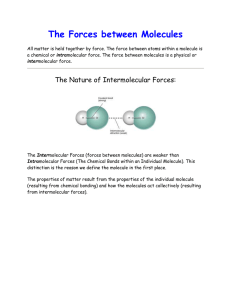
Intermolecular Forces Graphic Organizer Table of Contents: 1. Filled-out notes (Teacher’s guide) 2. Scaffolded notes (one box for each column is filled out as an example, and the “Key Point” is included) 3. Blank notes (non-scaffolded version) Notes: This graphic organizer can be used as a guide for class notes: students can fill it out as a class while the teacher lectures. This graphic organizer could also be used as an independent activity: students can fill it out as they read their textbook. Intermolecular Forces Type of Bond Van der Waals Forces Hydrogen Bonds Dipole interactions Dispersion forces Definition Oppositely charged regions of polar molecules are attracted to each other Random electron motion on one molecule affects the electron motion on the other, and the oppositely charged regions are attracted. **These are the weakest interactions between molecules. A hydrogen covalently bonded to a very electronegative atom is also weakly bonded to an unshared electron pair of another atom. Examples A polar molecule like ammonia (NH3) experiences dipole forces. Iodine is solid at room temperature because its dispersion forces are strong enough to hold molecules close together. Hydrogen bonds in water molecules give water many of its unique properties (like high surface tension). Picture Key Point: Intermolecular attractions are weaker than either ionic or covalent bonds but they are still important! They are the reason for many of the properties we observe in solids and liquids. Intermolecular Forces Type of Bond Van der Waals Forces Dipole interactions Dispersion forces Hydrogen Bonds Picture Definition Examples Random electron motion on one molecule affects the electron motion on the other, and the oppositely charged regions are attracted. **These are the weakest interactions between molecules. Hydrogen bonds in water molecules give water many of its unique properties (like high surface tension). Key Point: Intermolecular attractions are weaker than either ionic or covalent bonds but they are still important! They are the reason for many of the properties we observe in solids and liquids. Intermolecular Forces Type of Bond Van der Waals Forces Dipole interactions Dispersion forces Picture Definition Examples Key Point: Hydrogen Bonds