Notes on Procedure for Experiment No. 28
advertisement

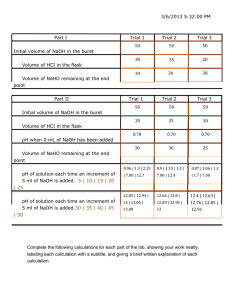
Notes on Procedure for Experiment No. 28 In this experiment, you will do a macroscale version of Item 3, “Potentiometric Titration of an Unknown Acid” on page 565 of the lab manual, as well as Items 6, “Calculation of the Equivalent Weight of the Unknown Acid” and 7, “Calculation of Ka of the Acid” described on page 566. For Items 1, 2, and 5, you will assume that the concentration of the standardized NaOH solution that you saved from Experiment 10A has not changed from the value that you determined a couple of weeks ago. You will perform Item 4 using the computer and software. Note that in the titration plot at the top of page 564, the curve starts out rather horizontally flat. The solution in this region consists of a combination of unreacted weak acid plus its conjugate base that resulted from partial neutralization of the acid, i.e., a buffer. The pH in this region changes only slightly as more base is added. Therefore, the NaOH can be added in moderate increments. As the equivalence point is approached more closely, however, the buffer capacity is exceeded, and the pH will increase more rapidly, so the NaOH solution must be added in smaller increments. In this region, the pH may increase by 4 to 7 units from an addition of only a fraction of a milliliter of NaOH solution. Here, you will need to add the base drop by drop. Once this portion of the curve is passed, it will become another horizontally flat region, and you can go back to adding the NaOH in larger increments. Record the pH at which the phenolphthalein changes color so that you can compare its end point to the equivalence point that you determine later. Get a 250 mL tall-form beaker and your unknown acid, and check out a stir bar. Weigh accurately about 120 mg of the unknown into the beaker (NOTE: for some of the unknowns, this mass may have to be adjusted) and add 100 to 120 mL of distilled water. Start stirring the mixture because some of the unknowns may dissolve slowly. Set up the titration apparatus. The correct way to remove the electrode storage bottle is to unscrew the bottle portion first and then slide off the lid (the ring). Place the bottle up out of the way so that you do not knock it over and spill the storage solution. When replacing, do the opposite; slide the ring on and then screw on the bottle. At the end of the last lab period of the week, we will have to ensure that there is sufficient storage solution in each storage bottle because these pH sensors will not be used again until next Fall. Rinse the buret with your NaOH solution and fill it. Flush the air out of the tip, and carefully clamp the buret in place. Note that the stopcock assembly will rotate within the barrel of the buret. If the graduations and handle are not conveniently located, just rotate. Use of Logger Pro to Plot Titration Data 1. Use a utility clamp to suspend the pH Sensor on the ring stand, as shown in the Figure below. Position the pH Sensor so that its tip is immersed in the unknown acid solution but is not struck by the stirring bar. Gently stir the beaker of acid solution. 2. Run the Logger Pro program on your computer. Open the file “07a Acid-Base” from the Advanced Chemistry with Vernier folder. 3. You are now ready to begin the titration. a. Before adding NaOH titrant, click b. c. d. e. . Once the displayed pH reading has stabilized, click . In the edit box, type 0 (for 0 mL added). Click to continue. Add the next increment of NaOH (enough to raise the pH about 0.15 units). When the pH stabilizes, . In the edit box, type the current buret reading as accurately as possible. Click again click to continue. Continue adding NaOH solution in increments that raise the pH by about 0.2 units and enter the buret reading after each increment. When a pH value of approximately 5.0 is reached, change to a one-drop increment. After a pH value of approximately 10 is reached, add larger increments that raise the pH by about 0.2 pH units, and enter the buret level after each increment. Continue adding NaOH solution until the pH value remains constant. . Dispose of the reaction mixture as directed. Rinse 4. When you have finished collecting data, click the pH Sensor with distilled water in preparation for the second titration. When finished, the two titrations, empty the flask, buret, and NaOH solution into the waste container. Rinse the buret, flask, and plastic bottle with distilled water and return to the storage location under the window. Return the stir bar. For the Thursday afternoon class: we will need to ensure that there is adequate storage solution before putting the pH sensor away. There will be more storage solution available, if needed. Locations of supplies for this experiment: BALANCE ROOM: 1 small + stir bar (check out) UNDER THE WINDOW: One 50 mL buret One 250 mL tall-form beaker AT THE LAB BENCHES: Phenolphthalein in dropping bottles TA’S DESK: Unknowns RIGHT-HAND HOOD: Waste jug Data Recording: Page 577: Page 578: Check with your TA Calculation of Equivalent Weight of Acid Calculation of Ka of the Acid