Orbital Filling Atoms & Building Up the Periodic Table From orbitals to atoms
advertisement
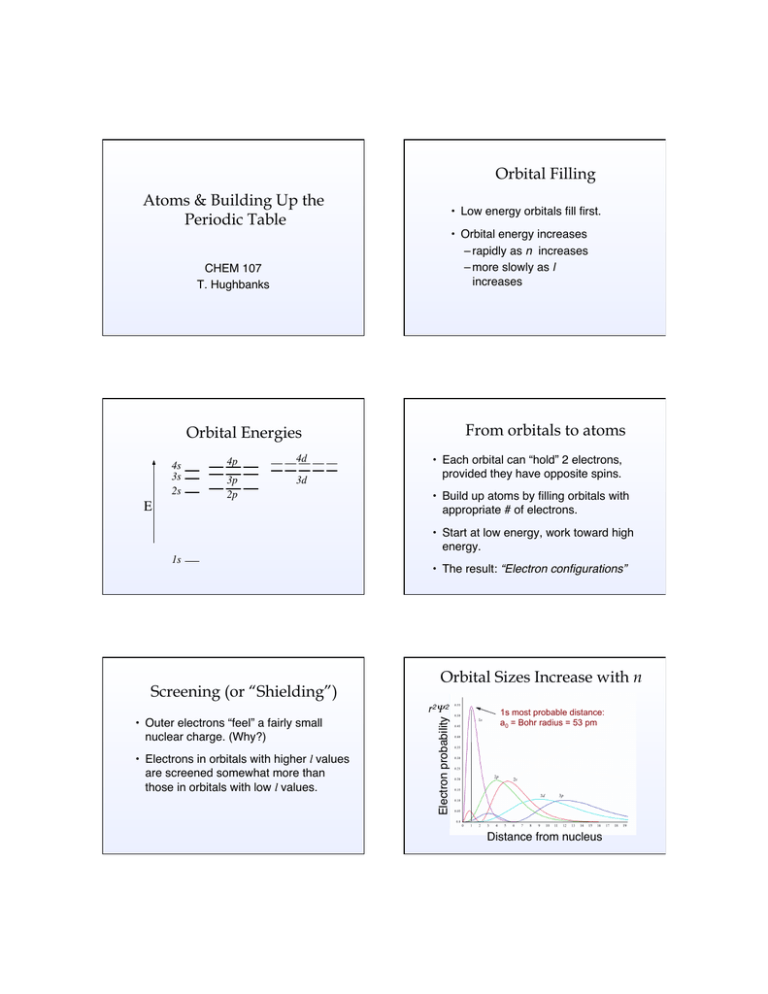
Orbital Filling Atoms & Building Up the Periodic Table • Low energy orbitals fill first. • Orbital energy increases – rapidly as n increases – more slowly as l increases CHEM 107 T. Hughbanks From orbitals to atoms Orbital Energies 4s 3s 2s E 4p 4d 3p 2p 3d • Each orbital can “hold” 2 electrons, provided they have opposite spins. • Build up atoms by filling orbitals with appropriate # of electrons. • Start at low energy, work toward high energy. 1s Screening (or “Shielding”) • The result: “Electron configurations” Orbital Sizes Increase with n • Electrons in orbitals with higher l values are screened somewhat more than those in orbitals with low l values. Electron probability r 2Ψ 2 • Outer electrons “feel” a fairly small nuclear charge. (Why?) 1s most probable distance: a0 = Bohr radius = 53 pm Distance from nucleus How Gravity Works (in the Newtonian sense) How Screening Works Example Li+ + e- Inner Core Orbitals of Cs How Screening Works Example: B atom orbitals Screening - Explain the Data Ionization Energies (units: aJ = 10-18J) Hydrogen He+ He atom n=1 2.18 8.72 3.94 (1s2) Excited atoms (electron comes from 2p): n=2 0.545 (2p1) 2.18 (2p1) 0.585(1s12p1) Recall H-atom formula E= −2.18 × 10-18 J n2 n - principal quantum no. Probability of finding electron at distance r from nucleus (4πr2)Ψ2 30 Some Plots for "Core" orbitals of Cs 25 20 1s 15 10 2s 5 3s 0 0 Distance from nucleus r 0.529 A most probable distance for a 1s electron in the hydrogen atom Orbital Filling: Electron Configurations • Low energy orbitals fill first. • Orbital energy increases as – n increases & l increases • Pauli exclusion principle: Electrons can’t have identical quantum nos. ∴ 2 e–’s per orbital, opposite spins • Hund’s rule: For lowest total energy, all unpaired e–’s will have the same spin. Approximate Orbital Filling order Electron Configurations • You should be able to write these easily for any “representative element.” (From s- or p- blocks of periodic table.) ☛ Write e– configurations for O, S, Ar. (Use both 1s2, ... , “rare-gas”, and “arrow” notations.) • Some irregularities in transition metals. Examples: Ti, Co, Zr, W Electron Configurations of Transition Metals

![6) cobalt [Ar] 4s 2 3d 7](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/009918562_1-1950b3428f2f6bf78209e86f923b4abf-300x300.png)