Fertility rate
advertisement

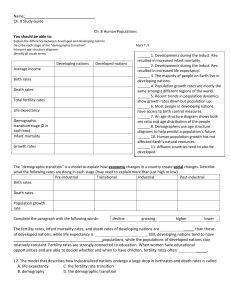
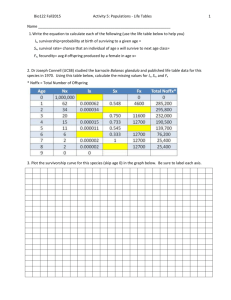
Our numbers expand, but Earth’s natural systems do not Lester R. Brown Human Populations Unit 9 Studying Human Populations • Demography: study of the characteristics of human populations. • -size and makeup of the populations. • -properties that affect population growth- economics and social structure. Demographics • Countries are grouped into two categories: developed and developing countries. • Developed countries have: -higher average incomes -slower population growth -diverse industrial economies -access to education Demographics (cont’d) Developing countries have: – lower average incomes – rapid population growth. – simple and agriculture-based economics – limited access to education The Human Population Over Time • Exponential growth began in the 1800s. • -due to increases in food production and improvements in hygiene that came with the industrial/scientific revolution. • FYI: It is unlikely that the Earth can sustain this growth for much longer World Population Over Time Age Structure • Age structure: the classification of a population according to reproductive age. • -countries with more young people have high growth rates • -countries with an even distribution of ages have slow or no growth Age Structure • Population pyramid: double-sided bar graph showing age structure. Survivorship • Survivorship: the percentage of newborns expected to survive to a given age. • -used to predict population trends • -to predict survivorship, demographers study a group of people born at the same time and notes when each member of the group dies. Survivorship Curve • The results of these studies are then plotted on a graph and might look like one of the types of survivorship graphs. Survivorship • Survivorship curves: • Type I: most people live to be very old. ex. Japan, Germany • Type II: population members have a similar death rate at all ages. • Type III: many children die. ex. India, subsaharan Africa • -Both Type I and Type III may result in populations that remain the same size or grow slowly. Fertility Rates • Fertility rate: number of births per 1,000 women of childbearing age (usually 15 to 44). • Replacement level: average number of children each parent must have in order to “replace” themselves. • -number is slightly more than 2 because not all children born will survive and reproduce. Fertility Rates • 1972: total fertility dropped below replacement level for the first time in US history. • Fertility rates remained below replacement level for most of the 1990s, but recently has been growing partly because the children of the baby boom grew up and had children. Fertility Rates Migration • Migration: any movement of individuals from one location to another. • -immigration: movement into an area. • -emigration: movement out of an area. Declining Death Rates • The dramatic increase in Earth’s human population in the last 200 years has happened because death rates have declined more rapidly than birth rates. • Death rates have declined because more people have access to: -adequate food -clean water -safe sewage disposal -vaccines Life Expectancy • Life expectancy: average length of time that an individual is expected to live. • -most affected by infant mortality, the death rate of infants less than a year old. • -infant health is most affected by the parents’ access to education, food, fuel, and clean water. Life Expectancy • The graph shows that average life expectancy worldwide has increased to more than 67 years old. But, new threats, such as tuberculosis and AIDS are arising as populations become denser. The Demographic Transition • Demographic transition: general pattern of demographic change from high birth and death rates to low birth and death rate. • -the theory behind the demographic transition is that industrial development causes economic and social progress which affects population growth rates. Stages of the Transition 1. Preindustrial stage: -high birth and death rates; population size is stable. 2. Transitional: -population explosion occurs. -death rates decline as hygiene, nutrition, and education improve. -birth rates remain high, so population grows fast. Stages of the Transition 3. Industrial: -population growth slows as birth rate decreases. -birth rate becomes close to the death rate; the population size stabilizes. 4. Postindustrial: -birth rate drops below replacement level; population begins to decrease. Women and Fertility • Factors most clearly related to a decline in birth rates: • -increasing education and economic independence for women. • (educated women find that they do not need to bear as many children to ensure that some will survive. They may also learn family planning techniques.) So… 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. What is demography? What does an age structure graph show? What is survivorship? What are the three types of survivorship curves? What is fertility rate? What is the difference between emigration and immigration? 7. What are the four stages to demographic transition? U.S. Population Growth • 1.66 million more births than deaths • 800,000- 1,000,000 legal immigrants -53% from Latin America -25% from Asia -14% from Europe 300,000 illegal immigrants (est 11 million) Projected growth by 2050: 41% to 86% (Pacific NW growth is higher than India!) Reasons for Projected U.S. Growth • Large numbers of baby boom woman still in child-bearing years • Increase in number of unmarried mothers High levels of immigrants Inadequate family-planning services Demographic Data Project • Choose a partner or you may work alone. • Choose a country that interests you (maybe country of origin of your ancestors). • Create a ppt presentation with the following data… Demographic Data • • • • • • • • Name of country Area in km; location on global (include a map) Number of people; population per square m Birth rate (per 1000) and death rate (per 1000) Projected population in 2025 (millions) Infant mortality Total fertility rate Life expectancy at birth for males; for females Presentations • Only use bulleted points, not whole sentences • Use font size 28-32 for body (titles can be 3644) • Must include the following visuals: map, people, land • Email your ppt to ann.erbele@sccpss.com Web Resources: Population Reference Bureau United Nations