Study Guide
Name:
Ch. 8 Study Guide
You should be able to:
Explain the difference between developed and developing nations
Describe each stage of the “demographic transition”
Interpret age structure diagrams
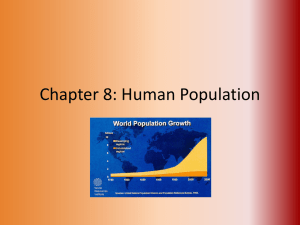
Ch. 8 Human Populations
Mark T /F
Identify all vocab terms
______ 1. Developments during the Indust. Rev. resulted in increased infant mortality.
Developing nations Developed nations
______ 2. Developments during the Indust. Rev.
Average income resulted in increased life expectancy.
______ 3. The majority of people on Earth live in
Birth rates developing nations.
______ 4. Population growth rates are mostly the
Death rates same amongst different regions of the world.
______ 5. Recent trends in population dynamics
Total fertility rates show growth rates down but population up.
______ 6. Most people in developing nations
Life expectancy have access to birth control measures.
______ 7. An age structure diagram shows both
Demographic sex ratio and age distribution of the people. transition stage (2 in ______ 8. Demographers use age structure each box) diagrams to help predict a population’s future.
Infant mortality ______ 10. Human population growth has not affected Earth’s natural resources.
Growth rates ______ 11. Affluent countries tend to also be developed.
The “demographic transition” is a model to explain how economic changes in a country create social changes. Describe what the following rates are doing in each stage (may need to explain more than just high or low)
Birth rates
Transitional Industrial Post-industrial Pre-industrial
Death rates
Population growth rate
Complete the paragraph with the following words: decline growing higher lower
The fertility rates, infant mortality rates, and death rates of developing nations are _____ than those of developed nations, while life expectancy is . Still, developing nations tend to have
__________________populations, while the populations of developed nations stay relatively constant. Fertility rates are strongly connected to education. When women have educational opportunities and are able to decide whether and when to have children, fertility rates often _____.
12. The model that describes how industrialized nations undergo a large drop in birthrates and death rates is called
A. life expectancy C. the fertility rate transition
B. demography D. the demographic transition
13. Which of the following factors do NOT affect population growth?
A. educating women C. statistics
B. poverty D. government policies
14. Regions of the world with the largest populations tend to
A. have the largest share of global wealth. C. use the most resources per person
B. have a smaller share of global wealth. D. have the largest ecological footprints
15. Which fertility rate keeps the population size stable?
A. replacement fertility C. balanced sex ratio
B. stable fertility D. total fertility rate
16. Explain why even though the world’s human growth rate is decreasing, the human population continues to grow._________________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________________
17. What is the demographic model used to explain? Be sure you understand each phase of it and can provide at
least 1 country for each!
______________________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________________
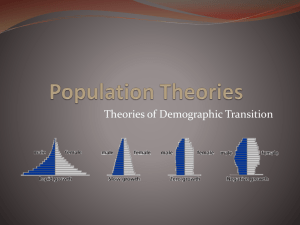
Country A Country B Country C Country D
Describe the type of growth each age structure diagram represent and EXPLAIN why the shape represents this type
(think about percentage of young to old, birth rate, death rate, etc.)
CountryA:__________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
CountryB:__________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
CountryC:__________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
CountryD:__________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________________