ESC110-Ch04-Questions
advertisement

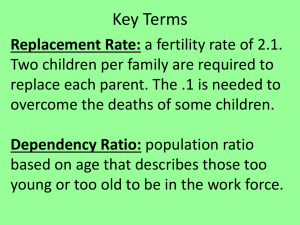
ESC110 - Chapter 4 Sample Questions 1. (p.74) Human populations began to grow rapidly after _______, partly due to increased communication among nations and better health care and hygiene. A. 5000 B.C. B. A.D. 1000 C. A.D. 1600 D. A.D. 1850 3. The human population is now in a(n) _______ pattern of growth. A. Logistic B. Exponential C. Oscillatory D. Cyclic 5. (p.76) According to the writings of _______, human populations inevitably outstrip their food supply and eventually collapse into starvation, crime, and misery. A. Karl Marx B. Justus von Liebig C. Thomas Malthus D. Victor Shelford 7. Which of the following is a neo-Malthusian belief? A. Population problems can be solved by making birth control a top priority. B. Population problems can only be solved through technological development and social justice. C. Population problems are caused primarily by the unfair distribution of wealth and resources. D. Population growth, poverty, and environmental degradation are all interrelated; no factor exclusively causes any other. 9. (p.77) _______ encompasses vital statistics about people, such as births, deaths, and population size. A. Taxonomy B. Demography C. Genealogy D. Entomology E. Histology 11. _______ has a negative population growth rate. A. China B. Nigeria C. Japan D. Ethiopia 1 13. _______ is the physical ability to reproduce, while _______ describes the actual production of offspring. A. Fertility, fecundity B. Fecundity, fertility C. Fertility, pregnancy D. Pregnancy, fertility 15. (p.80) The _______ is the number of children born to an average woman in a population during her entire reproductive life. A. Dependency ratio B. Birth ratio C. Total birth rate D. Total fertility rate 17. _______ occurs when births plus immigration in a population just equal deaths plus emigration. A. Zero population growth B. Negative population growth C. Demographic transition D. Demographic reversal E. Population dieback 19. (p.81) The world as a whole has an average fertility rate of _______ children per woman. A. 5.1 B. 4.3 C. 2.7 D. 1.2 21. Which of the following nations has the shortest life expectancy? A. United States B. Italy C. Chile D. Russia 23. A country’s _______ is the number of nonworking compared to working individuals in a population. A. Unemployment rate B. Dependency ratio C. Stabilization ratio D. Job reduction rate 25. Education and socioeconomic status are usually inversely related to fertility in developed nations. A. True B. False 2 27. Falling death rates and birth rates due to improved living conditions usually accompany economic development. This pattern is called _______. A. Population overshoot B. Irruptive growth C. Demographic transition D. Exponential growth E. Economic transition 29. In some countries, populations are growing so rapidly that human demands exceed the sustainable yield of local forests, grasslands, croplands, and water resources. These countries are said to be stuck in a _______ trap. A. Demographic B. Growth C. Dependency D. Logistic E. Prosperity 31. (p.87) A sustained drop in birth rates is usually preceded by a drop in infant and child mortality. A. True B. False 33. Family planning allows couples to _______. A. Control their reproductive lives B. Have fewer children C. Have more children D. A and B only E. A, B, and C 35. A _______ is a mechanical barrier that prevents contact between sperm and egg. A. Norplant insert B. Progesterone C. Tubal ligation D. Diaphragm E. Contraceptive patch 3