OBJ:4.1-4.2
advertisement

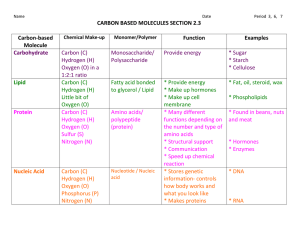
Biomolecules S What is Biochemistry S The study of the chemistry of life (involving matter). Element S Basic Building Block of matter that can not be broken down S About 26 found in living things S C=Carbon S H= Hydrogen S N=Nitrogen S O= Oxygen Atoms S Made of 3 types of subatomic particles In the nucleus S Protons : Positive S Neutrons :Neutral Orbiting the nucleus S Electrons : Negative Compound S 2 or more atoms chemically combined S What is H2O? Covalent? S Sharing of electrons between atoms CO2 Ionic: S transfer of electrons between atoms NaCl Buffers S Chemical that neutralize small amounts of acids/ bases Monomers vs. Polymers S Small parts of a long chain S Refers to a molecule that is a long chain of many smaller parts 4 major Biomolecules 1. Lipid 2. Carbohydrate 3. Nucleic Acid 4. Protein Lipid S Organic compound used for long term energy storage and makes up cell membrane. Contain carbon an hydrogen (fat, oil, wax) Lipid S Long term energy storage S Made up of Carbon and hydrogen Plasma Membrane: made of lipids EXAMPLES S Fats S Oils S Waxes Carbohydrate S Is the quickest energy storage for life. Contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Carbohydrate Energy storage (OSE=SUGAR) GLUCOSE: Simple sugar S The monomer of Carbohydrates CELLULOSE: Rigid, makes up cell wall Found in plants cell wall STARCHES: Complex (polysaccharides) S POLY? GLYCOGEN: Long-term backup glucose source Nucleic Acid S Monomer: Nucleotides S DNA: stores genetic info in the nucleus S RNA: Transmits genetic info for protein production Nucleotide PHOSPHATE, SUGAR, NITROGEN BASE DNA Structure Protein S Monomer: Amino Acid (aa) S Polypeptide chain (peptide bond) S Function : used for growth and repair. Provides essential enzymes and other structures that are used for growth and repair Protein S Contains carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen Insulin S Released by the pancreas; regulates blood sugar (helps body use sugar) S If you body can not reach the blood levels recommended you have to take insulin Enzymes S Catalysts(speed up reactions; break things down) Lock and Key S When the substrate binds to the enzyme! How Enzymes work Substrate: the molecule to which an enzyme binds to the substrate and acts upon (Puzzle pieces) What affects enzymes? S Temperature and pH S The shape is change ( denatured) Activation Energy S The necessary energy to start a chemical reaction Activation Energy pH Scale S The scale that is used to identify acids and bases (range 0-14) Acids below 7, bases above 7 Organic compound? S CONTAINS CAROBON Hemoglobin S Protein in red blood cells. Carries oxygen in the blood