channel structure
advertisement

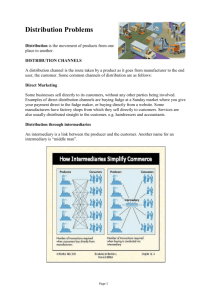
Managing international Channels of Distribution INTRODUCTION Channels Of Distribution describes the varieties of intermediaries (i.e., agents, wholesaler and retailers) involved in moving products between countries as well as within countries. The tasks and functions of the various intermediaries will be examined. It should be kept in mind that certain types of intermediaries do not exist in some countries and that the pattern of use as well as the importance of each type of intermediary varies widely from country to country . A manufacturer is required to make several decisions that will affect its channel strategy, including the length, width, and number of distribution channels to b used. DEFINITION THE AMERICAN MARKETING ASSOCIATION DEFINES:-CHANNEL OF DISTRIBUTION AS— “An organized network of agencies and institutions which in combination perform all the activities required to link producers with users to accomplish the marketing task.” DISTRIBUTION:Is the physical flow of goods through channels and CHANNELS:Is coordinated groups of individuals or firms that perform functions adding utility to a product or services. OBJECTIVES OF CHANNELS TO CREATE UTILITY FOR CUSTOMERS CHANNEL UTILITY ARE:PLACE TIME FORM INFORMATION Ex:-COKE’S LEADERSHIP:due to PLACE UTILITY The most effective channel arrangement is a clear focus of the company’s marketing effort on a target market and a determination of its needs and preferences. Channel strategy in global marketing must fit the company’s COMPETITIVE POSITION and MARKETING OBJECTIVE in each national market If a company wants to enter a competitive market,it has two basic choices:DIRECT INVOLVEMENT (sales force, retail stores etc.) INDIRECT INVOLVEMENT (independent agents, distributors, wholesalers) Distribution Channel Functions Information Transfer Payments Physical Distribution Risk Taking Communication Negotiation Ordering Financing ROLES OF CHANNEL MEMBERS 1. Facilitate the search process of buyers & sellers:- Lower the uncertainty among end-users In their absence, manufactures would also be confuse about how to approach customers 2. Sorting:Channel members eliminate the differences in the collection of goods & services offered by company CONTD. 3. Making transactions routine:Transactions involve ordering of goods or services, fulfilling orders & paying for goods & services purchased. i.e., Manufacture-Wholesaler-Retailer-Customer Help in making transactions routine through standardizations & automations 4. Contractual efficiency:Channel Intermediaries have to optimize the number of exchange relationships required to complete a transaction. DESIGNING MARKETING CHANNELS Dimensions to choose a channel design: The channel length – Number of intermediaries between the producer and customers The channel breadth – Number of outlets available to consumers The cost involved in selecting a particular channel CONTD. A channel decision depends on the following considerations:1. CHANNEL STRUCTURE:- It refers to the number of levels of channels intermediaries (Distributor, Wholesaler, Retailer). It depends on the number of intermediaries uses to distribute its product to end-users The channel levels are zero level, one level, two level & three level. Zero-level channel One-level channel Two-level channel Wholesalers Retailers Three-level channel Wholesalers Agents Retailers Consumers Manufactures Retailers CONTD. 2. CHANNEL INTENSITY:It refers to the number of intermediaries present in a distribution or marketing channel. Intensive distribution Producers of products stock their goods in as many outlets as possible as possible by considering time & place utility. Exclusive distribution Producers of some products limit the number of intermediaries handling their product to deliver maximum service quality to customers, try to develop a superior brand image for their product. CONTD. Selective distribution It is adopted when the manufacturer lacks the resources to adequately influences the policies of all the intermediaries who can carry a particular product. The manufacturer distributes products only to specific retailers selected on the basis of defined criteria. CONTD. 3. TYPE OF CHANNEL INTERMEDIARIES AT EACH LEVEL Manufacturer’s representatives They sell the manufacturer's product to the wholesalers, retailers, other businesses & also to institutions such as hospitals, libraries & school. They may represent more than one manufacturer. Also called account executives or sales engineers. Manufacturer’s sales force It comprises the salespersons who are on the company’s rolls & received a fixed salary. Devotes their entire time & effort to selling that product or service of that manufacturer. CONTD. Industrial distributors These are independent firms consisting of sales & support personnel. They differ from manufacturer's in that they take possession of the products they sell & have a partnership arrangement with the manufacturer. Examples: Norton, Pfizer & 3M. FACTORS AFFECTING SHAPING OF CHANNELS CUSTOMERS PRODUCTS MIDDLEMEN AND ENVIRONMENT CUSTOMER CHARACTERISTICS Customers number, geographic distribution, income, shopping habits and reactions to different selling methods all vary from country to country and therefore require different channel approaches. The need for multiple channel intermediaries increases as the customers increases. EX:- 10 customers must be directly contacted by either by manufacturer or an agent, For mass market products bought by millions of customers, retail distribution outlets or mail order distribution is required. Product characteristics Degree of standardization. Perishablity Bulk/Quantity Services (requirements and facilities) Unit price Types of products Product with high unit price rely on controlled sales force,(Ex. mainframes computers) since selling cost of this expensive distribution method is small part of the total SP. Cosmetics products and other consumer products rely on wide gross selling margins to compensate salespeople (Ex. Amway and avon) Perishable products need relatively direct channels to ensure proper conditions at the time of purchase by customers. (bread and eatables) Bulky products/large quantity (Ex.soft drinks )of product requires minimum shipping distances, charges and minimum amt. of transactions between intermediaries. Middleman characteristics Cherry picking. Practice of taking orders from manufacturers whose product require less efforts to promote. Bypassing of cherry picking can be done by going alternatives options like: •Setting own distribution organizations. •Going for cooperative arrangements/direct selling supports and distribution support systems. ( Rely on distributors own sales force by subsidizing the cost of the sales representatives the distributer had assigned to the company’s products). Middleman characteristics •Selection- finding most efficient and compatible distributers. (Ex. The local chamber of commerce or local trade associations in country can provide lists.) •Before signing make sure the presence of one key person in the organization who will make it a personal objective to achieve success with your product. •Distributer must be capable of assisting of providing necessary information about customers . •Distributer/agent should have core competency in related products. •Motivation in form of commissions is appreciable. •Clause of termination on the account of performance should be clearly expressed. (Ex. despite of mentioned clause foreign agent might sue you on basis of his native country norms.) Environmental characteristics •Economic •Social •Political Consumables and eatables are highly sensitive towards environment. Success of Supermarkets is classical example of this factor. Structure • Consumer products the hands of end user. Designed to directly put in •Industrial products Designed for manufacturers and organizational use. Consumer product : • Door to Door selling •Manufacturer- owned store •Franchise Operations •Combination Structures Industrial products M M Manufacturer-Owned Stores Consignment to Part – Time Salesperson House Party Mail order Door-to-Door Agents/ Brokers M MSF M MSF M M MSF W W W R R R R Customers M = Manufacturer W = Wholesaler MSF = Manufacturer’s Sales Force R = Retailer (including online e-commerce Figure :- Marketing Channel Alternatives – Consumer Product R Marketing channels alternatives for industrial product THANKS