Marketing mix: promotion
advertisement

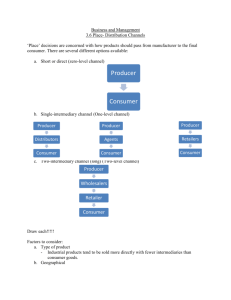
Unit 2:Growing as a Business Promotional activities Advertising – most widely recognised Other forms of promotion: PR – raise profile of business often through media Personal selling – dedicated sales team Sales promotions - BOGOF Promotional activities and a Growing Business Target audience – internet reaches many people, local paper a much smaller focused audience. Not just geographical but also income related – The Times v The Sun. generally a growing business will use methods designed to hit a bigger target audience Cost – as a business grows it’s resources increase which means they can afford more expensive forms of promotion like TV adverts Promotional activities and a Growing Business Methods of communication – TV is the most powerful but very expensive Factors to consider: cost, coverage no of people hit, quality, media ( sound v print v sound & images) Place How the products (goods and services) are distributed to the consumers Chain of distribution runs producers – wholesalersretailers Wth online selling the chain is being reduced sometimes to the extent that producers carry out all of the above functions Wholesalers and retailers are intermediaries in the distribution channel Distribution channel connections Online selling – most popular form of direct selling (also mail order and telesales) Most businesses have their own website and offer the customers the option to buy online Mail oreder – catalogues which customers order from Telesales – sell products over the phone e.g. double glazing Levels of Distribution Zero level – producers sell direct to the consumer 9most modern) One level – one intermediary between producer consumers Two level – two intermediaries between producer and consumer (traditional) Advantages of intermediaries Increased access to a wider market when selling through retailers Retailers offer a market where consumers can compare brands Disadvantages of intermediaries Obviously add cost to the product and therefore its price Loss of control over how the product is sold and the brand image of the product Selecting the right channel of distribution Ultimately decided by cost Loss of control over the brand Type of product sold – products wised often which are perishable mean that they have to be readily available in many places More expensive products need to be available in less places as bought very rarely – can be sold direct on the Internet.