Channels of Distribution
advertisement

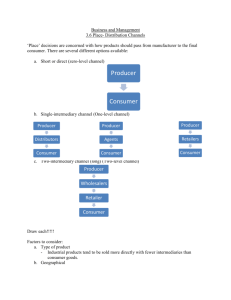
Channels of Distribution Chapter 21 Ch 21 Sec. 1 -- Distribution What you’ll learn • The concept of a channel of distribution • Who channel members are • The different non-store retailing methods • How channels of distribution differ for consumer and business-to-business products Distribution is Part of the Place Decision • Distribution deals with the physical movement, handling, and storage of goods and services. • Place decision deals with where and how goods and services will be distributed to consumers. Channel of Distribution The path a product takes from producer or manufacturer to the final user. Channel Members are called intermediaries • Intermediaries provide value to producers because they often have expertise in certain areas in distribution producers do not have. • Intermediaries are experts in displaying, merchandising, and providing convenient shopping locations and hours for customers. Channel Members are called intermediaries • Wholesalers – buy large quantities of goods from manufacturers, store the goods, then resell them to other businesses – Rack jobbers – manage inventory and merchandising for retailers by counting stock, filling it in when needed, and maintaining store displays. – Drop shippers –own the goods they sell but do not physically handle the actual products. Retailers – sell goods to the final consumer for personal use – Brick and mortar retailers – Automatic retailing – vending service – Direct mail and catalogs – TV home shopping – E-tailing – online retailing Agents – do not own the goods they sell. They bring buyers and sellers together Direct and Indirect Channels • Direct distribution occurs when the goods or services are sold from the producer directly to the customer – no intermediaries are involved. – Example: A farmer sells corn at a street market. • Indirect distribution involves one or more intermediaries. DISTRIBUTION INTENSITY Deals with how widely a product is distributed. Three Levels of Distribution Intensity • Exclusive Distribution – Involves protected territories for distribution of a product in a given geographic area. (i.e. Rolex) • Selective Distribution – Limited number of outlets in a given geographic area are used to sell product. (i.e. Nike) • Intensive Distribution – Involves the use of all suitable outlets to sell a product. (i.e. Coca Cola) Channels in the consumer markets Channels in industrial markets