-
Polarity
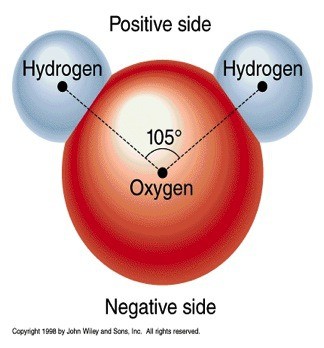 water is a polar molecule with one oxygen atom negatively charged and two hydrogen atoms positively charged.
water is a polar molecule with one oxygen atom negatively charged and two hydrogen atoms positively charged. -
Universal solvent
 Water - due to its polarity and ability to dissolve other polar molecules
Water - due to its polarity and ability to dissolve other polar molecules -
Hydrogen bonds
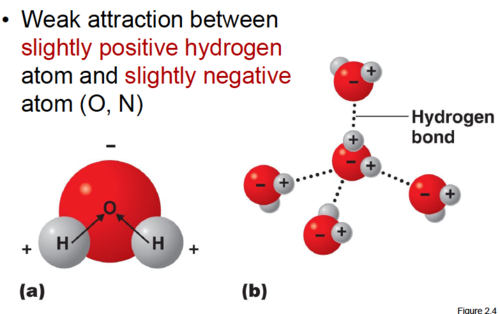 The weak intermolecular bonds that form between the hydrogen atom of one water molecule and the oxygen atom of another water molecule.
The weak intermolecular bonds that form between the hydrogen atom of one water molecule and the oxygen atom of another water molecule. -
Solvent
 Does the dissolving
Does the dissolving -
Solute
 Substance being dissolved
Substance being dissolved -
Solution
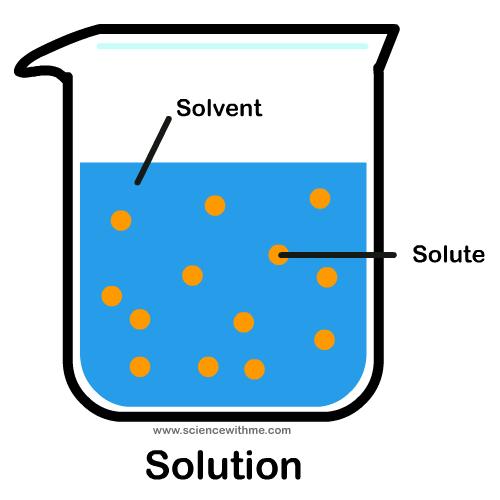 Solvent +Solute=Solution
Solvent +Solute=Solution -
density
 the ratio of the mass of a substance to the volume of the substance (The density of water is 1.0 g/cm3)
the ratio of the mass of a substance to the volume of the substance (The density of water is 1.0 g/cm3) -
Polar Molecule
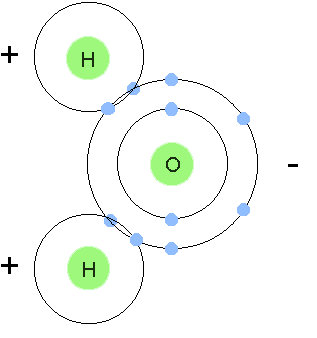 a molecule in which one side of the molecule is slightly negative and the opposite side is slightly positive
a molecule in which one side of the molecule is slightly negative and the opposite side is slightly positive -
BufferA solution that minimizes changes in pH when extraneous acids or bases are added to the solution. Proteins and Amino acids are intracellular fluid buffers. Carbonic acid/bicarbonate is an extracellular buffer. Hemoglobin / Oxyhemoglobin is an RBC buffer.
-
CohesionAttraction between molecules of the same substance
-
AdhesionAn attraction between molecules of different substances (water and another substance)
-
capillary actiontendency of water to rise in a thin tube against the force of gravity, and due of the cohesion and adhesion forces of attraction.
-
Surface TensionAn invisible film at the surface of water that allows objects to walk. This is caused by the cohesive forces.
-
high specific heat
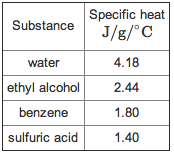 Water can absorb or release a tremendous amount of energy with little change in actual temperature. The ability of water to resist changes in temperature. 1 gram of water will need to absorb 4.18 Joules (amount of heat) in order to increase its temperature by 1 degree Celsius.
Water can absorb or release a tremendous amount of energy with little change in actual temperature. The ability of water to resist changes in temperature. 1 gram of water will need to absorb 4.18 Joules (amount of heat) in order to increase its temperature by 1 degree Celsius. -
Acidany compound that forms hydrogen (H+) ions in solution
-
Basea compound that produces hydroxide ions (OH-) in solution
-
pH scale
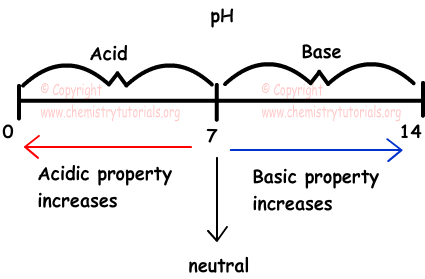 scale with values from 0 to 14, used to measure the concentration of H+ ions in a solution; a pH of 0 to 7 is acidic, a pH of 7 is neutral, and a pH of 7 to 14 is basic
scale with values from 0 to 14, used to measure the concentration of H+ ions in a solution; a pH of 0 to 7 is acidic, a pH of 7 is neutral, and a pH of 7 to 14 is basic -
Hydrophilic
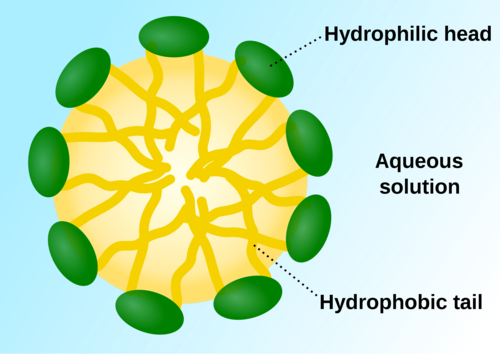 A substance that likes water. Having an affinity (love) for water; usually polar molecules.
A substance that likes water. Having an affinity (love) for water; usually polar molecules. -
HydrophobicA substance that water hates water (it is repealed by water); usually non-polar molecules, like oil.
-
Homeostasisthe process of maintaining the body chemical and thermal components in equilibrium. What hormone is responsible with maintaining the water homeostasis in human's body?
-
Liquid form of waterwater
-
Gas form of waterwater vapor or steam
-
Expansion upon freezing
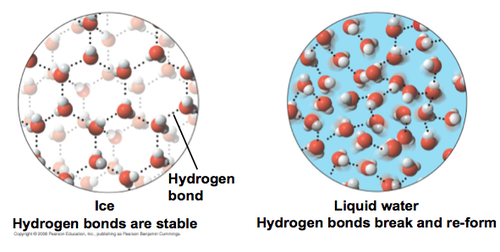 hydrogen bonds in ice are more "ordered and spaced out" making ice larger and LESS DENSE
hydrogen bonds in ice are more "ordered and spaced out" making ice larger and LESS DENSE


