-
What is angle of refraction always equal to?Angle of incidence
-
The magnification of a plane (aka flat) mirror is always equal to..1.0
-
The image formed by a plane mirror is always…Virtual
-
In plane mirror the image is…is unmagnified meaning it is equal to one and the same size as the object.
-
In a plane mirror, is the image upside down or upright?Upright
-
P is the distance…Of the object in front of a plane mirror
-
q is the distance…Of the image made by the object
-
In a real image, light…Actually, passes through the image point
-
In a virtual image, light...Does not actually pass through the image point but appears to come/diverge from there
-
Real images (can or cannot) be seen on a screenCan
-
Virtual images (can or cannot) be seen on a screencannot
-
The image formed by an object placed in front of a flat mirror is as far behind the mirror as the obiect is in front of the mirror...far behind the mirror as the object is in front of the mirror.
-
h denotes....Object height
-
h’ denotes…Image height
-
The image is as far behind the mirror…as the object is in front.
-
To find magnification use:
M=-q/p=h'/h
-
An object is in front of a plane mirror, 20 cm from it. What is the distance between the object and its virtual image? A. 10 cm B. 20 cm C. 40 cm D. There is no image in this caseC. 40 cm Since The image is as far behind the mirror as the object is in front… 20 + 20 = 40 .
-
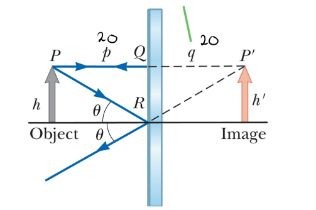 What if the object starts moving 2 m/s towards the mirror? What would the speed of its image relative to the object be?
What if the object starts moving 2 m/s towards the mirror? What would the speed of its image relative to the object be?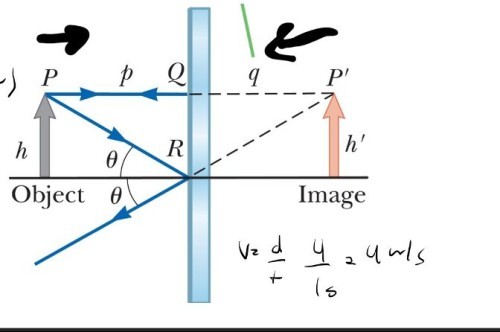 4 m/s toward the object
4 m/s toward the object -
A 170cm person is standing in front of a flat mirror hanged on the wall. What is the minimum height for the mirror if the person wants to see her entire height in the mirror?Always at least half of height of person so…85 cm.
-
In spherical mirrors, R denotesRadius of curvature
-
Point C on a spherical mirror is the...Center of curvature
-
Along point C is the...Principal axis
-
When light reflects the inside portion of a spherical mirror it is known as what type of mirror...Concave mirror Curves inward
-
In a concave mirror, the light rays...Converge Aka converging mirror
-
When light reflects the outside portion of a spherical mirror it is known as a...Convex mirror Curves outward
-
In convex mirrors, light rays...Diverge So it is known as a diverging mirror also
-
In spherical mirrors, whenever light actually passes through a point, The image formed there is...
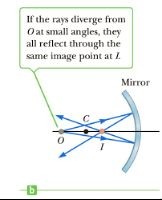 real.
real. -
In spherical mirrors, the parallel ray or P-ray reflects through..Focal point
-
The focal ray reflects parallel to... (F-ray)Axis
-
The center of a curvature reflects (C-ray)back
-
When the object is located so that the center of curvature lies between the object and a concave mirror surface the image is..
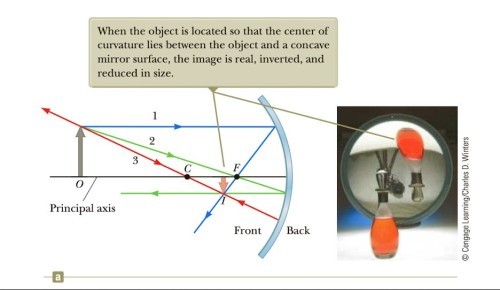 real, inverted, and reduced in size.
real, inverted, and reduced in size. -
When the object is located between the focal point and a concave mirror surface, the image is...
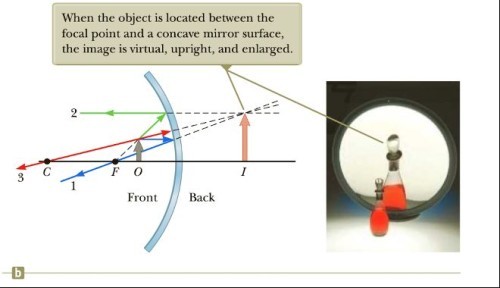 virtual, upright, and enlarged.
virtual, upright, and enlarged. -
When the object is in front of a convex mirror, the image is..
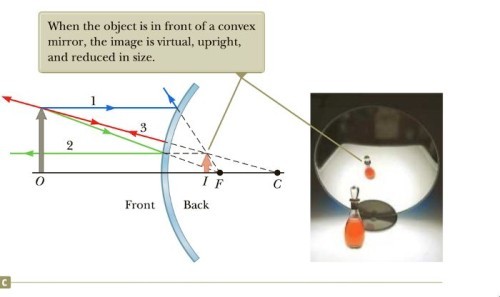 virtual, upright, and reduced in size
virtual, upright, and reduced in size -
An object, represented by a gray arrow, is placed in front of a plane mirror. Which of the diagrams below best describes the image, represented by the pink arrow?
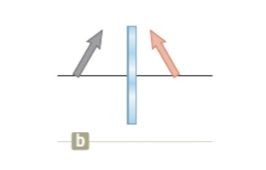 since this is a plane mirror the image must be uprightL/R flippedsame sizesame distance from mirror
since this is a plane mirror the image must be uprightL/R flippedsame sizesame distance from mirror -
Concave mirrors can form...(what type of images)Both real and virtual images
-
Convex mirrors can form...Only virtual images
-
True or False? A concave mirror only forms real images from (real) objects.False
-
True or False? A convex mirror only forms virtual images from (real) objects.True.
-
Real images are always (upside down or upright)Upside down
-
Virtual images are always (upside down or upright)upright
-
If a mirror forms a real upside down image, its magnification is...Negative
-
Focal length is equal to...
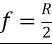 Radius divided by 2.
Radius divided by 2. -
What is the mirror equation?
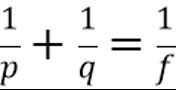
-
If q is positive, the image in in front of a mirror is...Real
-
If M is negativeThe image is inverted.
-
If |M| is less than 1.The image is smaller than the object.
-
If q is negative, the image is...virtual
-
If M is positiveThe image is upright
-
True or False? The focal point for a concave mirror is always real.True
-
True or False? The focal point for a convex mirror is always virtual.True
-
A 10 cm object is in front of a concave mirror. The focal length of the mirror is 10 cm. If the image formed by the mirror is real and 15 cm, what is the distance between the object and the mirror?

-
An object is 10 cm from a concave mirror. The focal length of the mirror is 20 cm. Which of the following describes the image correctly. A.) virtual, 30 cm from the mirror B.) virtual, 20 cm from the mirror C.) virtual, 10 cm from the mirror D.) real, 20 cm from the mirror.B.) virtual, 20 cm from the mirror a. 1/p + 1/q = 1/f, where p is the object distance, q is the image distance, and f is the focal length. We can plug in the given values and solve for q: b. 1/p + 1/q = 1/f 1/10 + 1/q = 1/20 q = -20 cm c. The negative sign of q means that the image is virtual and located behind the mirror. Therefore, the correct answer is B.) virtual, 20 cm from the mirror.
-
Focal length is (negative or positive) for a concave mirror.Positive
-
Focal length is (negative or positive) for a convex mirror.Negative
-
Focal length is (positive or negative) for a concave lens.Negative
-
Focal length is (positive or negative) for a convex lens.Positive
-

table
-
An object is at 10 cm from a convex mirror. The focal point of this mirror is also 10 cm from the mirror. What is the location of the image? A.) 5 cm from the mirror B.) 10 cm from the mirror C.) 20 cm from the mirror D.) There is no image in this case.A.) 5 cm from the mirror a. Since convex it will virtual. Since convex focal length is negative. b.
-
What is the difference between a virtual image and a real image? A.) A virtual image will focus on a screen but doesn't exist. B.) A real image only exists in the mirror. C.) A virtual image appears to be located where no light rays intersect, whereas a real image exists where light ravs actually intersect. D.) A virtual image appears to be in front of the mirror, and a real image appears to be behind the mirror.C.) A virtual image appears to be located where no light rays intersect, whereas a real image exists where light ravs actually intersect.
-
A mirror creates an image of an object; it is upright, and appears to be slightly smaller than the object itself. What kind of mirror is it? A.) concave B.) convex C.) flat D.) unknownB.) convex Virtual and smaller The only type of virtual images concave mirror produce are enlarged ones.
-
Your dentist uses a mirror to form a virtual image of your tooth which is larger than your tooth. What type of mirror could that be?Concave Not convex because that mirror can only produce smaller virtual images.

