-
monomer of carbohydrates
monosaccharides
-
polymer of carbohydrates
polysaccharides
-
monomer of lipids
fatty acids
-
polymer of lipids
triglycerides
-
monomer of proteins
amino acids
-
polymer of proteins
polypeptides
-
monomer of nucleic acids
nucleotides
-
polymer of nucleic acids
nucleic acids (DNA and RNA)
-
major function of carbs
short-term energy storage
-
major function of lipids
long-term energy storage
-
major functions of proteins
1. Enzymes
2. Hormones
3. Bones and muscles (eg collagen)
4. Transport substances (eg hemoglobins)
5. Antibodies
6. Movement (eg contractile proteins)
-
major function of nucleic acids
informational molecules (genetic info, instructions for making proteins)
-
example of a carbohydrate
sugars
-
example of a lipid
steroids
-
example of a protein
meats
-
example of a nucleic acid
DNA/RNA
-
relative energy storage of carbohydrates
4 cal/gram
-
relative energy storage of lipids
9 cal/gram
-
relative energy storage of proteins
4 cal/gram
-
relative energy storage of nucleic acids
0 cal/gram
-
order of body's consumption of macromolecules
1. carbs: go-to energy source
2. lipids: after carbs run out
3. proteins: last resort, unhealthy to use for energy
-
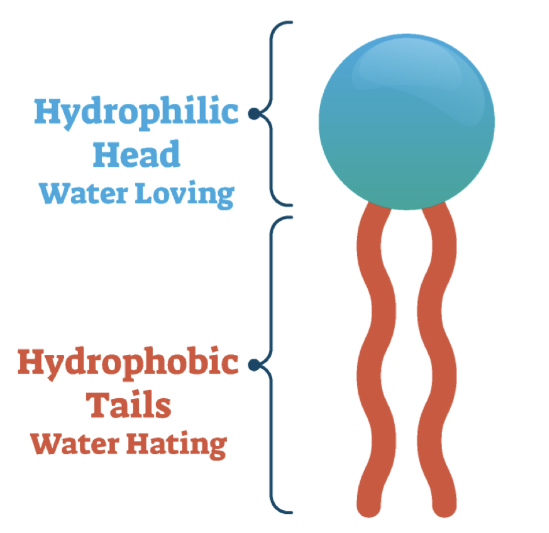
how do phospholipids' structure give the membrane a unique property
the membranes are selectively permeable; the water loving head stays on the outside, and the water hating tails stay inside and away from water.
-
what makes proteins the most diverse macromolecule?
structure and function
-
which macromolecule is not obtained from our food and where do we get it from?
nucleic acids, we get them from our parents.
-
macromolecules
large organic molecules that make up living things
-
monomer
polymer
-
monosaccharide
sincle sugar molecules
-
polysaccharide
larger sugar molecules


