-
What is a T-tubule?
Structural system of membrane folds characteristic of skeletal and cardiac muscle
-
What are Ryanodine receptors?
Calcium release channels in the sarcoplasmic reticulum
-
What is troponin?
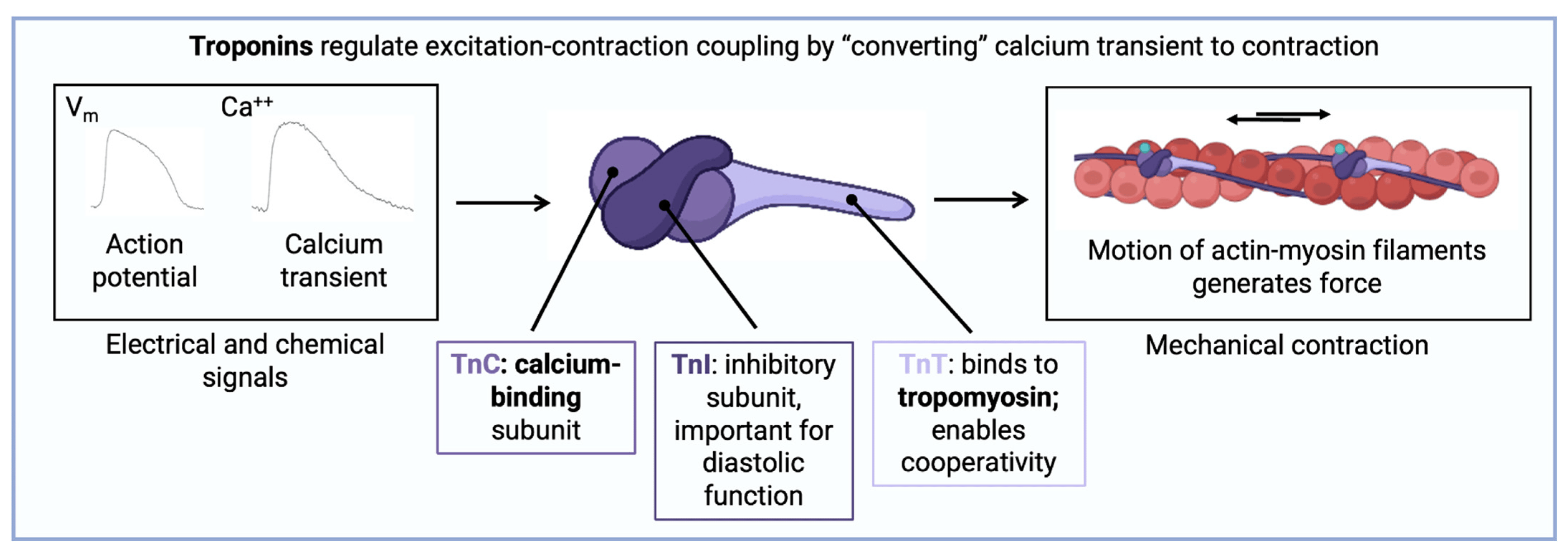
Calcium sensor in skeletal and cardiac muscle
-
What is Tropomyosin?
A protein associated with actin that prevents myosin binding
-
What is Calmodulin?
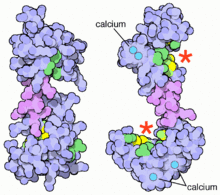
Calcium sensor in smooth muscle cells
-
Myosin Light Chain Kinase (MLCK) is activated by...?
Activated by calcium-calmodulin that converts smooth muscle myosin to a more active form.
-
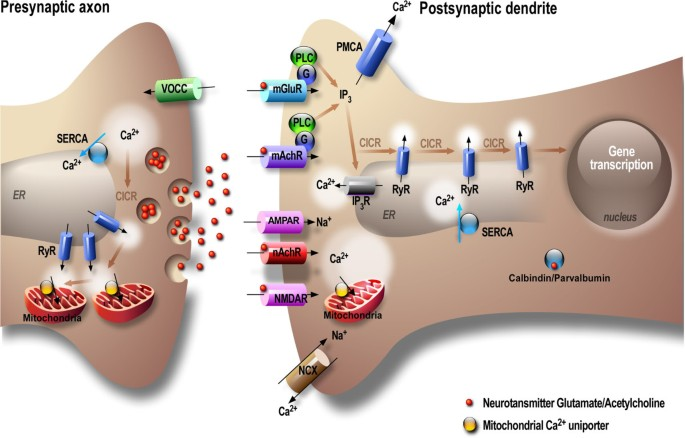
Neurotransmitters are packaged in?
Synaptic vesicles
-
What do snare proteins do?
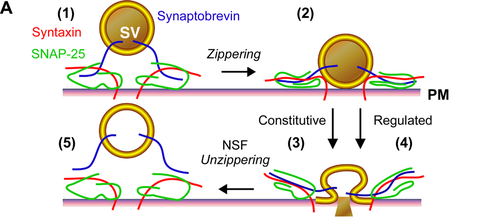
The primary role of SNARE proteins is to mediate the fusion of vesicles with the target membrane; this notably mediates exocytosis, but can also mediate the fusion of vesicles with membrane-bound compartments (such as a lysosome).
-
Types of snare proteins?
V-snares:in our vesicles (Vesicle-associated membrane protein, VAMP or synaptobrevin0
T-snares:in our membranes
-
What does calcium do when it comes to snares?
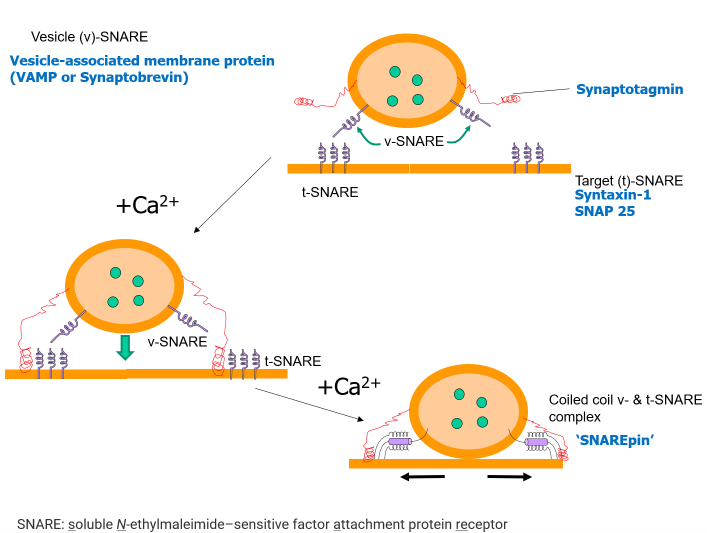
Calcium causes c-snares and t-snares to bind together, creating a SNARE pin
-
How does the botulinum toxin effect snare proteins?

1-Binds to a glycoprotein TO CHOLINERGIC NEURONES allowing toxin entry
2-produces cellular effects (in picture)
-
State key information about the Botulinum toxin (what bacteria create it? How many subunits? How is it destroyed?
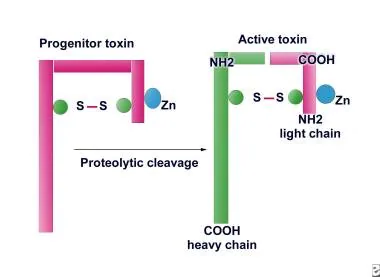
1-Clostridium botulinum
2-two subunits
3-destroyed by heating >85 degrees C for longer than 5 minutes
-
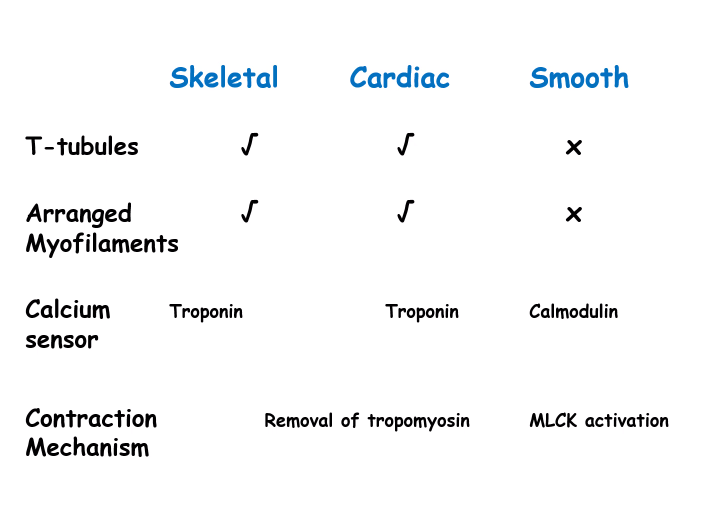
What are some general differences between skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle?
skeletal:
straight and uniform
many nuclei
cardiac:
branched
less nuclei
-
How is the muscle organised?
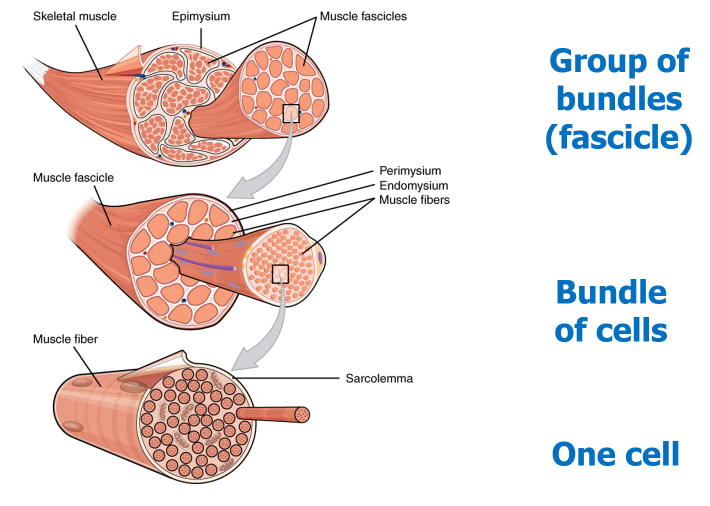
-
Picture demonstrating the anatomy of a skeletal muscle fibre (cell)
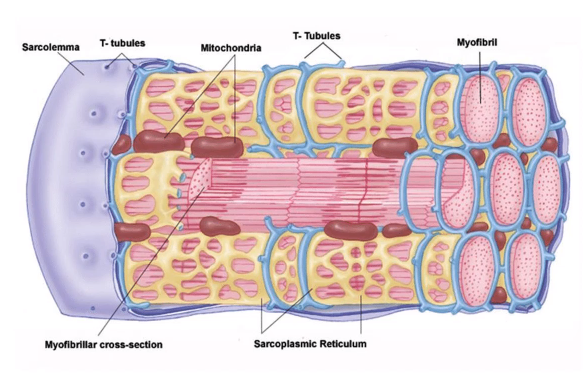
-
The sarcoplasmic reticulum stores a lot of? And has many mi.....?
1-calcium
2-mitochondria
-
Picture outlining the series of events to cause contraction of muscle
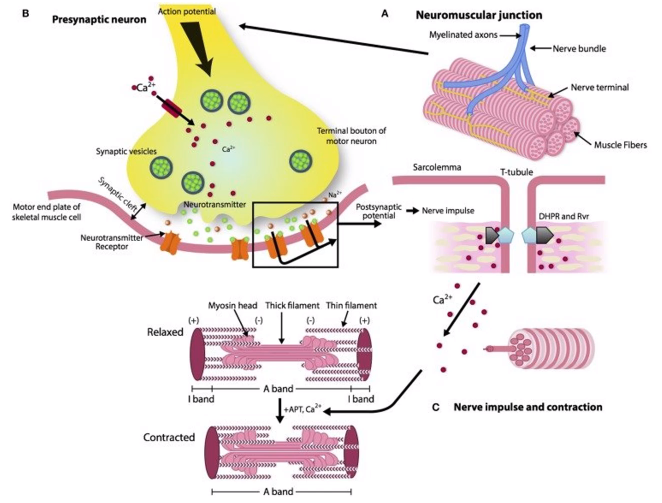
-
Picture outlining the series of events to cause contraction of muscle via membrane depolarisation
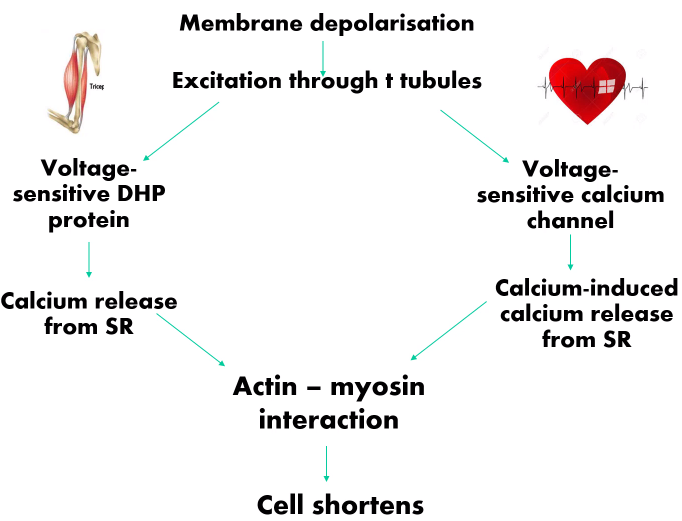
DHP-Dihydropyridine
-
What are the mechanisms of action of cardiac muscle vs skeletal muscle?
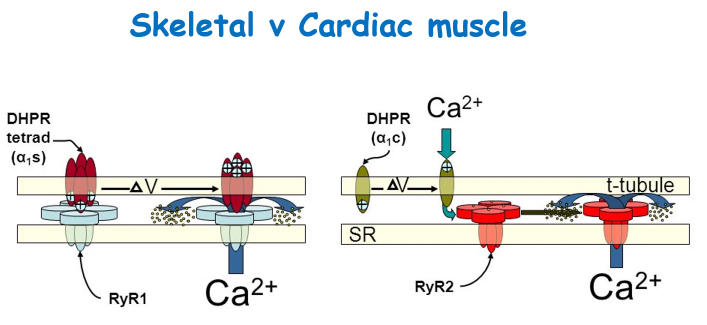
Skeletal:
-Physical interaction between DHP and RyR (Ryanodine receptors)
Cardiac:
-Opening calcium channel promotes CICR (Calcium-induced calcium release)
-
Troponin-C is associated with?
Calcium binding
-
Troponin-T is associated with?
Tropomyosin binding
-
Thin filaments are made out of...?
Actin
-
Thick filaments are made out of...?
Myosin
-
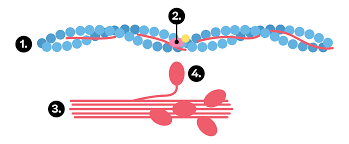
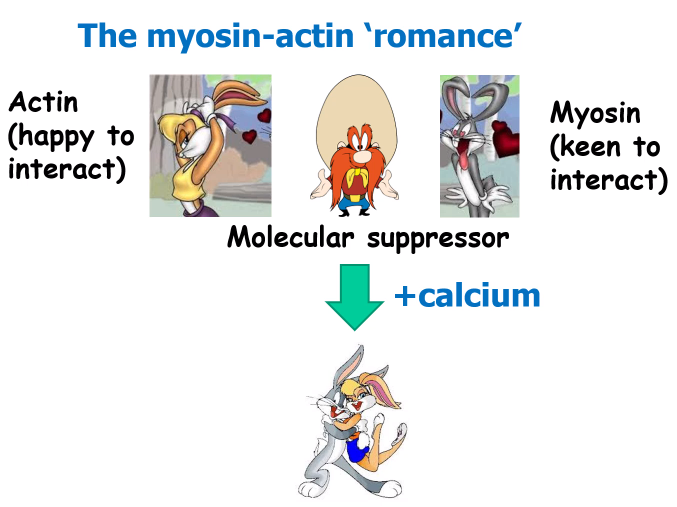
A picture displaying the myosin-actin 'romance'
-
Outline the general series/summary of contraction of skeletal and cardiac muscle
1)Increased [Ca2+] binds to Troponin-C
2)Removal of suppressive tropomyosin
3)Allows actin to interact with 'primed' myosin
4)ATP-dependent cross bridge cycling
5)Each myosin head cycles about 5x per sec
6)~15microm s-1
-
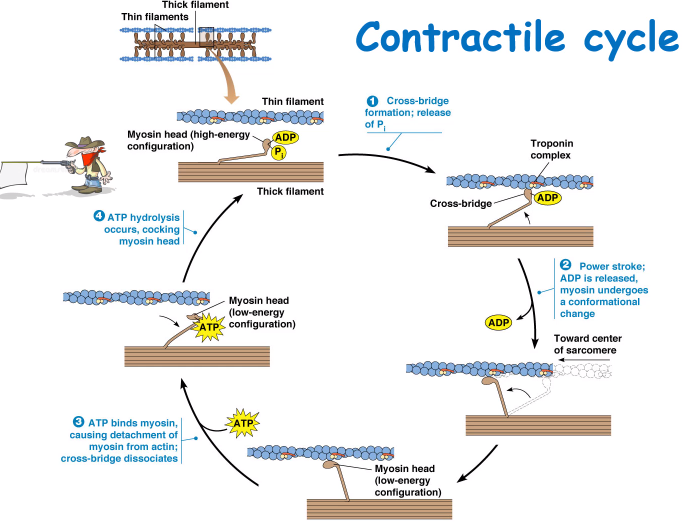
Outline the events of the Contractile cycle
-
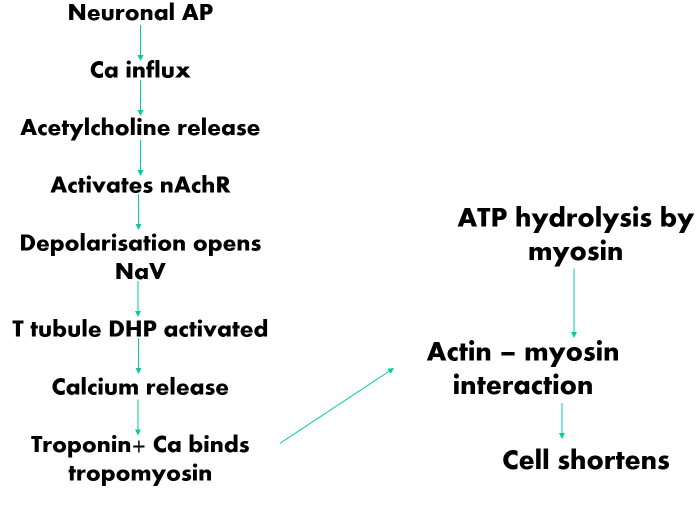
Summary of the general events
-
Smooth muscle has....?
-No troponin
-Tropomyosin does not interact with the myosin binding sites
-Myosin in smooth muscle is a different isoform than the skeletal muscle (MHY11 vs MYH1)
-Lower ATPase activity
-Lower affinity for ATP
-
When calcium increases in smooth muscle cell it binds to calmodulin which leads to the activation of...?
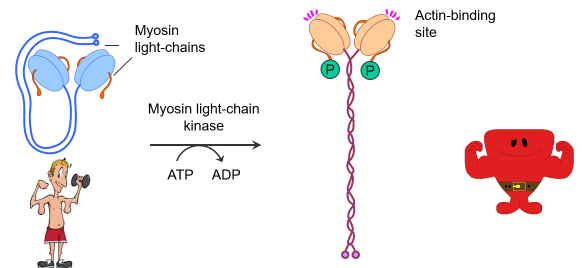
-Activation of Myosin Light chain kinase phosphorylates regulatory MLC at ser 19
-Increases the ATPase activity of the myosin head ~1000x
-Alters the structure of myosin
-
A general summary: