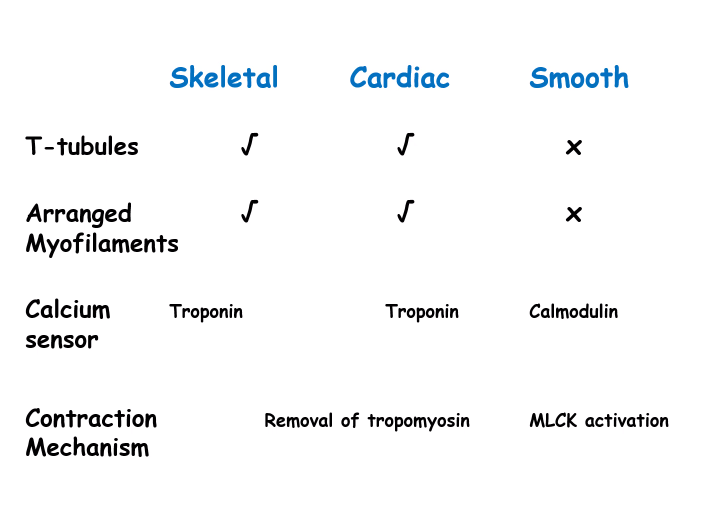
What is a T-tubule?
Structural system of membrane folds characteristic of skeletal and cardiac muscle
What are Ryanodine receptors?
Calcium release channels in the sarcoplasmic reticulum
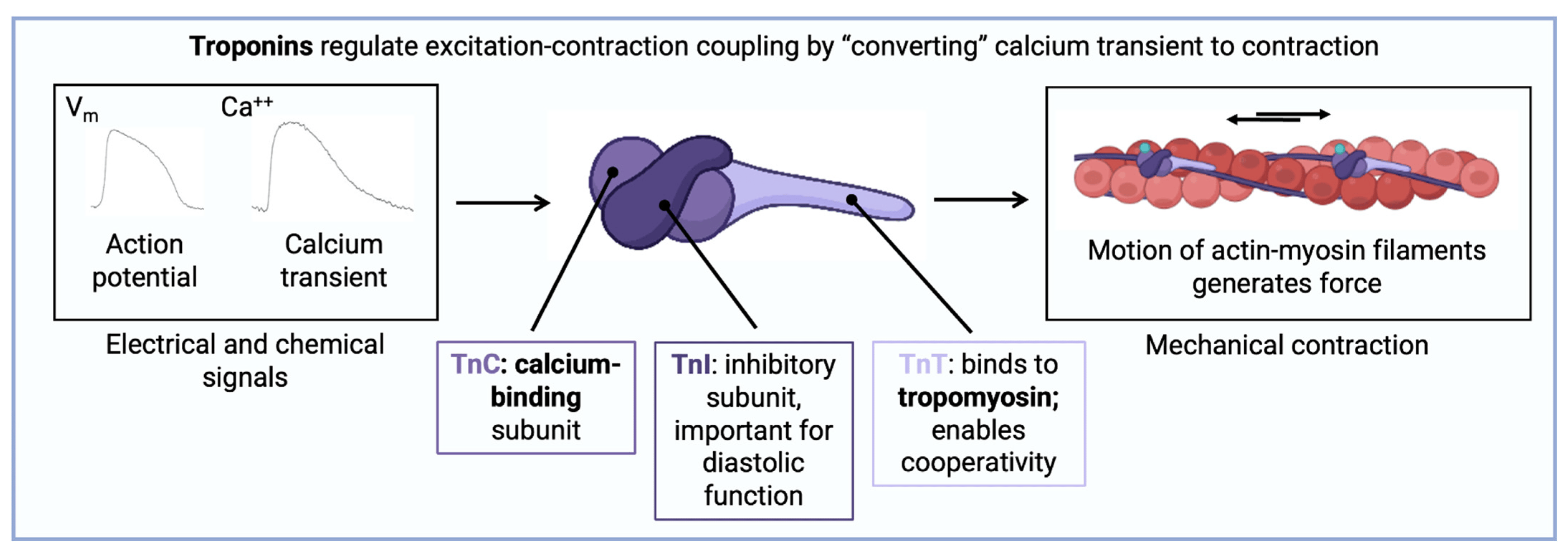
What is troponin?
Calcium sensor in skeletal and cardiac muscle
What is Tropomyosin?
A protein associated with actin that prevents myosin binding
What is Calmodulin?
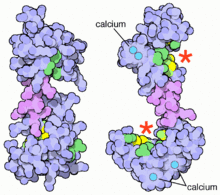
Calcium sensor in smooth muscle cells
Myosin Light Chain Kinase (MLCK) is activated by...?
Activated by calcium-calmodulin that converts smooth muscle myosin to a more active form.
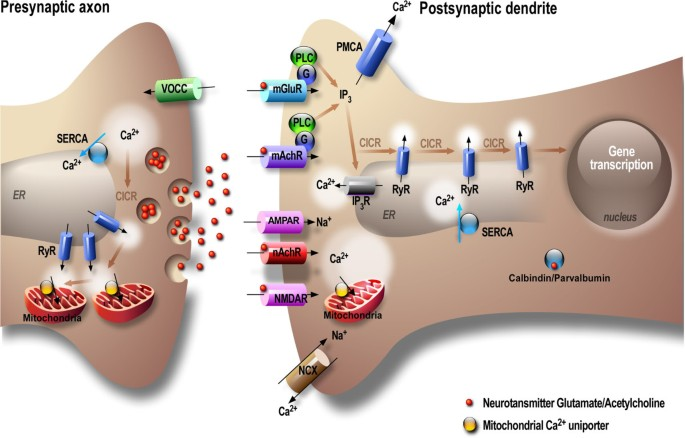
Neurotransmitters are packaged in?
Synaptic vesicles
What do snare proteins do?
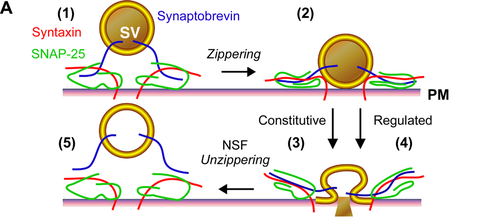
The primary role of SNARE proteins is to mediate the fusion of vesicles with the target membrane; this notably mediates exocytosis, but can also mediate the fusion of vesicles with membrane-bound compartments (such as a lysosome).
Types of snare proteins?
V-snares:in our vesicles (Vesicle-associated membrane protein, VAMP or synaptobrevin0
T-snares:in our membranes
What does calcium do when it comes to snares?
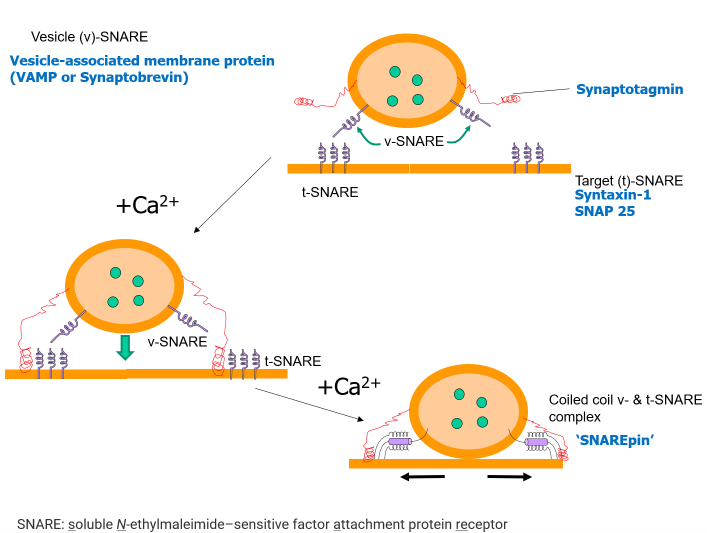
Calcium causes c-snares and t-snares to bind together, creating a SNARE pin
How does the botulinum toxin effect snare proteins?

1-Binds to a glycoprotein TO CHOLINERGIC NEURONES allowing toxin entry
2-produces cellular effects (in picture)
State key information about the Botulinum toxin (what bacteria create it? How many subunits? How is it destroyed?
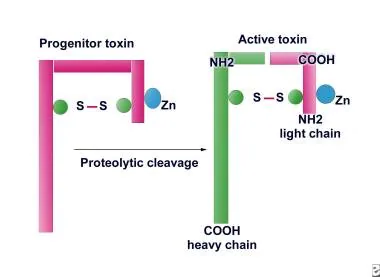
1-Clostridium botulinum
2-two subunits
3-destroyed by heating >85 degrees C for longer than 5 minutes
What are some general differences between skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle?
skeletal:
straight and uniform
many nuclei
cardiac:
branched
less nuclei
How is the muscle organised?
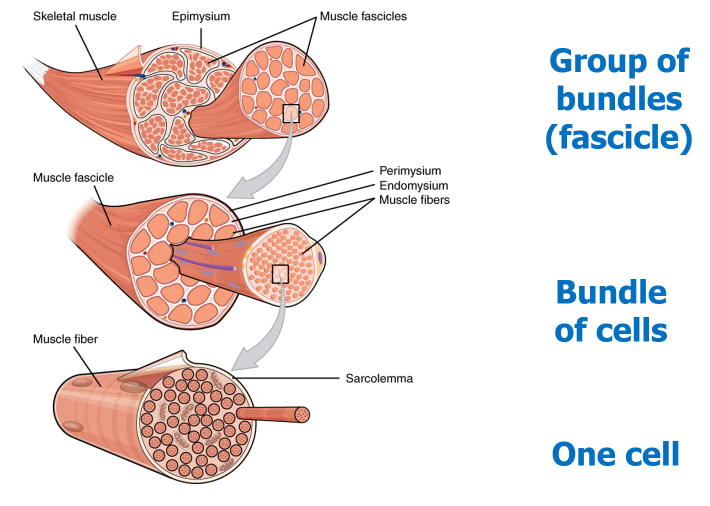
Picture demonstrating the anatomy of a skeletal muscle fibre (cell)
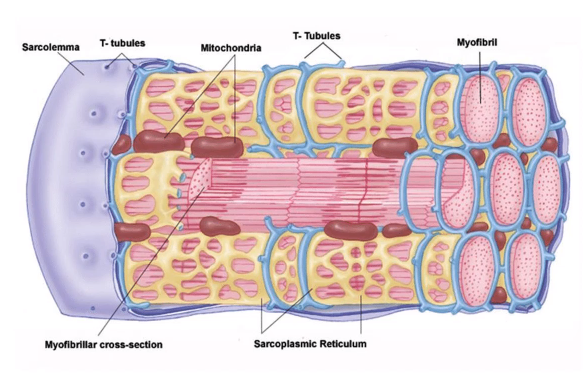
The sarcoplasmic reticulum stores a lot of? And has many mi.....?
1-calcium
2-mitochondria
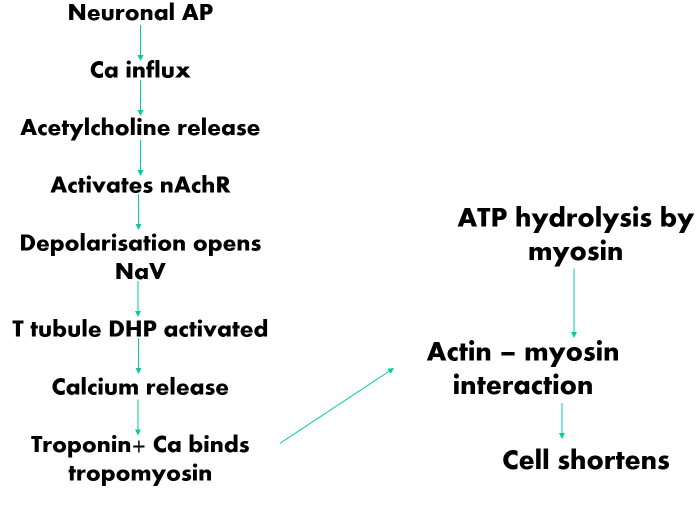
Picture outlining the series of events to cause contraction of muscle
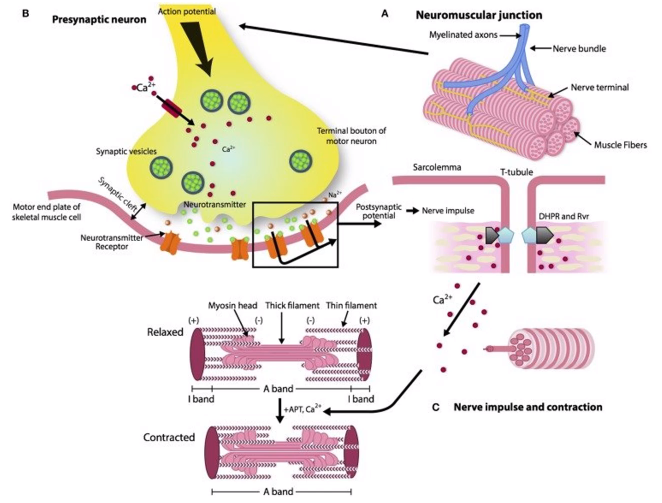
Picture outlining the series of events to cause contraction of muscle via membrane depolarisation
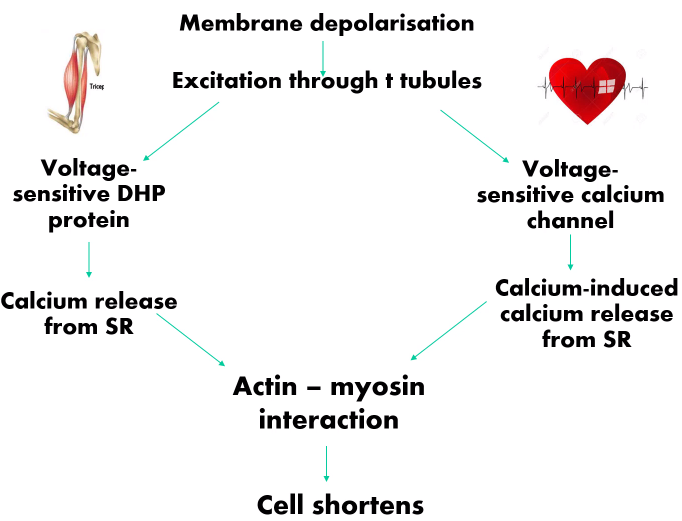
DHP-Dihydropyridine
What are the mechanisms of action of cardiac muscle vs skeletal muscle?
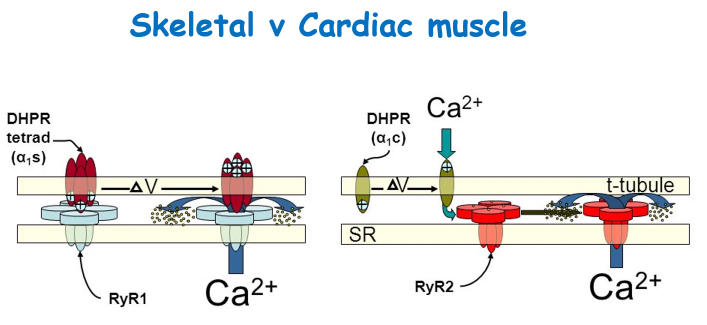
Skeletal:
-Physical interaction between DHP and RyR (Ryanodine receptors)
Cardiac:
-Opening calcium channel promotes CICR (Calcium-induced calcium release)
Troponin-C is associated with?
Calcium binding
Troponin-T is associated with?
Tropomyosin binding
Thin filaments are made out of...?
Actin
Thick filaments are made out of...?
Myosin
A picture displaying the myosin-actin 'romance'
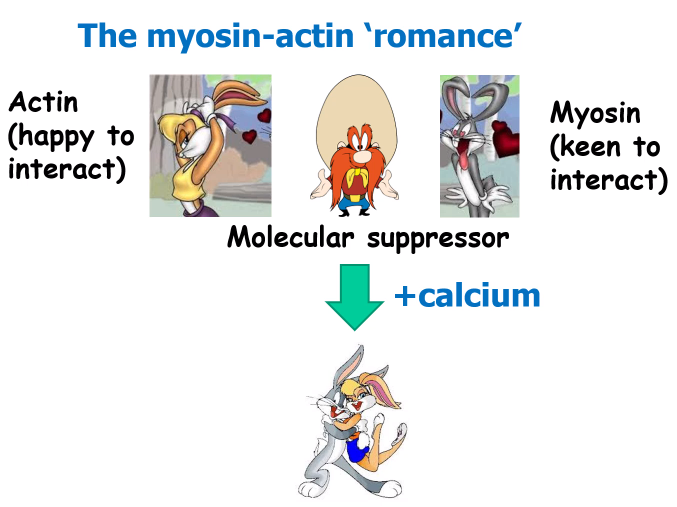
Outline the general series/summary of contraction of skeletal and cardiac muscle
1)Increased [Ca2+] binds to Troponin-C
2)Removal of suppressive tropomyosin
3)Allows actin to interact with 'primed' myosin
4)ATP-dependent cross bridge cycling
5)Each myosin head cycles about 5x per sec
6)~15microm s-1
Outline the events of the Contractile cycle
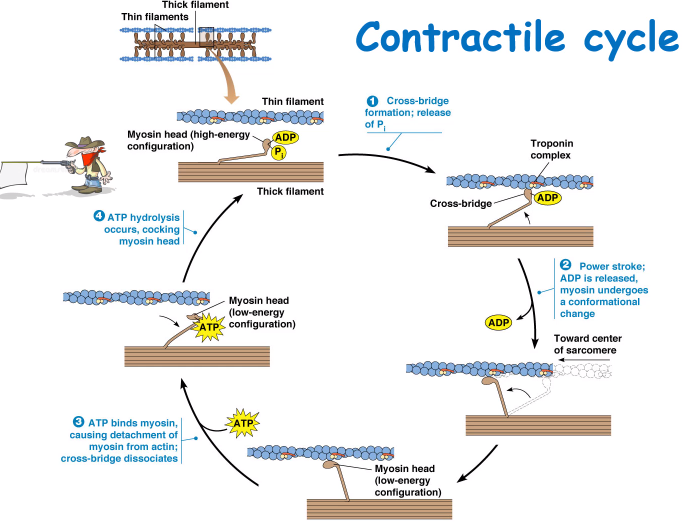
Summary of the general events
Smooth muscle has....?
-No troponin
-Tropomyosin does not interact with the myosin binding sites
-Myosin in smooth muscle is a different isoform than the skeletal muscle (MHY11 vs MYH1)
-Lower ATPase activity
-Lower affinity for ATP
When calcium increases in smooth muscle cell it binds to calmodulin which leads to the activation of...?
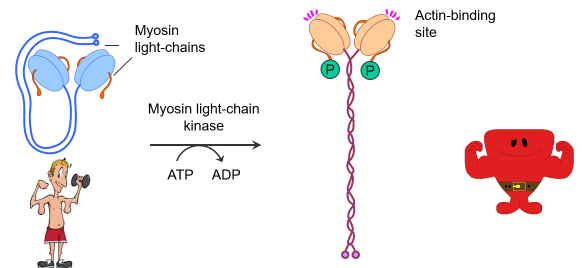
-Activation of Myosin Light chain kinase phosphorylates regulatory MLC at ser 19
-Increases the ATPase activity of the myosin head ~1000x
-Alters the structure of myosin
A general summary: