-
How do you get the marginal density of x given a joint probability density function f(x, y)?
Integrate in regards to y, and vice versa to find the density for y. Give the range in your answer
-
How do you calculate the expected value of a continuous random variable x
∫x f(x) over its range
-
How do you calculate the expected value of a discrete random variable x
Σ x p(x)
-
E(X) of X~U(a,b)
1/2 (a+b)
-
What is the geometric distribution equivalent to?
The probability distribution of the number 𝑋 of Bernoulli trials needed to get one success
-
Poisson distribution definition
A discrete probability distribution that expresses the probability of a given number of events occurring in a fixed interval of time if these events occur with a known constant mean rate and independently of the time since the last event
-
The most efficient estimator is the one with the _____ _______
lowest variance
-
is E(2X) the same as 2E(X)?
Yes
-
Standard error from the mean in a sample with sample size n formula
SE=σ/(√n). σ = population standard deviation
-
Standard error of the mean in a sample (aka standard deviation of sampling distribution from the mean) definition
measures the variability of the sample mean in regard to the population mean
-
Population mean and sample mean symbols, respectively
μ, x̄ (capital I think)
-
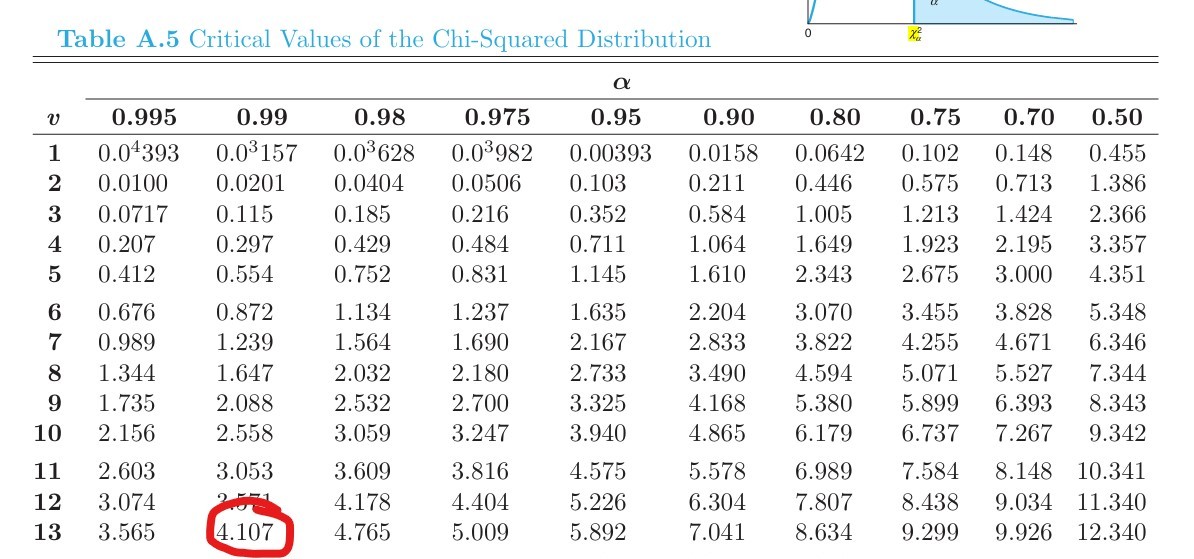
What does this value tell you?
χ2α, such that P(χ2 > χ2α) = 0.99, when ν = 13
-
Bayes rule
P(A|B) = (P(B|A) x P(A)) / P(B)
-
In a t-test: a p-value of 0.07 means there is a _____________
7% chance of obtaining the observed data (or more extreme) if the null hypothesis is true.
-
degrees of freedom formula for one-sample test
n - 1
-
degrees of freedom formula for two-sample test with equal population variances
n1 + n2 - 2
-
For a two tailed test, instead of alpha use _______
alpha / 2
-
Does this alternative hypothesis indicate a one tailed test? or two tailed? Students' performance is different (either better or worse) when listening to music compared to not listening to music.
Two-tailed (as it is either better or worse)
-
Point estimate (of some population parameter 𝜃) definition
is a single value ̂ 𝜃of a statistic Θ. For instance, x̄ is a point estimate of the population mean 𝜇.
-
When asked to provide the efficiency of an estimator, give its ______
variance
-
Does variance scale linearly when multiplied by a constant?
No, it scales by the constant squared
-
For Y=aX. Var(Y)=Var(aX)=_______
a^2 Var(X)
-
When is an estimator Θ unbiased?
E[Θ] = μ
-
Central limit theorem applied to sampling distribution of the sample mean - formula
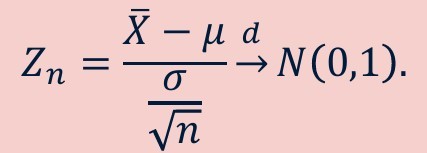
-
How large should n be (rule of thumb) for the central limit theorem to hold
n > 30
-
Sampling distribution of the sample mean notes
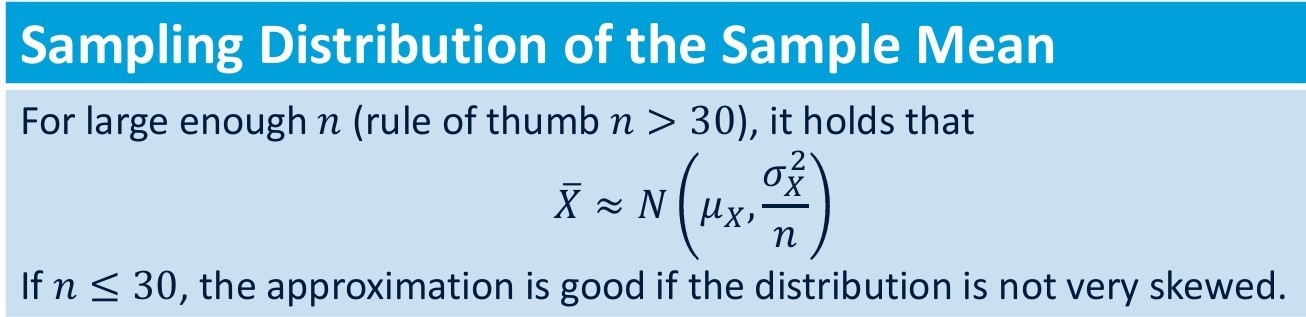
-
Sampling distribution of the sample: If we don't know the variance of the population but n is more than 30 we can replace it with _______. It will follow the ______ distribution
1) the sample variance 2)Student's distribution
-
For the central limit theorem to apply, variance must be ________
Finite
-
Central limit theorem applied to difference of sampling distribution of sample means of two populations - formula
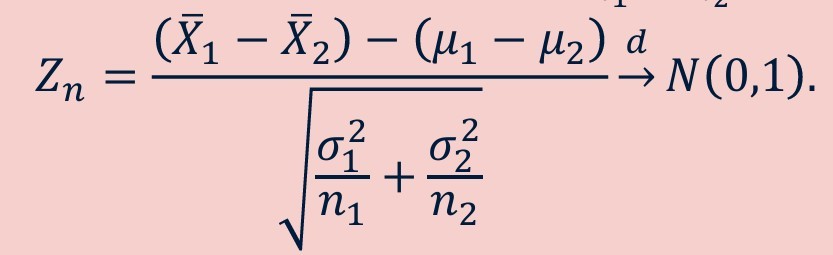
-
The sampling distribution of the sample variance follows a ________ distribution with _______ degrees of freedom
chi-squared, n-1
-
The probability of making a type 1 error is ___
α (significance level)
-
When is it appropriate to approximate a binomial random variable 𝑋 ∼ 𝐵 ( 𝑛 , 𝑝 ) with a normal distribution?
when 𝑛 is sufficiently large ( 𝑛 ≥ 5 0 ) and 𝑝 is close to 0.5 ( 0 . 4 ≤ 𝑝 ≤ 0 . 6 )
-
t-statistic general formula
(mean of sample 1 - mean of sample 2)/standard error (if both are samples but have unequal variance, use welch's method (degrees of freedom is different))(for 1-sample t statistic use x̄-μ as numerator)
-
type 1 error define
Falsely rejecting the null hypothesis
-
Which probability distribution does the Bernoulli process relate to?
Binomial
-
When is the normal approximation of the binomial distribution reasonable?
𝑛𝑝 ≥ 5 and 𝑛(1 − 𝑝) ≥ 5
-
Continuity correction meaning
When approximating a discrete probability distribution such as binomial with a continuous one such as normal, you must account for this difference by centering the discrete value between a unitary interval in the continuous one. Eg. P(X = 7) becomes P(6.5 >= X >= 7)
-
How to approximate binomial with normal
1) Ensure it will be a reasonable approximation.
2) correct for continuity by adding or subtracting 0.5 to x (depending on which is appropriate)
3)use the normal distribution with mean μ=np and standard deviation σ=√(npq) // (q=1−p)
-
How do you correct P (Y ≤ 30) (discrete) for continuity when approximating with a normal distribution?
P (Y ≤ 30.5)
-
How to standardize a normal distribution to N(0,1)?
Z = (X-μ)/σ2 (think about it like you are centering the graph about 0 (by subtracting the mean) and then changing the spread of it so its variance and standard deviation are 1)
-
What is a type II error?
Failure to reject the null hypothesis when it was false
-
How is the probability of a type II error denoted?
β
-
Power of a test formula
1 - β, where β is the probability of a type ii error
-
The time between events in a poisson distribution follows the __________ distribution
exponential, where λ = E[X]
-
What does a distribution P(4) entail?
A poisson distribution with a mean of 4
-
When to use Welch's t-test as opposed to a simple t-test
When you don't assume that the variance of both population is equal.
-
The critical region is (below/above)? the critical t-value
below
-
welch's t statistic formula denominator
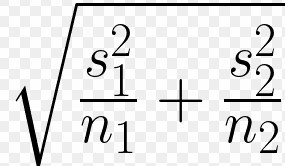
-
simple 2 sample t statistic (assuming variances are the same) formula denominator
Sp (pooled standard deviation) * sqrt(1/n1 + 1/n2)
-
How to get the z-critical value for a z-test? Knowing α
If α = 0.05, you would look up the value corresponding to AREA = (1 - α = 0.95) in the table (so look for the cell containing 0.9, then check the z value from the axes)
-
How to calculate the p value given a z-score

-
How to calculate the joined expectation of two dependent random variables
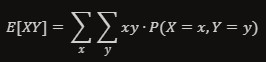
-
What does U tell you in geary's test for normality?
If the data is normally distributed, U should be close to 1.
-
What is oi in the goodness of fit test
The observed frequency (eg how many times you rolled a 2 when testing a die for fairness)
-
What is ei in the goodness of fit test
The expected frequency (eg how many you expect to roll a 2 when testing a die for fairness when throwing it 6 times (1 time))
-
What is k in the goodness of fit test
The number of categories (eg how many sides in a die, when testing a die for fairness)

