How do you get the marginal density of x given a joint probability density function f(x, y)?
Integrate in regards to y, and vice versa to find the density for y. Give the range in your answer
How do you calculate the expected value of a continuous random variable x
∫x f(x) over its range
How do you calculate the expected value of a discrete random variable x
Σ x p(x)
E(X) of X~U(a,b)
1/2 (a+b)
What is the geometric distribution equivalent to?
The probability distribution of the number 𝑋 of Bernoulli trials needed to get one success
Poisson distribution definition
A discrete probability distribution that expresses the probability of a given number of events occurring in a fixed interval of time if these events occur with a known constant mean rate and independently of the time since the last event
The most efficient estimator is the one with the _____ _______
lowest variance
is E(2X) the same as 2E(X)?
Yes
Standard error from the mean in a sample with sample size n formula
SE=σ/(√n). σ = population standard deviation
Standard error of the mean in a sample (aka standard deviation of sampling distribution from the mean) definition
measures the variability of the sample mean in regard to the population mean
Population mean and sample mean symbols, respectively
μ, x̄ (capital I think)
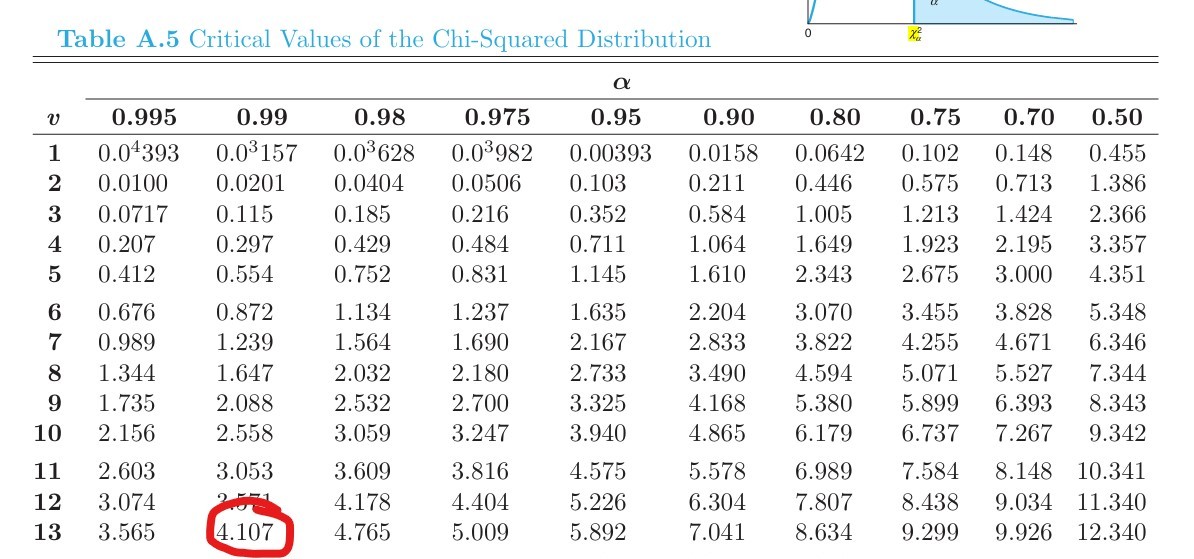
What does this value tell you?
χ2α, such that P(χ2 > χ2α) = 0.99, when ν = 13
Bayes rule
P(A|B) = (P(B|A) x P(A)) / P(B)
In a t-test: a p-value of 0.07 means there is a _____________
7% chance of obtaining the observed data (or more extreme) if the null hypothesis is true.
degrees of freedom formula for one-sample test
n - 1
degrees of freedom formula for two-sample test with equal population variances
n1 + n2 - 2
For a two tailed test, instead of alpha use _______
alpha / 2
Does this alternative hypothesis indicate a one tailed test? or two tailed? Students' performance is different (either better or worse) when listening to music compared to not listening to music.
Two-tailed (as it is either better or worse)
Point estimate (of some population parameter 𝜃) definition
is a single value ̂ 𝜃of a statistic Θ. For instance, x̄ is a point estimate of the population mean 𝜇.
When asked to provide the efficiency of an estimator, give its ______
variance
Does variance scale linearly when multiplied by a constant?
No, it scales by the constant squared
For Y=aX. Var(Y)=Var(aX)=_______
a^2 Var(X)
When is an estimator Θ unbiased?
E[Θ] = μ
Central limit theorem applied to sampling distribution of the sample mean - formula
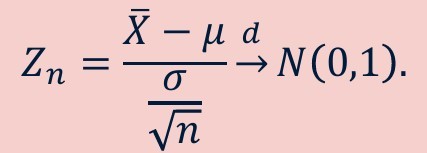
How large should n be (rule of thumb) for the central limit theorem to hold
n > 30
Sampling distribution of the sample mean notes
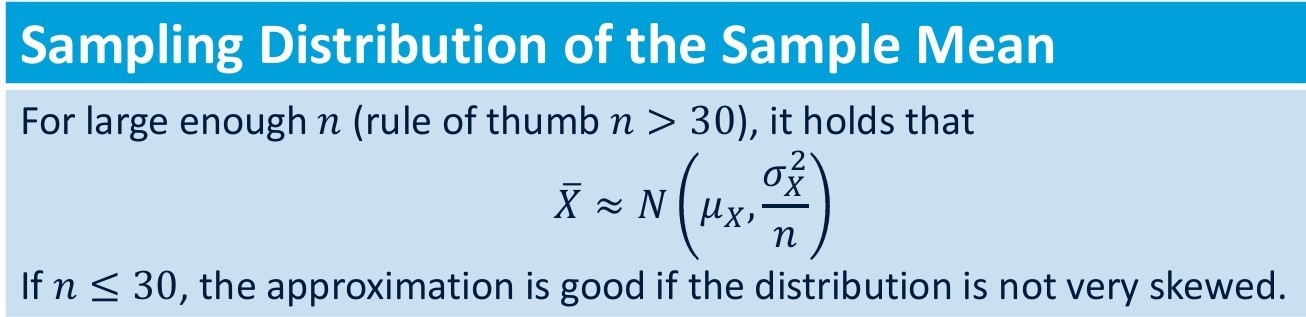
Sampling distribution of the sample: If we don't know the variance of the population but n is more than 30 we can replace it with _______. It will follow the ______ distribution
1) the sample variance 2)Student's distribution
For the central limit theorem to apply, variance must be ________
Finite
Central limit theorem applied to difference of sampling distribution of sample means of two populations - formula
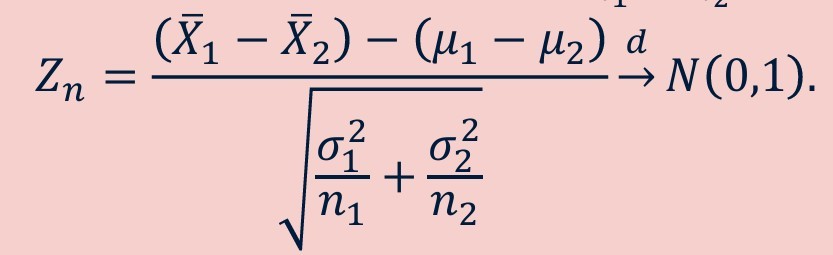
The sampling distribution of the sample variance follows a ________ distribution with _______ degrees of freedom
chi-squared, n-1
The probability of making a type 1 error is ___
α (significance level)
When is it appropriate to approximate a binomial random variable 𝑋 ∼ 𝐵 ( 𝑛 , 𝑝 ) with a normal distribution?
when 𝑛 is sufficiently large ( 𝑛 ≥ 5 0 ) and 𝑝 is close to 0.5 ( 0 . 4 ≤ 𝑝 ≤ 0 . 6 )
t-statistic general formula
(mean of sample 1 - mean of sample 2)/standard error (if both are samples but have unequal variance, use welch's method (degrees of freedom is different))(for 1-sample t statistic use x̄-μ as numerator)
type 1 error define
Falsely rejecting the null hypothesis
Which probability distribution does the Bernoulli process relate to?
Binomial
When is the normal approximation of the binomial distribution reasonable?
𝑛𝑝 ≥ 5 and 𝑛(1 − 𝑝) ≥ 5
Continuity correction meaning
When approximating a discrete probability distribution such as binomial with a continuous one such as normal, you must account for this difference by centering the discrete value between a unitary interval in the continuous one. Eg. P(X = 7) becomes P(6.5 >= X >= 7)
How to approximate binomial with normal
1) Ensure it will be a reasonable approximation.
2) correct for continuity by adding or subtracting 0.5 to x (depending on which is appropriate)
3)use the normal distribution with mean μ=np and standard deviation σ=√(npq) // (q=1−p)
How do you correct P (Y ≤ 30) (discrete) for continuity when approximating with a normal distribution?
P (Y ≤ 30.5)
How to standardize a normal distribution to N(0,1)?
Z = (X-μ)/σ2 (think about it like you are centering the graph about 0 (by subtracting the mean) and then changing the spread of it so its variance and standard deviation are 1)
What is a type II error?
Failure to reject the null hypothesis when it was false
How is the probability of a type II error denoted?
β
Power of a test formula
1 - β, where β is the probability of a type ii error
The time between events in a poisson distribution follows the __________ distribution
exponential, where λ = E[X]
What does a distribution P(4) entail?
A poisson distribution with a mean of 4
When to use Welch's t-test as opposed to a simple t-test
When you don't assume that the variance of both population is equal.
The critical region is (below/above)? the critical t-value
below
welch's t statistic formula denominator
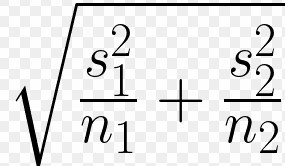
simple 2 sample t statistic (assuming variances are the same) formula denominator
Sp (pooled standard deviation) * sqrt(1/n1 + 1/n2)
How to get the z-critical value for a z-test? Knowing α
If α = 0.05, you would look up the value corresponding to AREA = (1 - α = 0.95) in the table (so look for the cell containing 0.9, then check the z value from the axes)
How to calculate the p value given a z-score

How to calculate the joined expectation of two dependent random variables
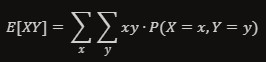
What does U tell you in geary's test for normality?
If the data is normally distributed, U should be close to 1.
What is oi in the goodness of fit test
The observed frequency (eg how many times you rolled a 2 when testing a die for fairness)
What is ei in the goodness of fit test
The expected frequency (eg how many you expect to roll a 2 when testing a die for fairness when throwing it 6 times (1 time))
What is k in the goodness of fit test
The number of categories (eg how many sides in a die, when testing a die for fairness)