-
Vmax (s)/ km + (s)
What is the equation for Michaelis-Menten?
-
reaction rate will increase
What happens if you increase the concentration of the substrate?
-
Vmax
represents the maximum rate achieved by the system
-
Km
is the substrate concentration at which the reaction rate if half of Vmax
-
double reciprocal; lineweaver-burk
Michaelis-Menton equation can be rearranged to _________ plot and this will give us a linear equation called ____________
-
increasing substrate concentration; decreasing product concentration
Inhibiting an enzyme blocks the degradation of its substrate by ___________ and blocks the formation of its product ____________
-
chemotherapy
-the use of drugs to combat foreign organisms and aberrant cells
-
by targeting enzyme that is vital for bacteria, but not humans
How do antibiotics work?
-
Ideal inhibitor
-totally specific for one target enzyme; rarely occurs
-
selective toxicity; due to higher metabolic needs
Chemotherapy kills tumor cells by virtue of _______
-
Irreversible
Inhibition of an enzyme that involves a covalent bond.
-
reversible
inhibition of enzyme activity that is typically noncovalent
-
competing with substrate at active site
The most common method reversible enzyme inhibitors use to inhibit enzymes is ____________
-
b
Smaller Ki tells us that the inhibitor is
a) ineffective at binding
b) more effective at binding
c) utilizing a covalent bond
d) irreversible
-
it will decrease & lead to less product
If I increase the concentration of inhibitor, what will happen to the [ES] complex?
-
IC50
-the inhibitor concentration that produces 50% enzyme inhibition or produce a 50% decrease in enzyme activity
-
more potent
Smaller IC50 value tells us what?
-
competitive
In _________ inhibition, the inhibitor competes with the substrate for the same binding site
-
c
In competitive inhibiton, the inhibitor binds to :
a) ES complex
b) Substrate only
c) Free enzyme only
d) all of the above
-
apparent Km; Vmax
Competitive inhibitors alter the ________ not the _________
-
c
In noncompetitive inhibition, the inhibitor binds to:
a) free enzyme only
b) ES substrate only
c) Free enzyme & the ES complex
d) none of the above
-
vmax; km
Noncompetitive inhibitor alters the ______ not the ________
-
A
In uncompetitive inhibition, the inhibitor binds to:
a) ES complex only
b) Free enzyme
c) Free enzyme & the ES complex
d) substrate only
-
B
Uncompetitive inhibitors decrease:
a) V max only
b) Vmax & Km
c) Km only
d) keeps them the same
-
noncompetitive
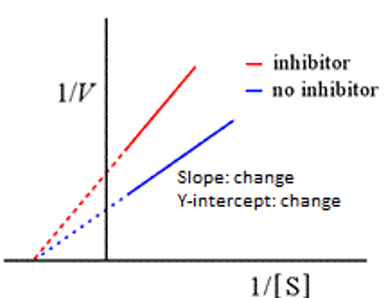
This graph represents:
-
uncompetitive
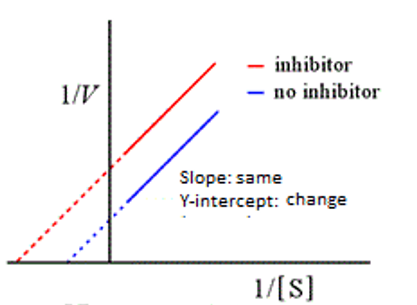
This graph represents:
-
competitive
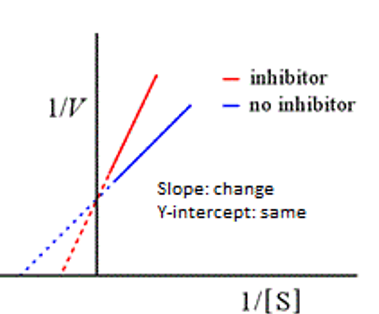
This graph represents

