-
Name the 4 different type of Receptors
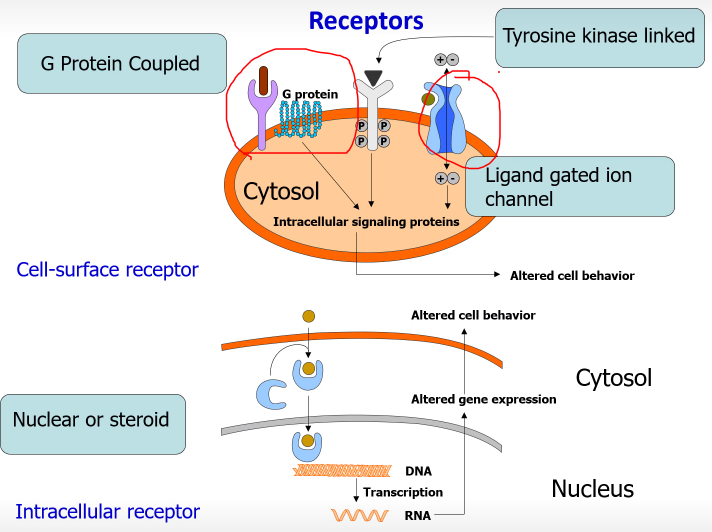
-
Order the 4 receptors from fastest to slowest
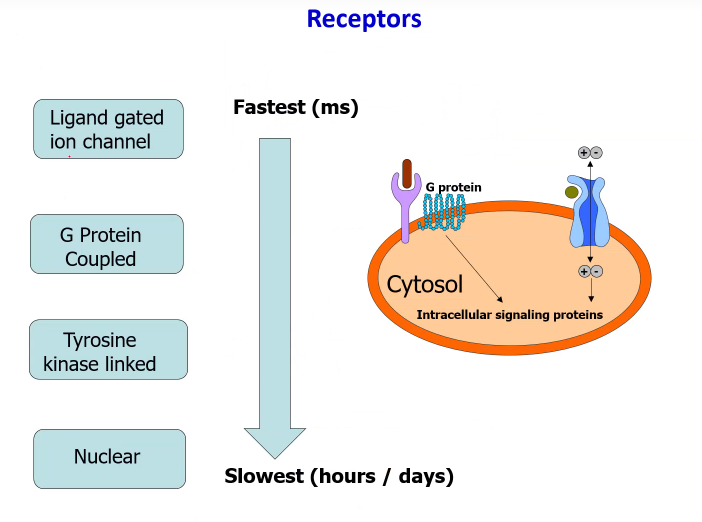
-
Acetylcholine Agonists and Antagonists? (Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors)
Agonists:NICOTINE and LOBELINE
Antagonists:TUBOCURARINE, HEXAMETHONIUM and PANCURONIUM
-
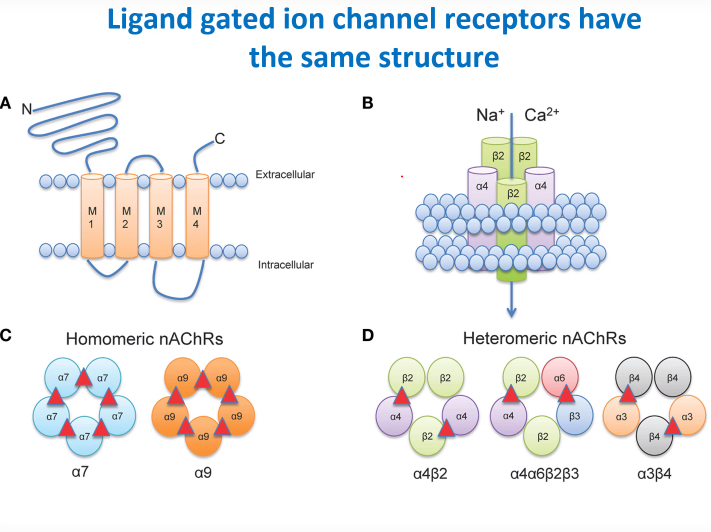
How many similar proteins does each ligand gated ion channel receptor contain?
5 similar proteins (pentamer)
-
What regions do ligand gated ion channels span across?
-Extracellular
-Transmembrane
-Intracellular
-
Picture demonstrating the structure of LGICR
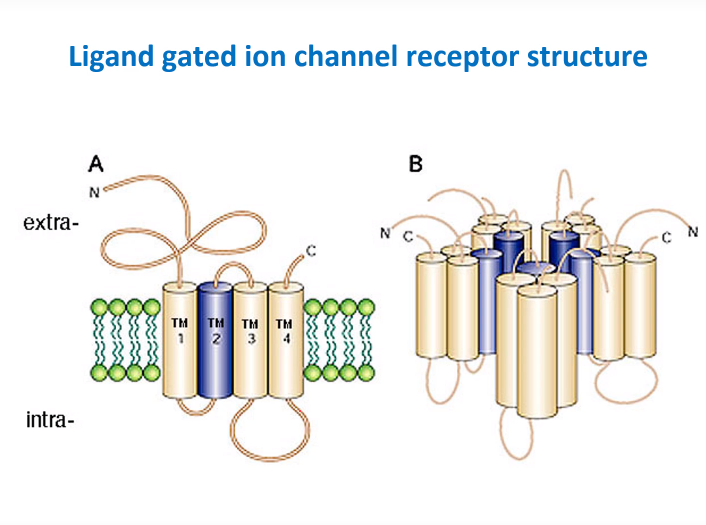
20 amino acids total
-
How does the LGICR open (binding)?
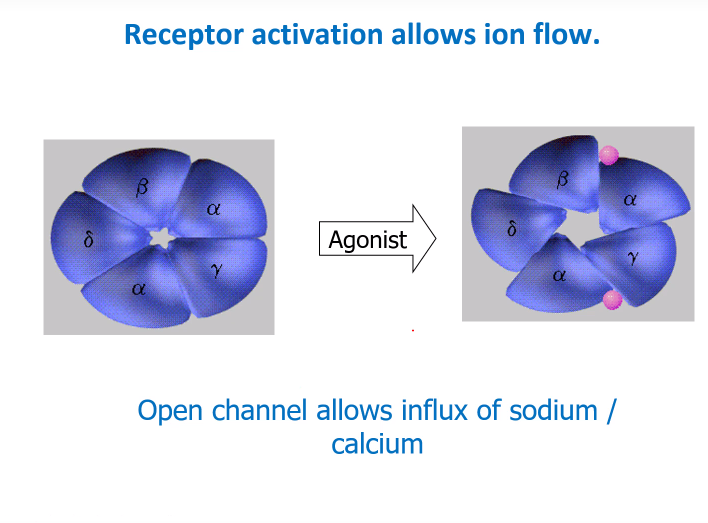
-Neurotransmitter acetylcholine will always bind to the a (alpha) subunits, in this case 2 AC binds
-
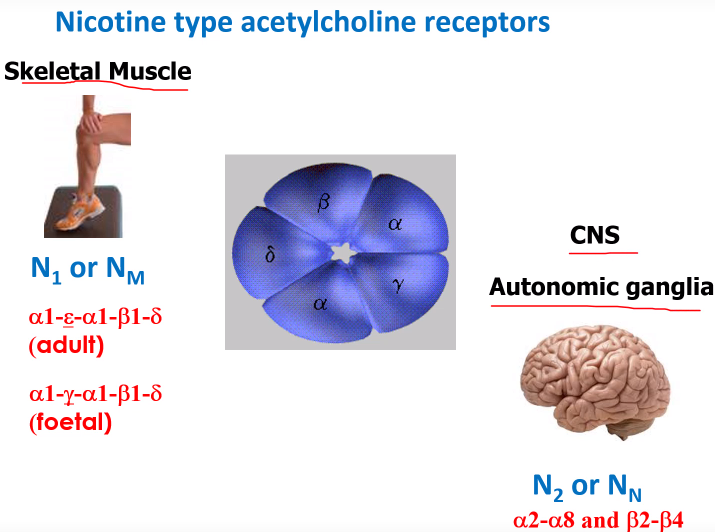
How many types of nicotine acetylcholine receptors are there?
2
Those found in skeletal muscle: N1 or Nm
And those found in the CNS (autonomic ganglia):N2 or Nn
-
Picture demonstrating nicotine type acetylcholine receptors
-
What is an EJP?
Excitatory junction potential
-A wave of depolarisation
-
What is Myasthenia gravis? What does it target? What occurs as a result? What receptors remain unaffected?

When the immune system mistakenly targets and attacks the acetylcholine receptors (AChR) on the muscle cells surfaces.
-
What agonist stimulates the Nicotinic cholinoceptor?
Acetylcholine
via depolarisation (Na/Ca influx)
-
What agonist stimulates 5HT3 Receptor?
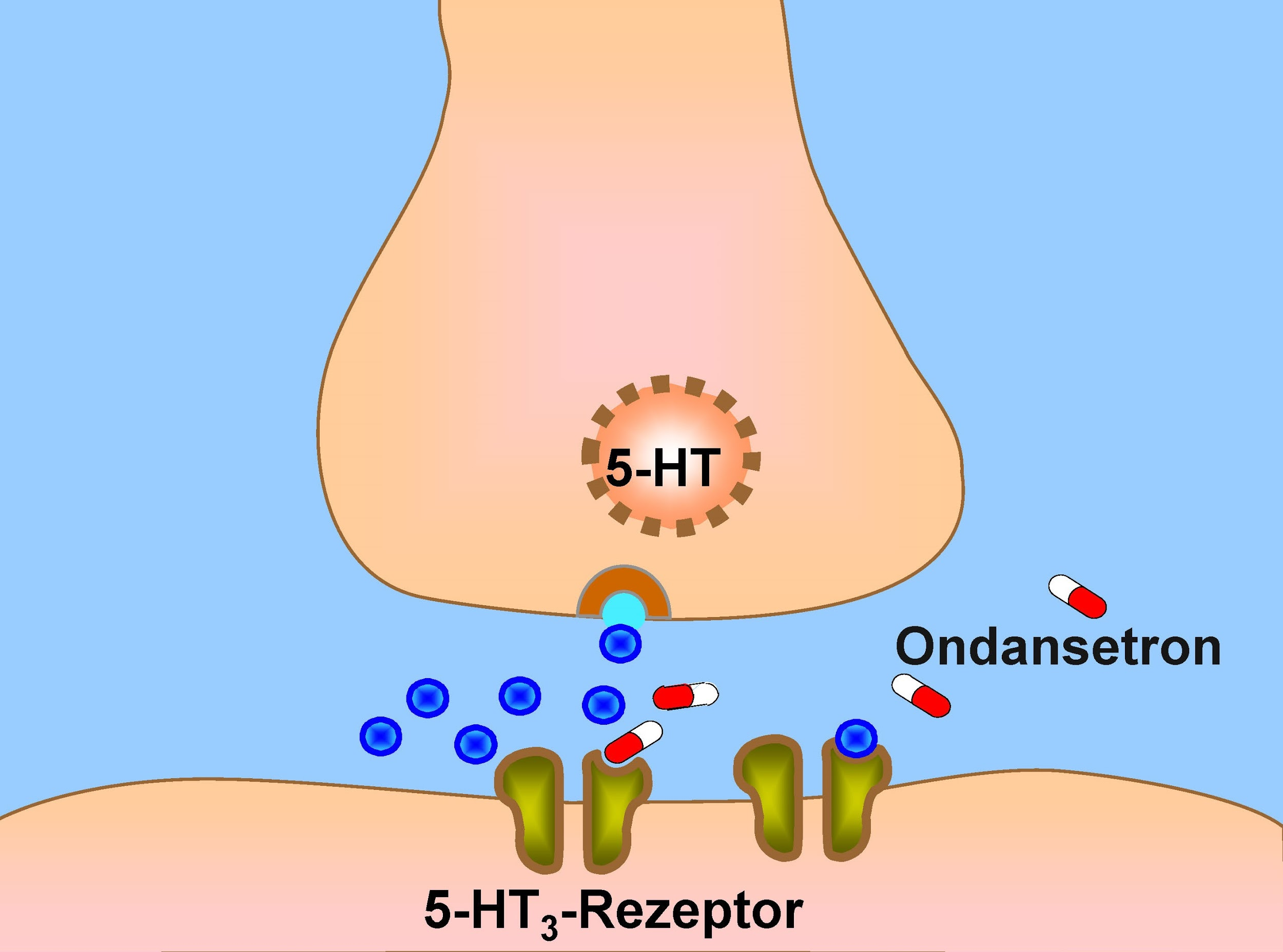
5-HT
via depolarisation (Na/Ca influx)
-
What agonist stimulates GABA A Receptor?
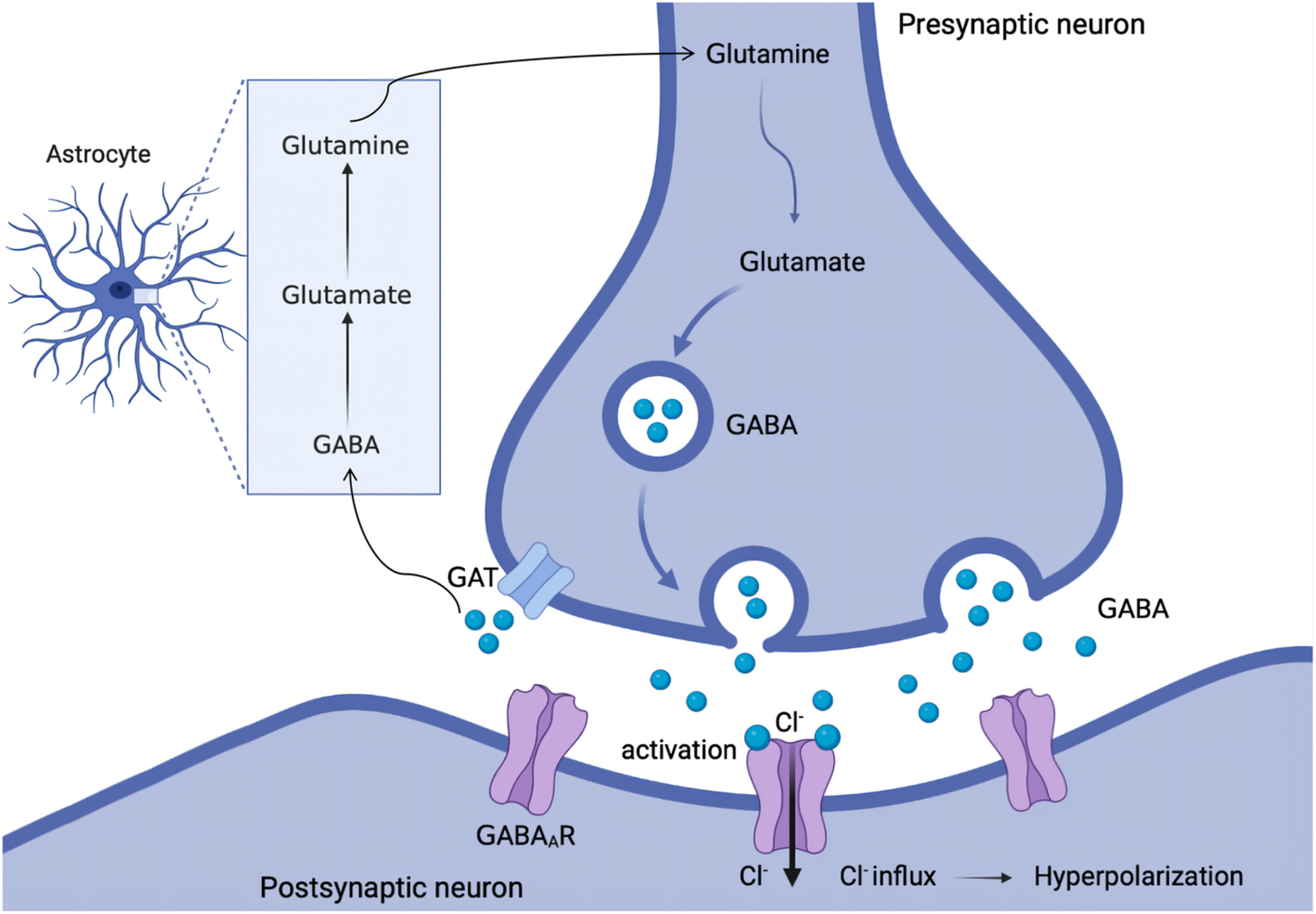
Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)
via hyperpolarisation (Chloride influx)
-
What agonist stimulates Glycine Receptor?
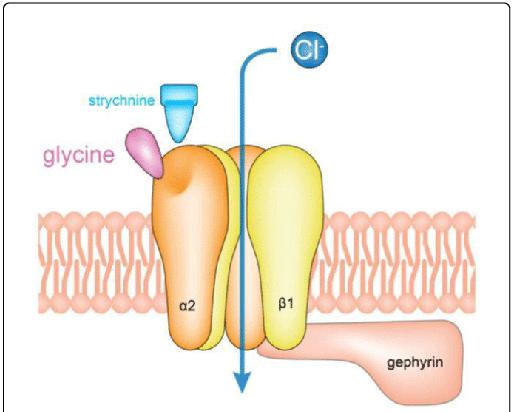
Glycine
via hyperpolarisation (Chloride influx)
-
Picture demonstrating the types of structure of LGICR